C++活动选择
成就一亿技术人 人气:0贪心算法总是作出在当前看来最好的选择。也就是说贪心算法并不从整体最优考虑,它所作出的选择只是在某种意义上的局部最优选择。
活动安排问题
问题描述: 设有n个活动的集合E = {1,2,…,n},其中每个活动都要求使用同一资源,如演讲会场等,而在同一时间内只有一个活动能使用这一资源。每个活i都有一个要求使用该资源的起始时间si和一个结束时间fi,且si < fi 。如果选择了活动i,则它在半开时间区间[si, fi)内占用资源。若区间[si, fi)与区间[sj, fj)不相交,则称活动i与活动j是相容的。也就是说,当si >= fj或sj >= fi时,活动i与活动j相容。
活动选择问题代码实现
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std ;
struct ActivityTime
{
public:
ActivityTime (int nStart, int nEnd)
: m_nStart (nStart), m_nEnd (nEnd)
{ }
ActivityTime ()
: m_nStart (0), m_nEnd (0)
{ }
friend
bool operator < (const ActivityTime& lth, const ActivityTime& rth)
{
return lth.m_nEnd < lth.m_nEnd ;
}
public:
int m_nStart ;
int m_nEnd ;
} ;
class ActivityArrange
{
public:
ActivityArrange (const vector<ActivityTime>& vTimeList)
{
m_vTimeList = vTimeList ;
m_nCount = vTimeList.size () ;
m_bvSelectFlag.resize (m_nCount, false) ;
}
// 活动安排
void greedySelector ()
{
__sortTime () ;
// 第一个活动一定入内
m_bvSelectFlag[0] = true ;
int j = 0 ;
for (int i = 1; i < m_nCount ; ++ i) {
if (m_vTimeList[i].m_nStart > m_vTimeList[j].m_nEnd) {
m_bvSelectFlag[i] = true ;
j = i ;
}
}
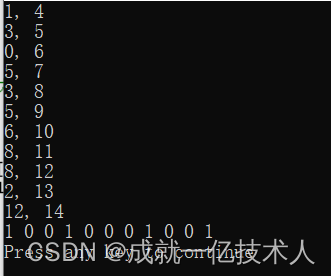
copy (m_bvSelectFlag.begin(), m_bvSelectFlag.end() ,ostream_iterator<bool> (cout, " "));
cout << endl ;
}
private:
// 按照活动结束时间非递减排序
void __sortTime ()
{
sort (m_vTimeList.begin(), m_vTimeList.end()) ;
for (vector<ActivityTime>::iterator ite = m_vTimeList.begin() ;
ite != m_vTimeList.end() ;
++ ite) {
cout << ite->m_nStart << ", "<< ite ->m_nEnd << endl ;
}
}
private:
vector<ActivityTime> m_vTimeList ; // 活动时间安排列表
vector<bool> m_bvSelectFlag ;// 是否安排活动标志
int m_nCount ; // 总活动个数
} ;
int main()
{
vector<ActivityTime> vActiTimeList ;
vActiTimeList.push_back (ActivityTime(1, 4)) ;
vActiTimeList.push_back (ActivityTime(3, 5)) ;
vActiTimeList.push_back (ActivityTime(0, 6)) ;
vActiTimeList.push_back (ActivityTime(5, 7)) ;
vActiTimeList.push_back (ActivityTime(3, 8)) ;
vActiTimeList.push_back (ActivityTime(5, 9)) ;
vActiTimeList.push_back (ActivityTime(6, 10)) ;
vActiTimeList.push_back (ActivityTime(8, 11)) ;
vActiTimeList.push_back (ActivityTime(8, 12)) ;
vActiTimeList.push_back (ActivityTime(2, 13)) ;
vActiTimeList.push_back (ActivityTime(12, 14)) ;
ActivityArrange aa (vActiTimeList) ;
aa.greedySelector () ;
return 0 ;
}结果
带权活动选择问题
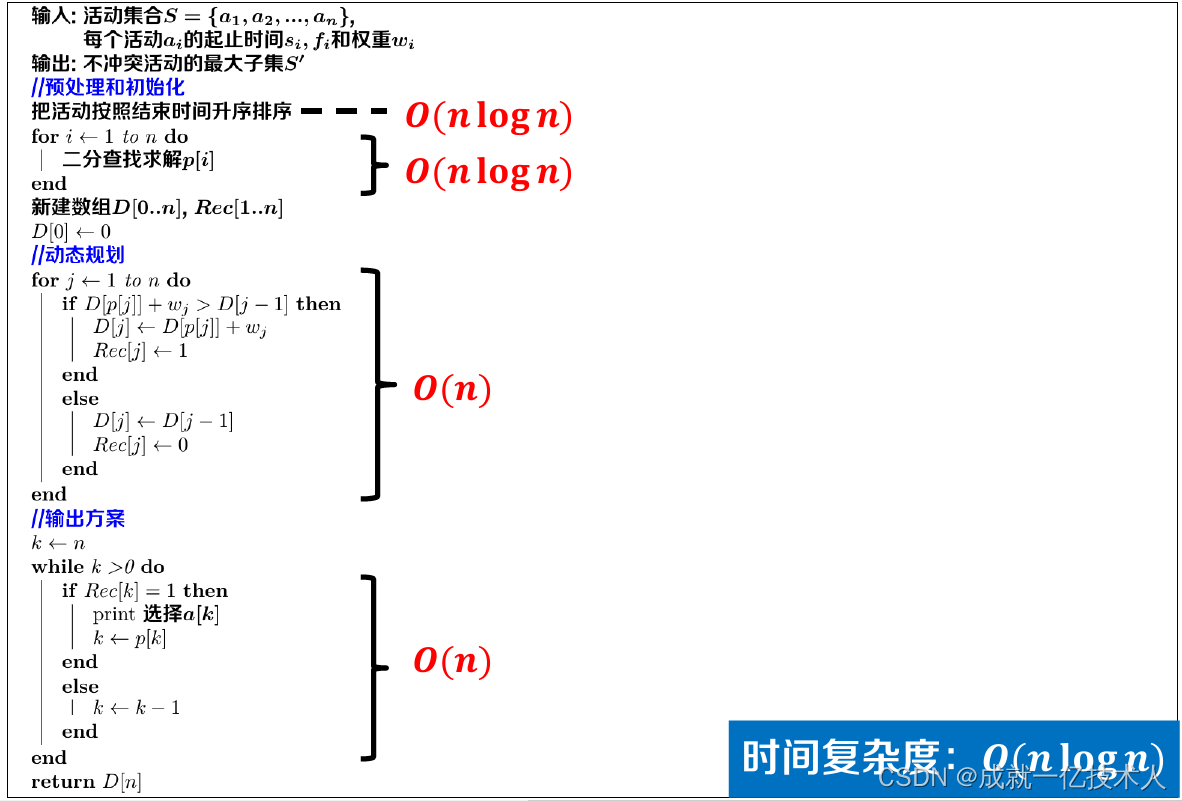
算法伪代码【核心算法】
问题描述:
会场出租:选择出租的活动时间不能冲突,怎样选择才能选更多的活动?

带权活动选择问题代码实现
package day1.java;
public class activityChoose {
private static class Activity{
int startTime;
int endTime;
int weight;
private Activity(int startTime, int endTime, int weight){
this.startTime = startTime;
this.endTime = endTime;
this.weight = weight;
}
}
private static void activityChoose(Activity[] S){
// 记录p:在a_i开始前最后结束的活动
int[] p = new int[S.length+1];
p[0] = 0;
p[1] = 0;
for(int i=2; i<=S.length; i++){
for(int j=i-1; j>0; j--){
if(S[j-1].endTime <= S[i-1].startTime){
p[i] = j;
break;
}
}
}
for(int i=1; i<=S.length; i++){
System.out.println(p[i]);
}
int[] D = new int[S.length+1];
int[] Rec = new int[S.length+1];
D[0] = 0;
// 动态规划
for(int j=1; j<S.length+1; j++){
if(D[p[j]]+S[j-1].weight > D[j-1]){
D[j] = D[p[j]] + S[j-1].weight;
Rec[j] = 1;
}else{
D[j] = D[j-1];
Rec[j] = 0;
}
}
// 输出方案
int k=S.length;
while(k > 0){
if(Rec[k] == 1){
System.out.println("选择:开始时间"+S[k-1].startTime+"结束时间"+S[k-1].endTime);
k = p[k];
}else{
k--;
}
}
}
// 按结束时间从小到大排序
private static void quickSortActivity(Activity[] S, int start, int end){
int i = start;
int j = end;
if (start < end){
Activity tmp = S[i];
while(i<j){
while(i<j && S[i].endTime <= S[j].endTime){
j--;
}
S[i] = S[j];
while (i < j && S[i].endTime >= S[j].endTime) {
i++;
}
S[j] = S[i];
}
S[i] = tmp;
quickSortActivity(S, start, i-1);
quickSortActivity(S, i+1,end);
}
}
public static void main(String[] args){
Activity[] S = new Activity[10];
S[0] = new Activity(1,4,1);
S[1] = new Activity(3,5,6);
S[2] = new Activity(0,6,4);
S[3] = new Activity(4,7,7);
S[4] = new Activity(3,9,3);
S[5] = new Activity(5,9,12);
S[6] = new Activity(6,10,2);
S[7] = new Activity(8,11,9);
S[8] = new Activity(8,12,11);
S[9] = new Activity(2,14,8);
quickSortActivity(S, 0, 9);
activityChoose(S);
}
}结果

加载全部内容