Python time时间格式化和设置时区实现代码详解
双天至尊-王天龙 人气:01、时间戳转换为指定格式日期
import time
t = time.strftime("%Y-%m-%d %H:%M:%S", time.localtime())
print(t)
timestamp = time.time()
tuple_time = time.localtime(timestamp)
print(tuple_time)
print(time.strftime("%Y-%m-%d %H:%M:%S", tuple_time))
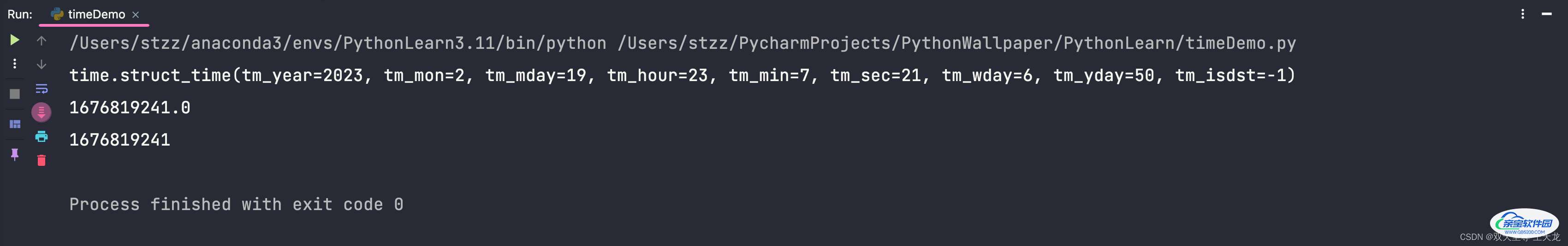
2、将字符串的时间转换为时间戳
import time import datetime time_str = "2023-02-19 23:07:21" time_struct = time.strptime(time_str, "%Y-%m-%d %H:%M:%S") print(time_struct) print(time.mktime(time_struct)) print(int(time.mktime(time_struct)))
3、Datetime详细介绍
Python提供了多个内置模块用于操作日期时间,像calendar,time,datetime。time模块我在之前的文章已经有所介绍,它提供 的接口与C标准库time.h基本一致。相比于time模块,datetime模块的接口则更直观、更容易调用。今天就来讲讲datetime模块。
datetime模块定义了两个常量:datetime.MINYEAR和datetime.MAXYEAR,分别表示datetime所能表示的最 小、最大年份。其中,MINYEAR = 1,MAXYEAR = 9999。(对于偶等玩家,这个范围已经足够用矣~~)
- datetime模块定义了下面这几个类:
- datetime.date:表示日期的类。常用的属性有year, month, day;
- datetime.time:表示时间的类。常用的属性有hour, minute, second, microsecond;
- datetime.datetime:表示日期时间。
- datetime.timedelta:表示时间间隔,即两个时间点之间的长度。
- datetime.tzinfo:与时区有关的相关信息。(这里不详细充分讨论该类,感兴趣的童鞋可以参考python手册)
注 :上面这些类型的对象都是不可变(immutable)的。
下面详细介绍这些类的使用方式。
date类
date类表示一个日期。日期由年、月、日组成(地球人都知道~~)。date类的构造函数如下:
class datetime.date(year, month, day):参数的意义就不多作解释了,只是有几点要注意一下:
- year的范围是[MINYEAR, MAXYEAR],即[1, 9999];
- month的范围是[1, 12]。(月份是从1开始的,不是从0开始的~_~);
- day的最大值根据给定的year, month参数来决定。例如闰年2月份有29天;
date类定义了一些常用的类方法与类属性,方便我们操作:
- date.max、date.min:date对象所能表示的最大、最小日期;
- date.resolution:date对象表示日期的最小单位。这里是天。
- date.today():返回一个表示当前本地日期的date对象;
- date.fromtimestamp(timestamp):根据给定的时间戮,返回一个date对象;
- datetime.fromordinal(ordinal):将Gregorian日历时间转换为date对象;(Gregorian Calendar :一种日历表示方法,类似于我国的农历,西方国家使用比较多,此处不详细展开讨论。)
4、获得三天前的时间的方法
import time
import datetime
time_str = "2023-02-19 23:07:21"
time_struct = time.strptime(time_str, "%Y-%m-%d %H:%M:%S")
print(datetime.datetime.now())
computed_time = datetime.datetime.now() - datetime.timedelta(days=3)
print(computed_time)
timestamp = time.mktime(computed_time.timetuple())
print(timestamp)
time_str = time.strftime("%Y-%m-%d %H:%M:%S", computed_time.timetuple())
print(time_str)
5、使用datetime模块来获取当前的日期和时间
import time
import datetime
time_str = "2023-02-19 23:07:21"
time_struct = time.strptime(time_str, "%Y-%m-%d %H:%M:%S")
currentDate = datetime.datetime.now()
print(time.strftime("%Y-%m-%d %H:%M:%S", currentDate.timetuple()))
print(currentDate.year)
print(currentDate.month)
print(currentDate.day)
print(currentDate.hour)
print(currentDate.minute)
print(currentDate.second)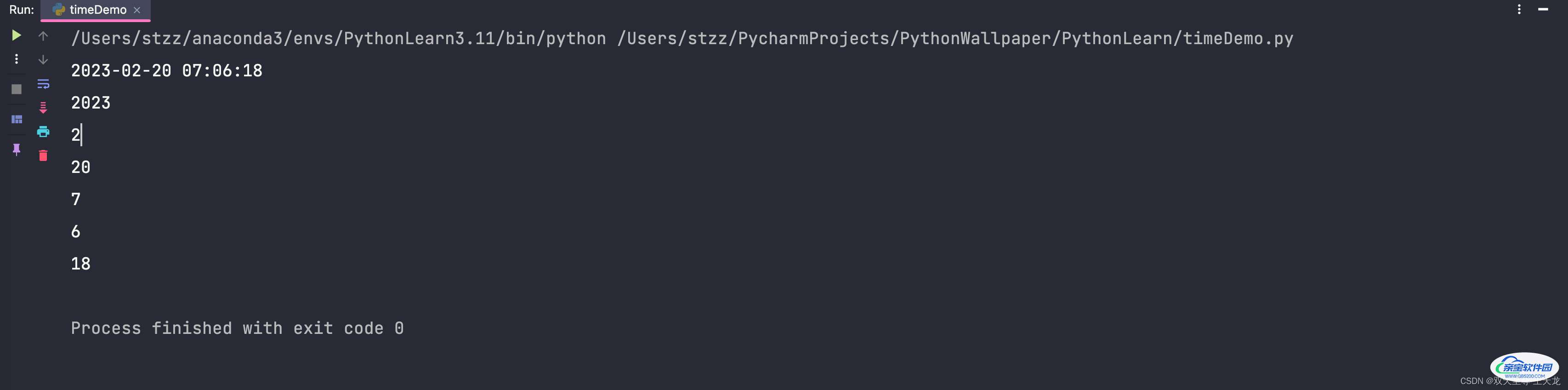
date提供的实例方法和属性:
- date.year、date.month、date.day:年、月、日;
- date.replace(year, month, day):生成一个新的日期对象,用参数指定的年,月,日代替原有对象中的属性。(原有对象仍保持不变)
- date.timetuple():返回日期对应的time.struct_time对象;
- date.toordinal():返回日期对应的Gregorian Calendar日期;
- date.weekday():返回weekday,如果是星期一,返回0;如果是星期2,返回1,以此类推;
- data.isoweekday():返回weekday,如果是星期一,返回1;如果是星期2,返回2,以此类推;
- date.isocalendar():返回格式如(year,month,day)的元组;
- date.isoformat():返回格式如'YYYY-MM-DD’的字符串;
- date.strftime(fmt):自定义格式化字符串。在下面详细讲解。
import time
from datetime import datetime, date
time_str = "2023-02-19 23:07:21"
time_struct = time.strptime(time_str, "%Y-%m-%d %H:%M:%S")
now = date(2023, 1, 18)
print(time.strftime("%Y-%m-%d %H:%M:%S", now.timetuple()))
print(now.weekday())
print(now.isoformat())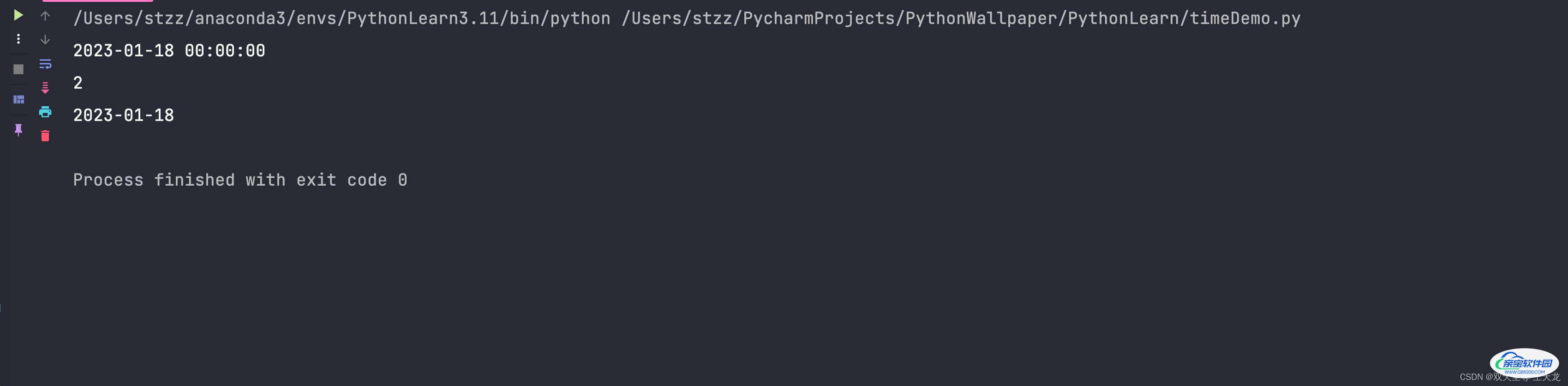
date还对某些操作进行了重载,它允许我们对日期进行如下一些操作:
- date2 = date1 + timedelta # 日期加上一个间隔,返回一个新的日期对象(timedelta将在下面介绍,表示时间间隔)
- date2 = date1 - timedelta # 日期隔去间隔,返回一个新的日期对象
- timedelta = date1 - date2 # 两个日期相减,返回一个时间间隔对象
- date1 < date2 # 两个日期进行比较
注: 对日期进行操作时,要防止日期超出它所能表示的范围。
import time
from datetime import datetime, date, timedelta
time_str = "2023-02-19 23:07:21"
time_struct = time.strptime(time_str, "%Y-%m-%d %H:%M:%S")
currentDate = date.today()
print(time.strftime("%Y-%m-%d %H:%M:%S", currentDate.timetuple()))
time_delta = currentDate - timedelta(days=1)
print(time.strftime("%Y-%m-%d %H:%M:%S", time_delta.timetuple()))
print(currentDate > time_delta)
print(currentDate - time_delta)
print(time_delta + timedelta(days=3))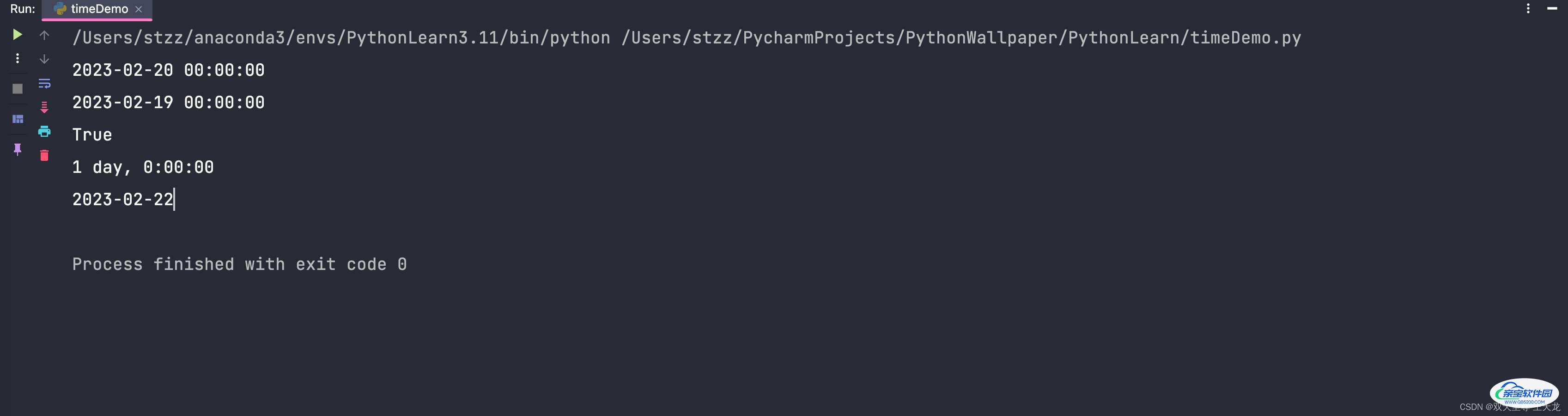
datetime类提供的实例方法与属性(很多属性或方法在date和time中已经出现过,在此有类似的意义,这里只罗列这些方法名,具体含义不再逐个展开介绍,可以参考上文对date与time类的讲解。):
- datetime.year、month、day、hour、minute、second、microsecond、tzinfo:
- datetime.date():获取date对象;
- datetime.time():获取time对象;
- datetime. replace ([ year[ , month[ , day[ , hour[ , minute[ , second[ , microsecond[ , tzinfo] ] ] ] ] ] ] ]):
- datetime. timetuple ()
- datetime. utctimetuple ()
- datetime. toordinal ()
- datetime. weekday ()
- datetime. isocalendar ()
- datetime. isoformat ([ sep] )
- datetime. ctime ():返回一个日期时间的C格式字符串,等效于time.ctime(time.mktime(dt.timetuple()));
- datetime. strftime (format)
像date一样,也可以对两个datetime对象进行比较,或者相减返回一个时间间隔对象,或者日期时间加上一个间隔返回一个新的日期时间对象。
加载全部内容