深入理解Golang Channel 结构
运维派 人气:0Golang 使用 Groutine 和 channels 实现了 CSP(Communicating Sequential Processes) 模型,channles在 goroutine 的通信和同步中承担着重要的角色。
在GopherCon 2017 中,Golang 专家 Kavya 深入介绍了 Go Channels 的内部机制,以及运行时调度器和内存管理系统是如何支持 Channel 的,本文根据 Kavya 的 ppt 学习和分析一下 go channels 的原理,希望能够对以后正确高效使用 golang 的并发带来一些启发。
以一个简单的 channel 应用开始,使用 goroutine 和 channel 实现一个任务队列,并行处理多个任务。
func main(){
//带缓冲的 channel
ch := make(chan Task, 3)
//启动固定数量的 worker
for i := 0; i< numWorkers; i++ {
go worker(ch)
}
//发送任务给 worker
hellaTasks := getTaks()
for _, task := range hellaTasks {
ch <- task
}
...
}
func worker(ch chan Task){
for {
//接受任务
task := <- ch
process(task)
}
} 从上面的代码可以看出,使用 golang 的 goroutine 和 channel 可以很容易的实现一个生产者-消费者模式的任务队列,相比 Java, c++简洁了很多。
channel 可以天然的实现了下面四个特性:
- goroutine 安全
- 在不同的 goroutine 之间存储和传输值 – 提供 FIFO 语义 (buffered channel 提供)
- 可以让 goroutine block/unblock
那么 channel 是怎么实现这些特性的呢?下面我们看看当我们调用 make 来生成一个 channel 的时候都做了些什么。
make chan
上述任务队列的例子第三行,使用 make 创建了一个长度为 3 的带缓冲的 channel,channel 在底层是一个 hchan 结构体,位于 src/runtime/chan.go 里。
其定义如下:
type hchan struct {
qcount uint // total data in the queue
dataqsiz uint // size of the circular queue
buf unsafe.Pointer // points to an array of dataqsiz elements
elemsize uint16
closed uint32
elemtype *_type // element type
sendx uint // send index
recvx uint // receive index
recvq waitq // list of recv waiters
sendq waitq // list of send waiters
// lock protects all fields in hchan, as well as several
// fields in sudogs blocked on this channel.
//
// Do not change another G's status while holding this lock
// (in particular, do not ready a G), as this can deadlock
// with stack shrinking.
lock mutex
} make 函数在创建 channel 的时候会在该进程的 heap 区申请一块内存,创建一个 hchan 结构体,返回执行该内存的指针,所以获取的的 ch 变量本身就是一个指针,在函数之间传递的时候是同一个 channel。
hchan 结构体使用一个环形队列来保存 groutine 之间传递的数据(如果是缓存 channel 的话),使用**两个 list **保存像该 chan 发送和从该 chan 接收数据的 goroutine,还有一个 mutex 来保证操作这些结构的安全。
发送和接收
向 channel 发送和从 channel 接收数据主要涉及 hchan 里的四个成员变量,借用 Kavya ppt 里的图示,来分析发送和接收的过程。
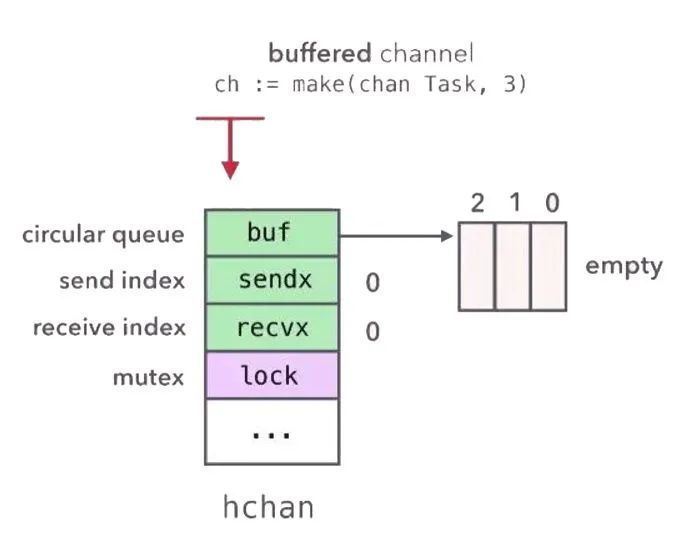
还是以前面的任务队列为例:
//G1
func main(){
...
for _, task := range hellaTasks {
ch <- task //sender
}
...
}
//G2
func worker(ch chan Task){
for {
//接受任务
task := <- ch //recevier
process(task)
}
} 其中 G1 是发送者,G2 是接收,因为 ch 是长度为 3 的带缓冲 channel,初始的时候 hchan 结构体的 buf 为空,sendx 和 recvx 都为 0,当 G1 向 ch 里发送数据的时候,会首先对 buf 加锁,然后将要发送的数据 copy 到 buf 里,并增加 sendx 的值,最后释放 buf 的锁。然后 G2 消费的时候首先对 buf 加锁,然后将 buf 里的数据 copy 到 task 变量对应的内存里,增加 recvx,最后释放锁。整个过程,G1 和 G2 没有共享的内存,底层通过 hchan 结构体的 buf,使用 copy 内存的方式进行通信,最后达到了共享内存的目的,这完全符合 CSP 的设计理念
Do not comminute by sharing memory;instead, share memory by communicating
一般情况下,G2 的消费速度应该是慢于 G1 的,所以 buf 的数据会越来越多,这个时候 G1 再向 ch 里发送数据,这个时候 G1 就会阻塞,那么阻塞到底是发生了什么呢?
Goroutine Pause/Resume
goroutine 是 Golang 实现的用户空间的轻量级的线程,有 runtime 调度器调度,与操作系统的 thread 有多对一的关系,相关的数据结构如下图:
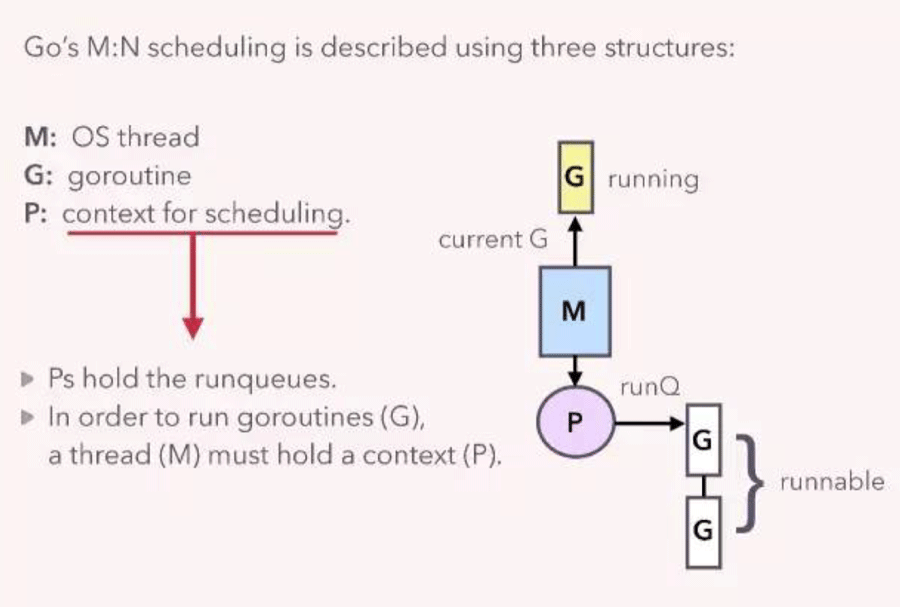
其中 M 是操作系统的线程,G 是用户启动的 goroutine,P 是与调度相关的 context,每个 M 都拥有一个 P,P 维护了一个能够运行的 goutine 队列,用于该线程执行。
当 G1 向 buf 已经满了的 ch 发送数据的时候,当 runtine 检测到对应的 hchan 的 buf 已经满了,会通知调度器,调度器会将 G1 的状态设置为 waiting, 移除与线程 M 的联系,然后从 P 的 runqueue 中选择一个 goroutine 在线程 M 中执行,此时 G1 就是阻塞状态,但是不是操作系统的线程阻塞,所以这个时候只用消耗少量的资源。
那么 G1 设置为 waiting 状态后去哪了?怎们去 resume 呢?我们再回到 hchan 结构体,注意到 hchan 有个 sendq 的成员,其类型是 waitq,查看源码如下:
type hchan struct {
...
recvq waitq // list of recv waiters
sendq waitq // list of send waiters
...
}
//
type waitq struct {
first *sudog
last *sudog
} 实际上,当 G1 变为 waiting 状态后,会创建一个代表自己的 sudog 的结构,然后放到 sendq 这个 list 中,sudog 结构中保存了 channel 相关的变量的指针(如果该 Goroutine 是 sender,那么保存的是待发送数据的变量的地址,如果是 receiver 则为接收数据的变量的地址,之所以是地址,前面我们提到在传输数据的时候使用的是 copy 的方式)
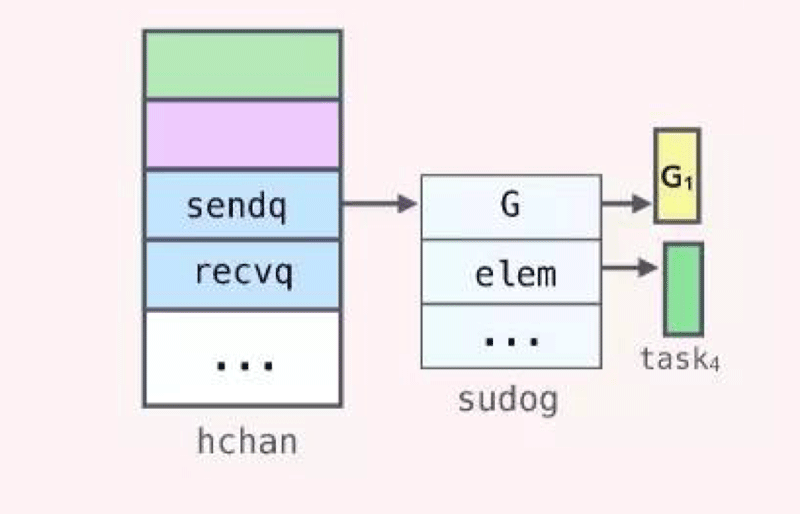
当 G2 从 ch 中接收一个数据时,会通知调度器,设置 G1 的状态为 runnable,然后将加入 P 的 runqueue 里,等待线程执行。

wait empty channel
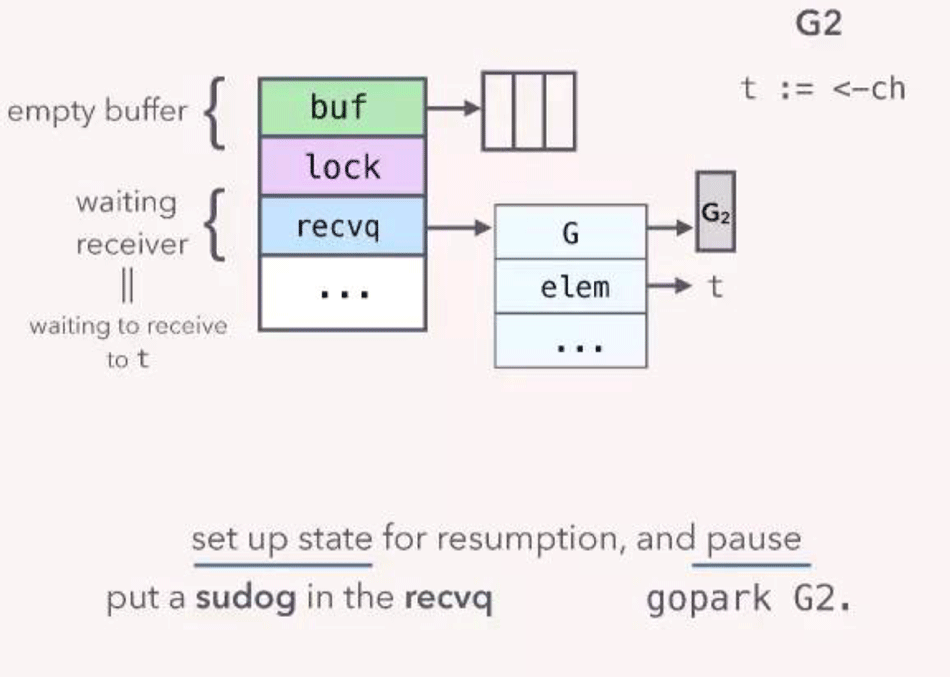
前面我们是假设 G1 先运行,如果 G2 先运行会怎么样呢?如果 G2 先运行,那么 G2 会从一个 empty 的 channel 里取数据,这个时候 G2 就会阻塞,和前面介绍的 G1 阻塞一样,G2 也会创建一个 sudog 结构体,保存接收数据的变量的地址,但是该 sudog 结构体是放到了 recvq 列表里,当 G1 向 ch 发送数据的时候,runtime 并没有对 hchan 结构体题的 buf 进行加锁,而是直接将 G1 里的发送到 ch 的数据 copy 到了 G2 sudog 里对应的 elem 指向的内存地址!
总结:
Golang 的一大特色就是其简单高效的天然并发机制,使用 goroutine 和 channel 实现了 CSP 模型。
理解 channel 的底层运行机制对灵活运用 golang 开发并发程序有很大的帮助,看了 Kavya 的分享,然后结合 golang runtime 相关的源码(源码开源并且也是 golang 实现简直良心!), 对 channel 的认识更加的深刻,当然还有一些地方存在一些疑问,比如 goroutine 的调度实现相关的,还是要潜心膜拜大神们的源码!
加载全部内容