C++ 单链表
琅時壹 人气:0(❁´◡`❁) 单链表
前言
上篇顺序表结尾了解了顺序表的诸多缺点,链表的特性很好的解决了这些问题,本期我们来认识单链表。
一、链表是什么
链表是一种物理存储结构上非连续、非顺序的存储结构,数据元素的逻辑顺序是通过链表中的指针链接依次实现的。

- 由图,链式结构在逻辑上是连续的,但是物理上不一定连续
- 显示中结点一般是从堆上申请出来的
- 从堆上申请的空间,是按照一定的策略划分的,两次申请的空间,可能连续,可能不连续,见顺序表

链表的分类
链表也可以分为很多种
1. 单向或者双向
2. 带头或者不带头
3. 循环或非循环



我们最常用的还是无头单向非循环链表和带头双向循环链表 本篇我们实现无头单向非循环链表增删查改
二、链表的实现
基本结点结构
typedef int SLTDateType;
typedef struct SListNode
{
SLTDateType data;
struct SListNode* next;
}SListNode;头文件
//llist.h
#pragma once
#include <stdio.h>
#include <assert.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
typedef int SLTDateType;
typedef struct SListNode
{
SLTDateType data;
struct SListNode* next;
}SListNode;
// 动态申请一个节点
SListNode* BuySListNode(SLTDateType x);
// 单链表打印
void SListPrint(SListNode* plist);
// 单链表尾插
void SListPushBack(SListNode** pplist, SLTDateType x);
// 单链表的头插
void SListPushFront(SListNode** pplist, SLTDateType x);
// 单链表的尾删
void SListPopBack(SListNode** pplist);
// 单链表头删
void SListPopFront(SListNode** pplist);
// 单链表查找
SListNode* SListFind(SListNode* plist, SLTDateType x);
// 单链表在pos位置之后插入x
// 分析思考为什么不在pos位置之前插入?
void SListInsertAfter(SListNode* pos, SLTDateType x);
// 单链表删除pos位置之后的值
// 分析思考为什么不删除pos位置?
void SListEraseAfter(SListNode* pos);
// 单链表的销毁
void SListDestory(SListNode* plist);动态申请一个节点

// 动态申请一个节点
SListNode* BuySListNode(SLTDateType x)
{
SListNode* newnode = (SListNode*)malloc(sizeof(SListNode));
if (newnode == NULL)//申请失败
{
printf("malloc fail\n");
exit(-1);
}
else
{
newnode->data = x;
newnode->next = NULL;
}
return newnode;
} 单链表打印
链表单个结点中,data存储数据,next存储下一个结点的地址,可以通过next访问下一个结点


// 单链表打印
void SListPrint(SListNode* plist)
{
SListNode* cur = plist;
while (cur != NULL)
{
printf("%d->", cur->data);
cur = cur->next;//访问下一个结点
}
printf("NULL\n");
}单链表尾插

这里传入了头结点的地址的指针,是因为有可能要改变头结点的情况,传址调用幻术,如果只传入*plist,相当于只改变形参,实参不会有实际改变,通过pplist可以解决这个问题

// 单链表尾插
void SListPushBack(SListNode** pplist, SLTDateType x)
{
SListNode* newnode = BuySListNode(x);
if (*pplist == NULL)//空链表
{
*pplist = newnode;
}
else
{
SListNode* tail = *pplist;//遍历至最后插入
while (tail->next != NULL)
{
tail = tail->next;
}
tail->next = newnode;
}
}单链表的尾删
一前一后遍历,找到空后直接free(tail),将prev->next置空即可

// 单链表的尾删
void SListPopBack(SListNode** pplist)
{
assert(pplist);
if (*pplist == NULL)//空链表,无需删除
{
return;
}
else
{
SListNode* prev = NULL;
SListNode* tail = *pplist;
{
while (tail->next != NULL)
{
prev = tail;
tail = tail->next;
}
free(tail);
tail = NULL;
prev->next = NULL;
}
}
}单链表的头插

有点绕,要多想想
// 单链表的头插
void SListPushFront(SListNode** pplist, SLTDateType x)
{
assert(pplist);
SListNode* newnode = BuySListNode(x);
newnode->next = *pplist;
*pplist = newnode;
}单链表头删

比较简单
// 单链表头删
void SListPopFront(SListNode** pplist)
{
assert(pplist);
if (*pplist == NULL)//链表为空
{
return;
}
else
{
SListNode* next = (*pplist)->next;
free(*pplist);
*pplist = next;
}
}
// 单链表查找
遍历即可
SListNode* SListFind(SListNode* plist, SLTDateType x)
{
SListNode* cur = plist;
while (cur != NULL)
{
if (cur->data = x)
{
return cur;
}
cur = cur->next;
}
retuen NULL;
}*单链表在pos位置之后插入x
为什么不在pos之前插入,由于我们是单向链表,需要从头遍历查找pos,如果在pos之前插入,找到pos还需找到pos之前的地址,对所传参数不友好,所以我们一般在后插入

//单链表在pos位置之后插入x
void SListInsertAfter(SListNode* pos, SLTDateType x)
{
assert(pos);
SListNode* newnode = BuySListNode(x);
newnode->next = pos->next;
pos->next = newnode;
}单链表删除pos位置之后的值 为什么不删除pos位置,同上,在逻辑上和传参不友好.

// 单链表删除pos位置之后的值
void SListEraseAfter(SListNode* pos)
{
assert(pos);
SListNode* next = pos->next;
if (next)
{
pos->next = next->next;
free(next);
next = NULL;
}
}单链表的销毁 链表不像顺序表连续删头就可以,由于链表是一个一个分散的结点,需要逐一删除
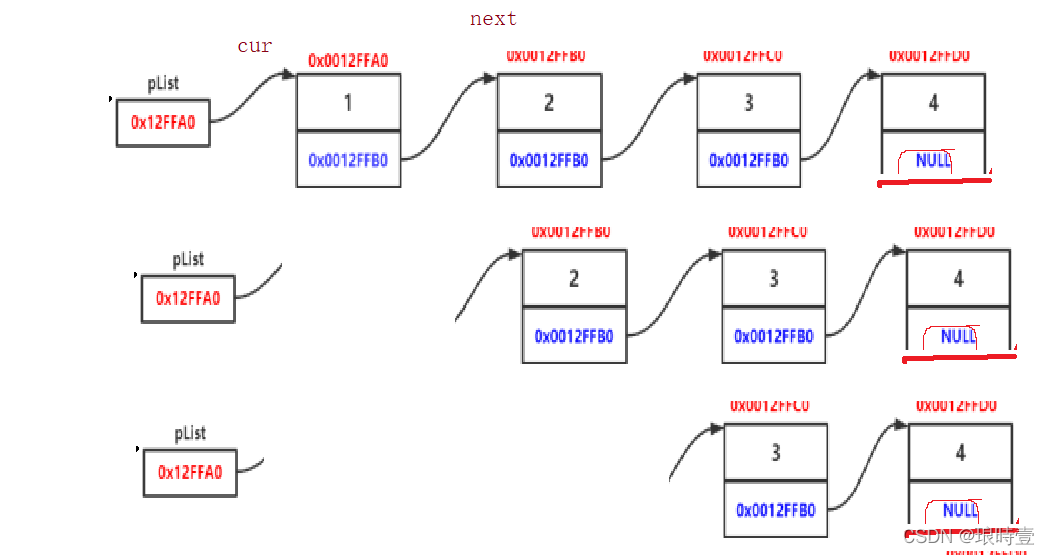
// 单链表的销毁
void SListDestory(SListNode** pplist)
{
assert(*pplist);
SListNode* cur = *pplist;
while (cur)
{
SListNode* next = cur->next;
free(cur);
cur = next;
}
*pplist = NULL;
}总结
链表相比但链表难度提升不少,对c的掌握也变大,不清晰的地方要多想多画图。还请斧正
加载全部内容