Vue3 diff算法的简单解刨
mick 人气:0上篇我们介绍了vue2中的双端diff算法的优势(相比于简单算法相同场景下移动DOM次数更少)。如今Vue3的势头正盛,在diff算法方面也做了相应的变化,利用到了最长递增子序列把性能又提升了一个档次。对于技术栈使用Vue的同学来说又是必须要学习的一部分。
性能比较
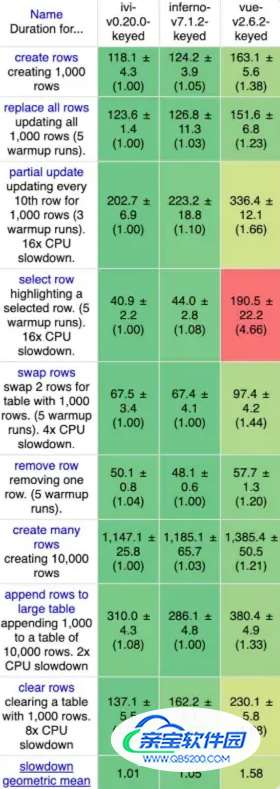
此图借鉴了《Vuejs设计与实现》这本书
ivi和inferno所采用的快速diff算法的性能要稍优于Vue2的双端diff算法。既然快速diff算法这么高效,我们当然有必要了解它咯。
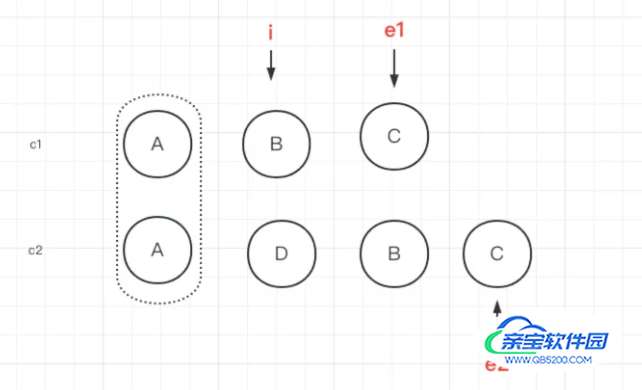
前置与后置的预处理

这里有两组子节点,c1表示老的子节点,c2表示新的子节点。首先将从c1和c2的头部节点开始对比,如果节点相同则通过patch更新节点的内容。e1表示老的子节点的尾部索引,e2表示新的子节点的尾部索引。
while (i <= e1 && i <= e2) {
const n1 = c1[i]
const n2 = (c2[i] = optimized
? cloneIfMounted(c2[i] as VNode)
: normalizeVNode(c2[i]))
// 如果节点相同 则进行递归执行patch更新节点
if (isSameVNodeType(n1, n2)) {
patch(
n1,
n2,
container,
null,
parentComponent,
parentSuspense,
isSVG,
slotScopeIds,
optimized
)
} else {
// 如果节点不相同,则直接退出
break
}
i++
}然后将索引递增,发现c1中节点B和c2中节点D不是同一节点,则循环退出。接着将从c1和c2的尾部节点开始对比,如果节点相同则通过patch更新节点的内容。
while (i <= e1 && i <= e2) {
const n1 = c1[e1]
const n2 = (c2[e2] = optimized
? cloneIfMounted(c2[e2] as VNode)
: normalizeVNode(c2[e2]))
// 如果是相同节点 则递归执行patch
if (isSameVNodeType(n1, n2)) {
patch(
n1,
n2,
container,
null,
parentComponent,
parentSuspense,
isSVG,
slotScopeIds,
optimized
)
} else {
// 如果节点不相同 则退出
break
}
e1--
e2--
}此过程经历了c1的节点C和c2的节点C对比,c1的节点B和c2的节点B对比,节点相同则通过patch更新节点的内容,每次循环e1 e2向前推进。当循环到了c1中节点B和c2中节点D不是同一节点,则循环退出
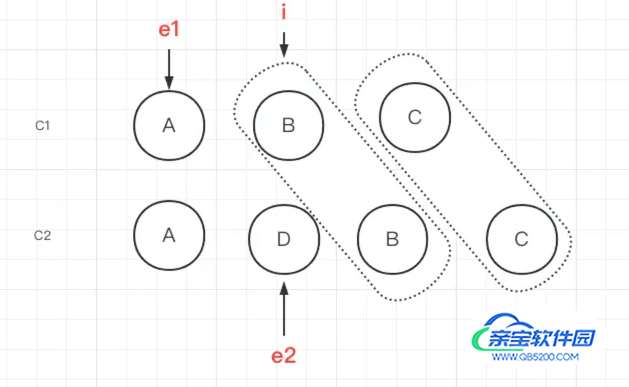
此时当新节点中还有剩余,则需要添加新节点。 相反的,如果旧节点有剩余需要删除旧节点
if (i > e1) {
// 当索引大于老节点的尾部
if (i <= e2) {
// 当索引小于新节点的尾部 需要将剩余的节点添加
const nextPos = e2 + 1
const anchor = nextPos < l2 ? (c2[nextPos] as VNode).el : parentAnchor
while (i <= e2) {
patch(
null,
(c2[i] = optimized
? cloneIfMounted(c2[i] as VNode)
: normalizeVNode(c2[i])),
container,
anchor,
parentComponent,
parentSuspense,
isSVG,
slotScopeIds,
optimized
)
i++
}
}
}
else if (i > e2) {
// 当索引i大于尾部索引e2 则直接删除旧子树从索引i开始到e1部分的节点
while (i <= e1) {
unmount(c1[i], parentComponent, parentSuspense, true)
i++
}
}上面的情况是有序的,下面我们看下无序的情况
节点无序
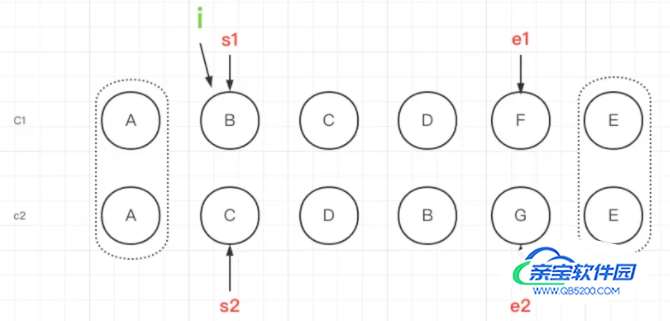
上图是经过上面的两层循环之后的结果。我们首先看下代码,由于节点无序情况的代码比较长,我们一段段的解刨
const s1 = i // prev starting index 旧子序列开始索引 从i开始记录
const s2 = i // next starting index 新子序列开始索引 从i开始记录
// 5.1 build key:index map for newChildren
// 根据key 建立新子序列的索引图
const keyToNewIndexMap: Map<string | number | symbol, number> = new Map()
for (i = s2; i <= e2; i++) {
// 获取新节点
const nextChild = (c2[i] = optimized
? cloneIfMounted(c2[i] as VNode)
: normalizeVNode(c2[i]))
if (nextChild.key != null) {
if (__DEV__ && keyToNewIndexMap.has(nextChild.key)) {
warn(
`Duplicate keys found during update:`,
JSON.stringify(nextChild.key),
`Make sure keys are unique.`
)
}
// 根据新节点的key 和 对应的索引做映射关系
// <key, index>
keyToNewIndexMap.set(nextChild.key, i)
}
}
let j
// 新子序列已经更新的节点数量
let patched = 0
// 新子序列待更新节点的数量,等于新子序列的长度
const toBePatched = e2 - s2 + 1
// 是否存在需要移动的节点
let moved = false
// 用于跟踪判断是否有节点需要移动的节点
let maxNewIndexSoFar = 0
// 这个数组存储新子序列中的元素在旧子序列节点出的索引,用于确定最长递增子序列
const newIndexToOldIndexMap = new Array(toBePatched)
// 初始化数组 为0
// 0是一个特殊的值,如果遍历之后仍有元素的值为0,则说明这个新节点没有对应的旧节点
for (i = 0; i < toBePatched; i++) newIndexToOldIndexMap[i] = 0
s1表示旧子节点开始遍历的索引,从i开始记录,s2表示新子节点开始遍历的索引,也从i开始记录。根据新子节点的key建立新子序列的索引图keyToNewIndexMap。patched表示新子序列已经更新的节点数量,toBePatched表示新子序列待更新节点的数量,等于新子序列的长度。moved表示是否存在需要移动的节点。maxNewIndexSoFar用于跟踪判断是否有节点需要移动的节点。newIndexToOldIndexMap存储新子序列中的节点在旧子序列节点的索引,用于确定最长递增子序列,初始化全部为0,0是一个特殊的值,如果遍历之后仍有元素的值为0,则说明这个新节点没有对应的旧节点。我们在图中表示一下

然后正序遍历旧子序列
// 正序遍历旧子序列
for (i = s1; i <= e1; i++) {
const prevChild = c1[i]
if (patched >= toBePatched) {
// 所有新的子序列节点都已经更新,删除剩余的节点
// all new children have been patched so this can only be a removal
unmount(prevChild, parentComponent, parentSuspense, true)
continue
}
let newIndex
if (prevChild.key != null) {
// 查找旧子序列中的节点在新子序列中的索引
newIndex = keyToNewIndexMap.get(prevChild.key)
} else {
// key-less node, try to locate a key-less node of the same type
for (j = s2; j <= e2; j++) {
if (
newIndexToOldIndexMap[j - s2] === 0 &&
isSameVNodeType(prevChild, c2[j] as VNode)
) {
newIndex = j
break
}
}
}
if (newIndex === undefined) {
// 找不到说明旧子序列需要删除
unmount(prevChild, parentComponent, parentSuspense, true)
} else {
// 更新新子序列中的元素在旧子序列中的索引,这里 +1 偏移是为了避免i为0的特殊情况 影响后面最长递增子序列的求解
newIndexToOldIndexMap[newIndex - s2] = i + 1
//maxNewIndexSoFar 存储的是上次旧值的newIndex 如果不是一直递增 则说明有移动
if (newIndex >= maxNewIndexSoFar) {
maxNewIndexSoFar = newIndex
} else {
moved = true
}
patch(
prevChild,
c2[newIndex] as VNode,
container,
null,
parentComponent,
parentSuspense,
isSVG,
slotScopeIds,
optimized处
)
patched++
}
}每次遍历拿到旧子节点的值prevChild,如果patched >= toBePatched也就是说新子序列已经更新的节点数量大于等于待更新的节点数量,说明新子序列的所有节点更新完毕,旧子序列中剩余的节点删除即可。
如果每次循环拿到的旧子节点的值的key存在,则查找旧子序列中的节点在新子序列中的索引标记为newIndex。如果key不存在,则遍历新子序列待更新的节点,如果prevChild和遍历新子序列待更新的节点有相同的节点,则将索引赋值给newIndex。接着判断newIndex是否存在,如果不存在,则说明新子序列中找不到旧子序列中的这个节点,则直接删除。如果存在,则更新新子序列中的元素在旧子序列中的索引,这里 ‘+1’ 偏移是为了避免i为0的特殊情况,影响后面最长递增子序列的求解,因为我们现在规定的newIndexToOldIndexMap中的元素为0说明这个元素没有对应的老节点,如果不'+1'我们避免不了i为0的情况,这样就影响了最长递增子序列的求解。我们看下newIndexToOldIndexMap重新赋值之后的结果
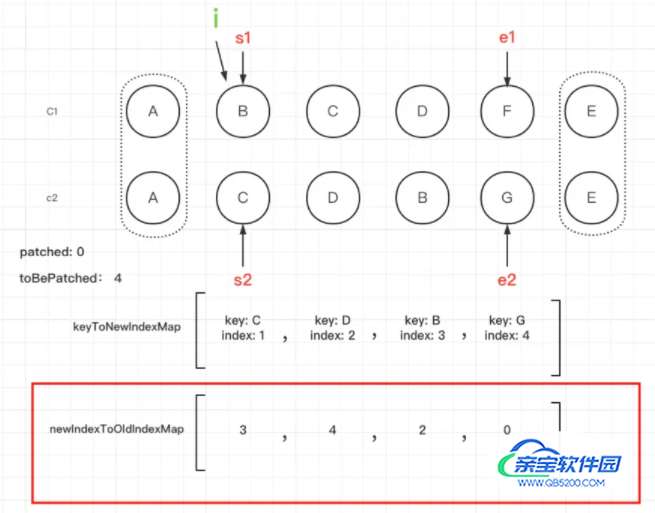
maxNewIndexSoFar存储的是上次旧值的newIndex,如果不是一直递增 则说明有移动,则moved设置为ture。然后将newIndex对应的新节点和prevChild老节点进行patch,然后patched++记录更新的次数。
我们继续看下面的代码
const increasingNewIndexSequence = moved
? getSequence(newIndexToOldIndexMap)
: EMPTY_ARR
j = increasingNewIndexSequence.length - 1
// 倒序遍历 以便使用更新的节点作为锚点
for (i = toBePatched - 1; i >= 0; i--) {
const nextIndex = s2 + i
const nextChild = c2[nextIndex] as VNode
// 锚点指向上一个更新的节点, 如果nextIndex超过新节点的长度,则指向parentAnchor
const anchor =
nextIndex + 1 < l2 ? (c2[nextIndex + 1] as VNode).el : parentAnchor
if (newIndexToOldIndexMap[i] === 0) {
// mount new
// 挂载新节点
patch(
null,
nextChild,
container,
anchor,
parentComponent,
parentSuspense,
isSVG,
slotScopeIds,
optimized
)
} else if (moved) {
// 没有最长递增子序列或者当前节点索引不在最长递增子序列中, 需要移动
if (j < 0 || i !== increasingNewIndexSequence[j]) {
move(nextChild, container, anchor, MoveType.REORDER)
} else {
j--
}
}
}首先判断是否需要移动,如果需要移动怎么才能以移动最少的步数完成更新呢?这就需要用到最长递增子序列(getSequence这个方法代码我们贴到文章最后)。我们得到了最长递增子序列的索引值的集合increasingNewIndexSequence,我们看下结果。
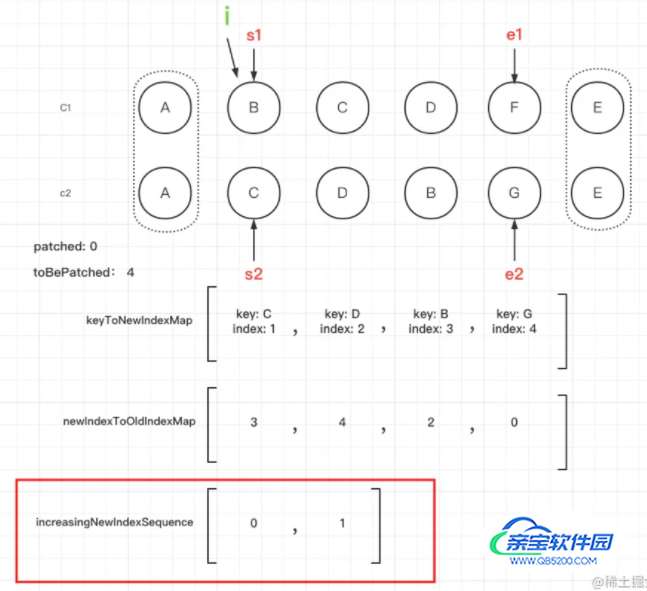
根据结果我们发现在newIndexToOldIndexMap中只有索引为0和1的节点是递增的,所以只有这两个对应的旧的子序列的节点是不需要移动的,其他的则需要移动。
倒序遍历。为什么要倒序遍历呢?因为我们将节点插入到已经更新的节点前面(从后往前遍历可以始终保持当前遍历的节点的下一个节点是更新过的)这里使用的是insertBefore。

比如这个例子节点‘G’就要插入到节点‘E’的前面,节点‘E’是已经更新过的了。
继续往前推进,节点‘B’不在最长递增子序列increasingNewIndexSequence中,所以需要移动。然后拿到节点‘B’对应的el插入到节点‘G’的前面。这个节点‘B’的el我们从节点‘B’的Vnode上面就可以获取到了。因为当两个新旧节点进行对比的时候会进行下面的操作
加载全部内容