PyTorch中Torch.arange函数详解
_湘江夜话_ 人气:0torch.arange函数详解
官方文档:torch.arange
函数原型
arange(start=0, end, step=1, *, out=None, dtype=None, layout=torch.strided, device=None, requires_grad=False) -> Tensor
用法
返回大小为 的一维张量,其值介于区间
的一维张量,其值介于区间 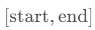 为步长等间隔取值
为步长等间隔取值
参数说明
| 参数 | 类型 | 说明 |
|---|---|---|
| start | Number | 起始值,默认值:0 |
| end | Number | 结束值 |
| step | Number | 步长,默认值:1 |
关键字参数
| 关键字参数 | 类型 | 说明 |
|---|---|---|
| out | Tensor | 输出张量 |
| dtype | torch.dtype | 期望的返回张量的数据类型。默认值:如果是None,则使用全局默认值。如果未给出 dtype,则从其他输入参数推断数据类型。如果 start、end 或 stop 中的任何一个是浮点数,则 dtype被推断为默认值,参见 get_default_dtype()。否则,dtype 被推断为 torch.int64 |
| layout | torch.layout | 返回张量的期望 layout。默认值:torch.strided |
| device | torch.device | 返回张量的期望设备。默认值:如果是None,则使用当前设备作为默认张量类型,参见torch.set_default_tensor_type()。对于 CPU 类型的张量,则 device 是 CPU ,若是 CUDA 类型的张量,则 device 是当前的 CUDA 设备 |
| requires_grad | bool | autograd 是否记录返回张量上所作的操作。默认值:False |
代码示例
>>> torch.arange(5) # 默认以 0 为起点
tensor([ 0, 1, 2, 3, 4])
>>> torch.arange(1, 4) # 默认间隔为 1
tensor([ 1, 2, 3])
>>> torch.arange(1, 2.5, 0.5) # 指定间隔 0.5
tensor([ 1.0000, 1.5000, 2.0000])
pyTorch中torch.range()和torch.arange()的区别
torch.range()和torch.arange()的区别
x = torch.range(-8, 8) y = torch.arange(-8, 8) print(x, x.dtype) print(y, y.dtype)
output:
tensor([-8., -7., -6., -5., -4., -3., -2., -1., 0., 1., 2., 3., 4., 5.,6., 7., 8.]) torch.float32
tensor([-8, -7, -6, -5, -4, -3, -2, -1, 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7]) torch.int64
可以看到,torch.range()的范围是[-8, 8],类型为torch.float32
torch.arange()的范围是[-8, 8),类型为torch.int64
在梯度设置时会出现错误:
x = torch.range(-8, 8, 1, requires_grad=True) y = torch.arange(-8, 8, 1, requires_grad=True) print(x, x.dtype) print(y, y.dtype)
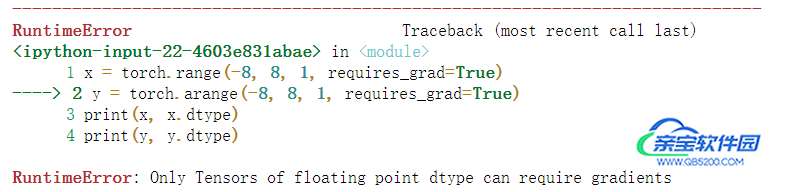
即只有当类型为float时才可设置requires_grad=True,故可将
y = torch.arange(-8, 8, 1, requires_grad=True)
改为以下,即手动改变数据类型即可。
y = torch.arange(-8.0, 8.0, 1.0, requires_grad=True)
output:
tensor([-8., -7., -6., -5., -4., -3., -2., -1., 0., 1., 2., 3., 4., 5.,6., 7., 8.], requires_grad=True)
torch.float32
tensor([-8., -7., -6., -5., -4., -3., -2., -1., 0., 1., 2., 3., 4., 5.,6., 7.], requires_grad=True)
torch.float32
总结
加载全部内容
 爱之家商城
爱之家商城 氢松练
氢松练 Face甜美相机
Face甜美相机 花汇通
花汇通 走路宝正式版
走路宝正式版 天天运动有宝
天天运动有宝 深圳plus
深圳plus 热门免费小说
热门免费小说