C++ 回溯算法
ymz123_ 人气:0扑克牌全排列
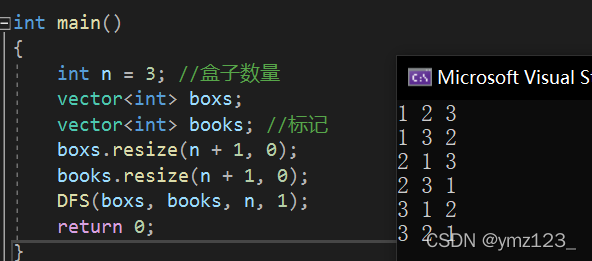
假如有编号为1~ 3的3张扑克牌和编号为1~3的3个盒子,现在需要将3张牌分别放到3个盒子中去,且每个盒子只能放一张牌,一共有多少种不同的放法。
解题思路:假定按照牌面值从小到大依次尝试,即将1号牌放入第一个盒子中。按此顺序继续向后走,放完第三个盒子时,手中的牌也已经用完,再继续往后则到了盒子的尽头。此时一种放法已经完成了,即这条路走到了尽头,需要折返,重新回到上一个盒子。这里回到第三个盒子,把第三个盒子中的牌回收,再去尝试能否放其它的牌。但这时手里只有一张3号牌,所以需要继续向后回退,到2号盒子。按照上述步骤依次会产生所有结果。 用一个数组book标记手里是否有这张牌。
Dfs(当前这一步的处理逻辑)
{
1. 判断边界,是否已经一条道走到黑了:向上回退
2. 尝试当下的每一种可能
3. 确定一种可能之后,继续下一步 Dfs(下一步)
}
代码实现:
void DFS(vector<int>& boxs, vector<int>& books, int n, int index)
{
if (index >= n + 1)
{
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
cout << boxs[i] << " "; //打印每一种结果
cout << endl;
return;
}
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
{
if (books[i] == 0) //如果i号牌仍在手上
{
boxs[index] = i;
books[i] = 1;
DFS(boxs, books, n, index + 1);
books[i] = 0;
}
}
}
员工的重要性
问题描述:
给定一个保存员工信息的数据结构,它包含了员工 唯一的 id ,重要度 和 直系下属的 id 。 比如,员工 1 是员工 2 的领导,员工 2 是员工 3 的领导。他们相应的重要度为 15 , 10 , 5 。那么员工 1 的数据结构是 [1, 15, [2]] ,员工 2的 数据结构是 [2, 10, [3]] ,员工 3 的数据结构是 [3, 5, []] 。注意虽然员工 3 也是员工 1 的一个下属,但是由于 并不是直系 下属,因此没有体现在员工 1 的数据结构中。
现在输入一个公司的所有员工信息,以及单个员工 id ,返回这个员工和他所有下属的重要度之和。
解题思路:
边界:下属为空
每次先加第一个下属的重要性
按照相同的操作再去加下属的第一个下属的重要性。
代码实现:
/*
// Definition for Employee.
class Employee {
public:
int id;
int importance;
vector<int> subordinates;
};
*/
class Solution {
public:
int DFS(unordered_map<int, Employee*>& info, int id)
{
int curImpo = info[id]->importance;
for(const auto& sid : info[id]->subordinates)
{
curImpo += DFS(info, sid);
}
return curImpo;
}
int getImportance(vector<Employee*> employees, int id) {
if(employees.empty())
return 0;
unordered_map<int, Employee*> info;
for(const auto& e : employees)
{
info[e->id] = e;
}
return DFS(info, id);
}
};
图像渲染
问题描述:
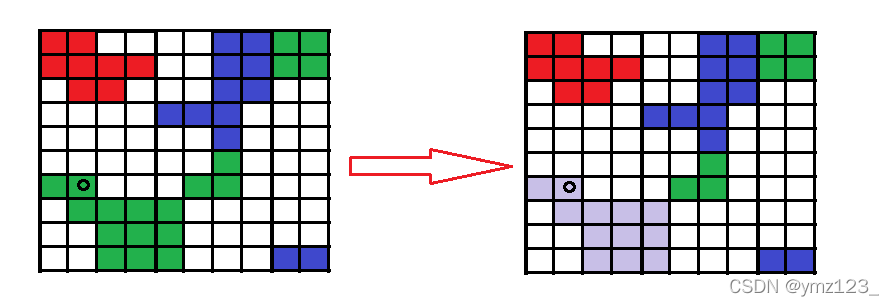
有一幅以二维整数数组表示的图画,每一个整数表示该图画的像素值大小,数值在 0 到 65535 之间。 给你一个坐标 (sr, sc) 表示图像渲染开始的像素值(行 ,列)和一个新的颜色值 newColor,让你重新上色这幅图像。 为了完成上色工作,从初始坐标开始,记录初始坐标的上下左右四个方向上像素值与初始坐标相同的相连像素点,接着再记录这四个方向上符合条件的像素点与他们对应四个方向上像素值与初始坐标相同的相连像素点,……,重复该过程。将所有有记录的像素点的颜色值改为新的颜色值。
最后返回经过上色渲染后的图像。
解题思路:
从所给坐标开始,向上下左右四个方向渲染,只要渲染点的颜色值和原坐标相同,则继续向外渲染。 边界:位置是否越界。
这里需要用标记避免重复修改,使时间复杂度不超过O(row*col)
代码实现:
int nextP[4][2] = {{-1, 0}, {1, 0}, {0, 1}, {0, -1}};
class Solution {
public:
void DFS(vector<vector<int>>& image, vector<vector<int>>& book, int sr, int sc, int newColor, int oldColor, int row, int col)
{
image[sr][sc] = newColor;
book[sr][sc] = 1;
for(int i = 0; i < 4; i++)
{
int curX = sr + nextP[i][0];
int curY = sc + nextP[i][1];
//判断是否越界
if(curX < 0 || curX >= row || curY < 0 || curY >= col)
continue;
//颜色符合要求且之前没被渲染过则继续渲染
if(image[curX][curY] == oldColor && book[curX][curY] == 0)
{
DFS(image, book, curX, curY, newColor, oldColor, row, col);
}
}
}
vector<vector<int>> floodFill(vector<vector<int>>& image, int sr, int sc, int newColor) {
int row = image.size();
int col = image[0].size();
int oldColor = image[sr][sc];
vector<vector<int>> book(row, vector<int>(col, 0));
DFS(image, book, sr, sc, newColor, oldColor, row, col);
return image;
}
};
被围绕的区域
问题描述:
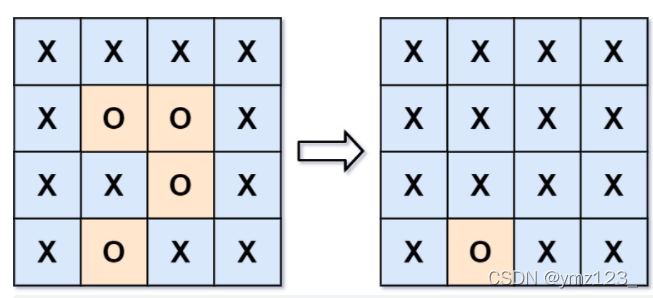
给你一个 m x n 的矩阵 board ,由若干字符 ‘X' 和 ‘O' ,找到所有被 ‘X' 围绕的区域,并将这些区域里所有的 ‘O' 用 ‘X' 填充。
解题思路: 从每个边缘的O开始,只要和边缘的O连通,则它就没有被包围。
1.首先寻找边上的每一个O,如果没有,表示所有的O都被包围。
2.对于边上的每一个O进行dfs扩散,先把边上的每一个O用特殊符号标记(除了X和O以外)。把和它相邻的O都替换为特殊符号,每一个新的位置都做相同的dfs操作。
3.所有扩散结束之后,把特殊符号的位置(和边界连通)还原为O,原来为O的位置(和边界不连通)替换为X即可。
代码实现:
int nextP[4][2] = {{-1, 0}, {1, 0}, {0, -1}, {0, 1}};
class Solution {
public:
void DFS(vector<vector<char>>& board, int curX, int curY, int row, int col)
{
board[curX][curY] = 'A';
for(int i = 0; i < 4; i++)
{
int x = curX + nextP[i][0];
int y = curY + nextP[i][1];
if(x < 0 || x >= row
||y < 0 || y >= col)
continue;
if(board[x][y] != 'A' && board[x][y] != 'X')
DFS(board, x, y, row, col);
}
}
void solve(vector<vector<char>>& board) {
if(board.empty())
return;
int row = board.size();
int col = board[0].size();
//第一行和最后一行
for(int i = 0; i < col; i++)
{
if(board[0][i] == 'O')
DFS(board, 0, i, row, col);
if(board[row-1][i] == 'O')
DFS(board, row-1, i, row, col);
}
//第一列和最后一列
for(int i = 0; i < row; i++)
{
if(board[i][0] == 'O')
DFS(board, i, 0, row, col);
if(board[i][col-1] == 'O')
DFS(board, i, col-1, row, col);
}
for(int i = 1; i < row-1; i++)
{
for(int j = 0; j < col; j++)
{
if(board[i][j] == 'A')
board[i][j] = 'O';
else if(board[i][j] == 'O')
board[i][j] = 'X';
}
}
}
};
岛屿数量
问题描述:
给你一个由 ‘1'(陆地)和 ‘0'(水)组成的的二维网格,请你计算网格中岛屿的数量。 岛屿总是被水包围,并且每座岛屿只能由水平方向和/或竖直方向上相邻的陆地连接形成。 此外,你可以假设该网格的四条边均被水包围。
示例 1:
输入:grid = [ [“1”,“1”,“1”,“1”,“0”], [“1”,“1”,“0”,“1”,“0”], [“1”,“1”,“0”,“0”,“0”], [“0”,“0”,“0”,“0”,“0”] ]
输出:1
解题思路:
本题可以采用类似渲染的做法,尝试以每个点作为渲染的起点,可以渲染的陆地都算作一个岛屿,最后看渲染了多少次,即深度优先算法执行了多少次,就是岛屿的数量。
代码实现:
int nextP[4][2] = { { 0, 1 }, { 1, 0 }, { 0, -1 }, { -1, 0 } };
class Solution {
public:
void DFS(vector<vector<char>>& grid, vector<vector<int>>& book, int x, int y, int row, int col)
{
book[x][y] = 1;
for(int i = 0; i < 4; i++)
{
int curX = x + nextP[i][0];
int curY = y + nextP[i][1];
if(curX < 0 || curX >= row || curY < 0 || curY >= col)
continue;
if(grid[curX][curY] == '1' && book[curX][curY] == 0)
DFS(grid, book, curX, curY, row, col);
}
}
int numIslands(vector<vector<char>>& grid) {
if(grid.empty())
return 0;
int row = grid.size();
int col = grid[0].size();
int num = 0;
vector<vector<int>> book(row, vector<int>(col, 0));
for(int i = 0; i < row; i++)
{
for(int j = 0; j < col; j++)
{
if(grid[i][j] == '1' && book[i][j] == 0)
{
++num;
DFS(grid, book, i, j, row, col);
}
}
}
return num;
}
};
电话号码的字母组合
问题描述:
给定一个仅包含数字 2-9 的字符串,返回所有它能表示的字母组合。答案可以按 任意顺序 返回。 给出数字到字母的映射如下(与电话按键相同)。注意 1 不对应任何字母。

解题思路:
首先使用数组(也可使用哈希表)存储每个数字对应的所有可能的字母,然后进行回溯操作。回溯算法用于寻找所有的可行解,如果发现一个解不可行,则会舍弃不可行的解。在这道题中,由于每个数字对应的每个字母都可能进入字母组合,因此不存在不可行的解,直接穷举所有的解即可。
代码实现:
string mapString[] = {"", "", "abc", "def", "ghi", "jkl", "mno", "pqrs", "tuv", "wxyz"};
class Solution {
public:
void DFS(string& digits, vector<string>& result, string curStr, int curDepth)
{
//边界,找到一种组合,放入数组中,结束此路径,向上回溯
if(curDepth == digits.size())
{
if(!curStr.empty())
result.push_back(curStr);
return;
}
//找到当前字符映射在mapString种的位置
int curMapIndex = digits[curDepth] - '0';
string curMap = mapString[curMapIndex];
//遍历每一种可能
for(const auto& ch : curMap)
{
DFS(digits, result, curStr+ch, curDepth+1);
}
}
vector<string> letterCombinations(string digits) {
vector<string> result;
DFS(digits, result, "", 0);
return result;
}
};
组合总数
问题描述:
给你一个 无重复元素 的整数数组 candidates 和一个目标整数 target ,找出 candidates 中可以使数字和为目标数 target 的 所有不同组合 ,并以列表形式返回。你可以按 任意顺序 返回这些组合。
candidates 中的 同一个 数字可以 无限制重复被选取 。如果至少一个数字的被选数量不同,则两种组合是不同的。
对于给定的输入,保证和为 target 的不同组合数少于 150 个。
输入:candidates = [2,3,6,7], target = 7
输出:[[2,2,3],[7]]
解题思路:
此题相加的元素可以重复,所以去下一个元素的位置可以从当前位置开始,DFS+回溯。为了保证组合不重复(顺序不同,元素相同,也算重复),不再从当前位置向前看。
1.从第一个元素开始相加
2.让局部和继续累加候选的剩余值
3.局部和等于目标值,保存组合,向上回退,寻找其它组合
代码实现:
class Solution {
public:
void DFS(vector<int>& candidates, vector<vector<int>>& result, vector<int> curCand, int prePos, int curSum, int target)
{
if(curSum >= target)
{
if(curSum == target)
result.push_back(curCand);
return;
}
for(int i = prePos; i < candidates.size(); i++)
{
if(candidates[i] <= target)
{
curCand.push_back(candidates[i]);
DFS(candidates, result, curCand, i, curSum+candidates[i], target);
//回溯
curCand.pop_back();
}
}
}
vector<vector<int>> combinationSum(vector<int>& candidates, int target) {
vector<vector<int>> result;
vector<int> curCand;
DFS(candidates, result, curCand, 0, 0, target);
return result;
}
};
活字印书
问题描述:
你有一套活字字模 tiles,其中每个字模上都刻有一个字母 tiles[i]。返回你可以印出的非空字母序列的数目。
注意:本题中,每个活字字模只能使用一次。
示例 1:
输入:“AAB”
输出:8
解释:可能的序列为 “A”, “B”, “AA”, “AB”, “BA”, “AAB”, “ABA”, “BAA”。
解题思路:
此题组合的长度不唯一,最小组合长度为1,最大组合长度为tiles的长度。按照题意tiles中每一个位置的字符在组合中只能出现一次,所以可以用一个标记辅助。当组合新的组合时,可以与tiles种的每一个位置组合,但是如果当前位置已经在当前组合中出现过,则跳过。虽然此题种每一个位置的字符在组合中只能出现一次,但是tiles中可能有相同的字符,所以需要考虑重复的组合。而用unordered_set可以天然去重。
DFS+回溯:
1.当前组合不为空,则插入set中
2.继续给当前组合拼接新的组合,尝试拼接tiles每一个位置的字符
3.如果当前位置已经在组合中出现过,返回到2,否则标记当前位置,继续拼接更长的组合
4.回溯,尝试组合其它位置,返回2
当所有位置都已经使用过时,当前递归就结束了,继续向上层DFS回退
最终返回set大小即为组合数目
代码实现:
class Solution {
public:
void DFS(string& tiles, vector<int>& book, string curStr, unordered_set<string>& totolaString)
{
if(!curStr.empty())
{
totolaString.insert(curStr);
}
for(int i = 0; i < tiles.size(); i++)
{
//当前字符已用过,跳过
if(book[i] == 1)
continue;
book[i] = 1;
DFS(tiles, book, curStr+tiles[i], totolaString);
book[i] = 0;
}
}
int numTilePossibilities(string tiles) {
vector<int> book(tiles.size(), 0);
unordered_set<string> totolaString;
DFS(tiles, book, "", totolaString);
return totolaString.size();
}
};
N皇后
问题描述:
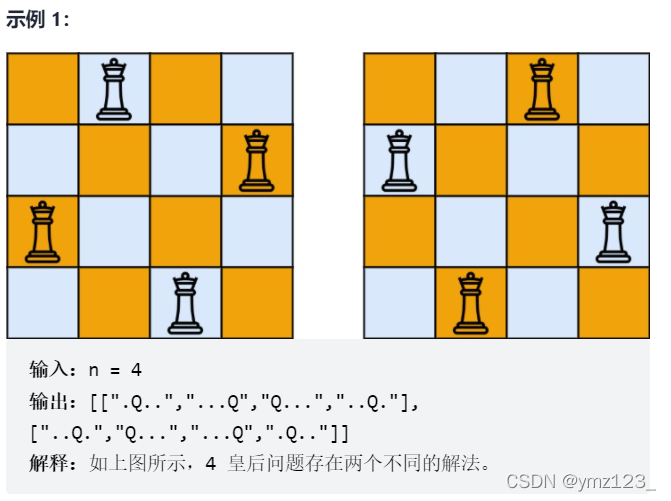
n 皇后问题 研究的是如何将 n 个皇后放置在 n×n 的棋盘上,并且使皇后彼此之间不能相互攻击。
给你一个整数 n ,返回所有不同的 n 皇后问题 的解决方案。
每一种解法包含一个不同的 n 皇后问题 的棋子放置方案,该方案中 ‘Q' 和 ‘.' 分别代表了皇后和空位。
解题思路:
DFS+回溯
从第一行开始放置皇后,每确定一个位置,判断是否会冲突(是否在同一列、同一斜线,已经不可能在同一行)
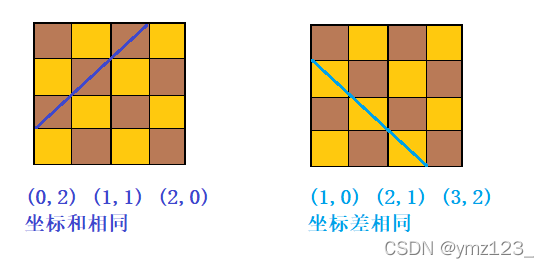
同一列:纵坐标相同
同一斜线:坐标差或坐标和相同。
当前行位置确定后,继续确定下一行的位置。
回退,尝试其他行的其它位置。
代码实现:
class Solution {
public:
bool isValidPos(vector<pair<int, int>>& curRet, int row, int col)
{
for(pair<int, int> pos : curRet)
{
if(pos.second == col || pos.first + pos.second == row + col
|| pos.first - pos.second == row - col)
return false;
}
return true;
}
void DFS(vector<vector<pair<int, int>>>& allRet, vector<pair<int, int>>& curRet, int curRow, int n)
{
//如果每一行都没有冲突,则是一种可行的方案
if(curRow == n)
{
allRet.push_back(curRet);
return;
}
//确定当前行的每一个位置是否和已确定的位置有冲突
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
if(isValidPos(curRet, curRow, i))
{
curRet.push_back(make_pair(curRow,i));
//处理下一行
DFS(allRet, curRet, curRow+1, n);
//回溯
curRet.pop_back();
}
}
}
vector<vector<string>> transResult(vector<vector<pair<int, int>>>& allRet, int n)
{
vector<vector<string>> allMap;
//所有方案
for(vector<pair<int, int>> curRet : allRet)
{
vector<string> curMap(n, string(n, '.'));
//一种方案中的所有皇后的位置
for(pair<int, int> pos : curRet)
{
curMap[pos.first][pos.second] = 'Q';
}
allMap.push_back(curMap);
}
return allMap;
}
vector<vector<string>> solveNQueens(int n) {
vector<vector<pair<int, int>>> allRet;
vector<pair<int, int>> curRet;
DFS(allRet, curRet, 0, n);
return transResult(allRet, n);
}
};
加载全部内容