springMVC之HandlerExceptionResolver使用
原之殇 人气:0请求异常的处理
Handler查找以及执行期间可能会出现异常,需要对其进行处理,HandlerExceptionResolver就被设计出来了,
大致逻辑如下:
// 此段逻辑可以在dispatcherServlet中找到相似部分
ModelAndView mv = null;
try{
mv = hanlder.handle();
}catch(Exception e){
mv = handlerExceptionResolver.handle();
}springMVC也是这么设计的,当然比这要复杂一点,我们先来看一下HandlerExceptionResolver这个接口设计。
public interface HandlerExceptionResolver {
// 处理异常,返回视图信息
@Nullable
ModelAndView resolveException(
HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, @Nullable Object handler, Exception ex);
}可用的HandlerExceptionResolver
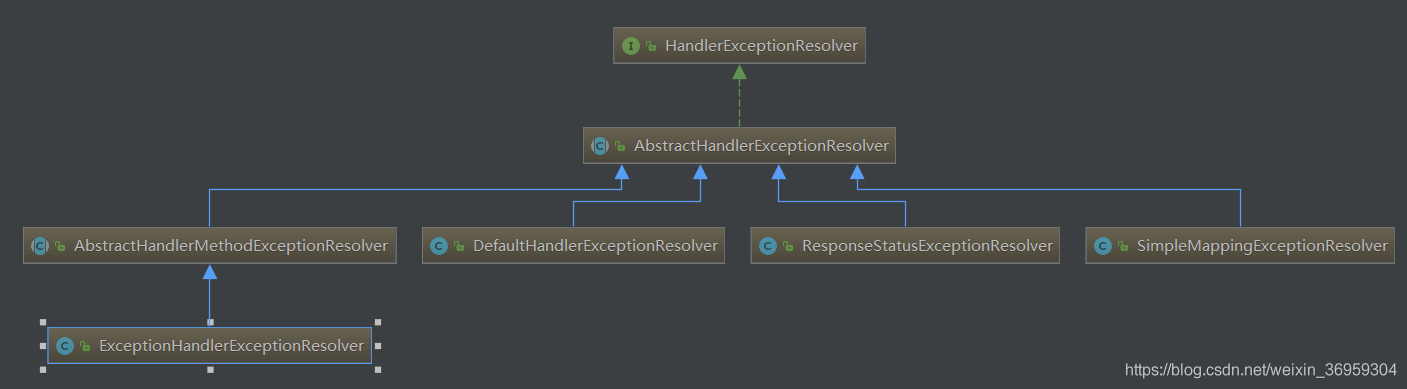
AbstractHandlerExceptionResolver这个抽象类的设计可以帮助我们针对不同的handler配置不同的HandlerExceptionResolver。
// AbstractHandlerExceptionResolver中解析异常的实现
public ModelAndView resolveException(
HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, @Nullable Object handler, Exception ex) {
// 检查这个解析器是否适用于这个处理器
if (shouldApplyTo(request, handler)) {
// 添加响应头,阻止响应缓存
prepareResponse(ex, response);
// 解析异常 交给子类覆盖实现
ModelAndView result = doResolveException(request, response, handler, ex);
// 日志记录,这里我将代码省略了
return result;
}else {
return null;
}
}
protected boolean shouldApplyTo(HttpServletRequest request, @Nullable Object handler) {
if (handler != null) {
// 可以通过设置mappedHandlers或mappedHandlerClasses来指定只为某个handler解析
if (this.mappedHandlers != null && this.mappedHandlers.contains(handler)) {
return true;
}
if (this.mappedHandlerClasses != null) {
for (Class<?> handlerClass : this.mappedHandlerClasses) {
if (handlerClass.isInstance(handler)) {
return true;
}
}
}
}
// 这里就是判断mappedHandlers或mappedHandlerClasses是否为空,都为空返回false
// 意味着异常解析器可以适用于任何handler
return !hasHandlerMappings();
}
接下来我们来看看不同子类对于doResolveException方法的实现。
1. SimpleMappingExceptionResolver
首先我们来看一下该类提供了哪些属性供我们进行设置。
// 1 配置的异常映射 key为异常名称 value为视图名称 private Properties exceptionMappings; // 2 排除的异常类型数组 private Class<?>[] excludedExceptions; // 3 默认的错误视图名称 private String defaultErrorView; // 4 默认的响应状态码 private Integer defaultStatusCode; // 5 key为异常名,value为响应状态码 private Map<String, Integer> statusCodes = new HashMap<>();
protected ModelAndView doResolveException(
HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, @Nullable Object handler, Exception ex) {
// 确定视图名称。
String viewName = determineViewName(ex, request);
if (viewName != null) {
// 根据视图名称去statusCodes中确定响应状态码
Integer statusCode = determineStatusCode(request, viewName);
if (statusCode != null) {
applyStatusCodeIfPossible(request, response, statusCode);
}
return getModelAndView(viewName, ex, request);
}else {
return null;
}
}protected String determineViewName(Exception ex, HttpServletRequest request) {
String viewName = null;
// 如果排除的异常数组中包含发生的异常,则返回null
if (this.excludedExceptions != null) {
for (Class<?> excludedEx : this.excludedExceptions) {
if (excludedEx.equals(ex.getClass())) {
return null;
}
}
}
// 检查特定的异常映射。
if (this.exceptionMappings != null) {
viewName = findMatchingViewName(this.exceptionMappings, ex);
}
// 定义了默认错误视图
if (viewName == null && this.defaultErrorView != null) {
viewName = this.defaultErrorView;
}
return viewName;
}protected String findMatchingViewName(Properties exceptionMappings, Exception ex) {
String viewName = null;
String dominantMapping = null;
int deepest = Integer.MAX_VALUE;
for (Enumeration<?> names = exceptionMappings.propertyNames(); names.hasMoreElements();) {
String exceptionMapping = (String) names.nextElement();
// depth =0 表示刚好找到;depth =-1 表示没找到,这是一个递归方法,
// 会一直沿着异常的继承结构向上找,每向上一层,depth+1
int depth = getDepth(exceptionMapping, ex);
if (depth >= 0 && (depth < deepest || (depth == deepest &&
dominantMapping != null && exceptionMapping.length() > dominantMapping.length()))) {
// 这里将深度赋值了,意味着一旦有匹配的异常结果时,即使下一次更匹配,但是
// depth < deepest这个条件也无法满足
deepest = depth;
dominantMapping = exceptionMapping;
viewName = exceptionMappings.getProperty(exceptionMapping);
}
}
return viewName;
} private int getDepth(String exceptionMapping, Class<?> exceptionClass, int depth) {
// 需要注意,这里使用的是contains,如果异常名称不适用全限定名
// 一旦出现多个异常映射项匹配的情况,将直接选择第一个匹配的结果
if (exceptionClass.getName().contains(exceptionMapping)) {
return depth;
}
if (exceptionClass == Throwable.class) {
return -1;
}
return getDepth(exceptionMapping, exceptionClass.getSuperclass(), depth + 1);
}demo
/**
* 通过SimpleMappingExceptionResolver做全局异常处理
*/
@Configuration
public class ExceptionConfig {
@Bean
public SimpleMappingExceptionResolver simpleMappingExceptionResolver() {
SimpleMappingExceptionResolver resolver = new SimpleMappingExceptionResolver();
Properties exceptionMappings= new Properties();
/**
* 这里是不建议的使用方式,如果出现异常java.lang.ArithmeticException,最终得到的视图却为
* error,这是我们不希望的,所以请使用全限定名
*/
mappers.put("Exception", "error");
mappers.put("ArithmeticException", "error1");
mappers.put("java.lang.ArithmeticException", "error2");
resolver.setExceptionMappings(exceptionMappings);
resolver.setDefaultErrorView("error3");
return resolver;
}
}2. DefaultHandlerExceptionResolver
(解决标准的Spring MVC异常并将其转换为相应的HTTP状态码),使用时我们不用设置order,默认的最小的优先级。
protected ModelAndView doResolveException(
HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, @Nullable Object handler, Exception ex) {
try {
if (ex instanceof HttpRequestMethodNotSupportedException) {
return handleHttpRequestMethodNotSupported(
(HttpRequestMethodNotSupportedException) ex, request, response, handler);
}
// 这里有很多if语句,就是针对标准的Spring MVC异常,返回对应的状态码进行处理
}catch (Exception handlerEx) {
// 日志打印...
}
return null;
}3. ResponseStatusExceptionResolver
protected ModelAndView doResolveException(
HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, @Nullable Object handler, Exception ex) {
try {
if (ex instanceof ResponseStatusException) {
return resolveResponseStatusException((ResponseStatusException) ex, request, response, handler);
}
// 找到异常上使用的ResponseStatus注解
ResponseStatus status = AnnotatedElementUtils.findMergedAnnotation(ex.getClass(), ResponseStatus.class);
if (status != null) {
return resolveResponseStatus(status, request, response, handler, ex);
}
// ResponseStatus为空,异常链仍未结束,递归调用
if (ex.getCause() instanceof Exception) {
return doResolveException(request, response, handler, (Exception) ex.getCause());
}
}catch (Exception resolveEx) {
...
}
return null;
}ResponseStatus注解使用方式挺多的,这里是其中一种,就是在自定义异常的类上添加此注解。还有其他用法大家可以去看看这篇文章,@ResponseStatus注解的更多用法。
4. ExceptionHandlerExceptionResolver
在看这个类解析异常的方法之前,我们先认识一下两个缓存,分别为局部和全局异常方法解析器映射缓存,源码中也就是这两个变量。
// 局部异常方法解析器缓存,下面统称为局部缓存 private final Map<Class<?>, ExceptionHandlerMethodResolver> exceptionHandlerCache = new ConcurrentHashMap<>(64); // 全局异常方法解析器缓存,下面统称为全局缓存 private final Map<ControllerAdviceBean, ExceptionHandlerMethodResolver> exceptionHandlerAdviceCache = new LinkedHashMap<>();
全局缓存在bean初始化的时候就会加载,将会把容器中含有注解ControllerAdvice的bean收集起来。
// bean 初始化的时候会加载这个方法
public void afterPropertiesSet() {
// 初始化全局缓存
initExceptionHandlerAdviceCache();
if (this.argumentResolvers == null) {
// 设置请求参数解析器
}
if (this.returnValueHandlers == null) {
// 设置返回值解析器
}
}
private void initExceptionHandlerAdviceCache() {
if (getApplicationContext() == null) {
return;
}
// 获取含有注解ControllerAdvice的bean
List<ControllerAdviceBean> adviceBeans = ControllerAdviceBean.findAnnotatedBeans(getApplicationContext());
for (ControllerAdviceBean adviceBean : adviceBeans) {
Class<?> beanType = adviceBean.getBeanType();
if (beanType == null) {
throw new IllegalStateException("Unresolvable type for ControllerAdviceBean: " + adviceBean);
}
ExceptionHandlerMethodResolver resolver = new ExceptionHandlerMethodResolver(beanType);
if (resolver.hasExceptionMappings()) {
// 加入全局缓存
this.exceptionHandlerAdviceCache.put(adviceBean, resolver);
}
// MARK:如果该类实现了ResponseBodyAdvice接口
if (ResponseBodyAdvice.class.isAssignableFrom(beanType)) {
this.responseBodyAdvice.add(adviceBean);
}
}
// ...
}有关MARK部分ResponseBodyAdvice接口的用处,这里不展开了。
而局部缓存是在解析异常的方法中动态加载的。
protected ModelAndView doResolveHandlerMethodException(HttpServletRequest request,
HttpServletResponse response, @Nullable HandlerMethod handlerMethod, Exception exception) {
// 根据异常类型,处理器找到处理异常的方法
ServletInvocableHandlerMethod exceptionHandlerMethod = getExceptionHandlerMethod(handlerMethod, exception);
// 异常方法调用...
// 返回ModelAndView...
}protected ServletInvocableHandlerMethod getExceptionHandlerMethod(
@Nullable HandlerMethod handlerMethod, Exception exception) {
if (handlerMethod != null) {
handlerType = handlerMethod.getBeanType();
// 从局部缓存中查找,找不到,则构建一个
ExceptionHandlerMethodResolver resolver = this.exceptionHandlerCache.get(handlerType);
if (resolver == null) {
resolver = new ExceptionHandlerMethodResolver(handlerType);
this.exceptionHandlerCache.put(handlerType, resolver);
}
// 解析异常获取对应方法
Method method = resolver.resolveMethod(exception);
if (method != null) {
return new ServletInvocableHandlerMethod(handlerMethod.getBean(), method);
}
// 如果是代理类,则要获取到原目标类型
if (Proxy.isProxyClass(handlerType)) {
handlerType = AopUtils.getTargetClass(handlerMethod.getBean());
}
}
// 局部缓存没有找到,则去全局缓存中找
for (Map.Entry<ControllerAdviceBean, ExceptionHandlerMethodResolver> entry : this.exceptionHandlerAdviceCache.entrySet()) {
ControllerAdviceBean advice = entry.getKey();
// MARK:检查是否应该通过给定的bean类型
if (advice.isApplicableToBeanType(handlerType)) {
ExceptionHandlerMethodResolver resolver = entry.getValue();
Method method = resolver.resolveMethod(exception);
if (method != null) {
return new ServletInvocableHandlerMethod(advice.resolveBean(), method);
}
}
}
return null;
} 上述代码MARK部分涉及到另一知识点,有关注解ControllerAdvice的设置部分,这里就不展开了。
同前面一样,在看解析异常获取对应方法前,我先介绍另一个缓存-异常映射方法缓存。这个缓存在ExceptionHandlerMethodResolver实例化的时候被加载。
// 用于选择@ExceptionHandler方法的过滤器。
public static final MethodFilter EXCEPTION_HANDLER_METHODS = method ->
AnnotatedElementUtils.hasAnnotation(method, ExceptionHandler.class);
// 异常映射方法缓存 key为异常类型 value为方法
private final Map<Class<? extends Throwable>, Method> mappedMethods = new HashMap<>(16);
public ExceptionHandlerMethodResolver(Class<?> handlerType) {
for (Method method : MethodIntrospector.selectMethods(handlerType, EXCEPTION_HANDLER_METHODS)) {
// 检测方法映射的异常
for (Class<? extends Throwable> exceptionType : detectExceptionMappings(method)) {
// 加入缓存
addExceptionMapping(exceptionType, method);
}
}
}
private List<Class<? extends Throwable>> detectExceptionMappings(Method method) {
List<Class<? extends Throwable>> result = new ArrayList<>();
// 获取注解ExceptionHandler的value属性
detectAnnotationExceptionMappings(method, result);
// 如果注解value没有设置
if (result.isEmpty()) {
for (Class<?> paramType : method.getParameterTypes()) {
// 方法参数中需要设置异常字段
if (Throwable.class.isAssignableFrom(paramType)) {
result.add((Class<? extends Throwable>) paramType);
}
}
}
if (result.isEmpty()) {
throw new IllegalStateException("No exception types mapped to " + method);
}
return result;
}了解这个缓存后,再回过头来看解析异常获取对应方法,其实就是从缓存中找而已。
private Method getMappedMethod(Class<? extends Throwable> exceptionType) {
List<Class<? extends Throwable>> matches = new ArrayList<>();
for (Class<? extends Throwable> mappedException : this.mappedMethods.keySet()) {
// 只要出现的异常是指定异常的子类,就算作匹配
if (mappedException.isAssignableFrom(exceptionType)) {
matches.add(mappedException);
}
}
if (!matches.isEmpty()) {
// 有可能出现同一个异常匹配到多个映射的情况,这里按异常层级关系,从小大大排序
matches.sort(new ExceptionDepthComparator(exceptionType));
// 取最小层级的
return this.mappedMethods.get(matches.get(0));
}else {
return null;
}
}以上为个人经验,希望能给大家一个参考,也希望大家多多支持。
加载全部内容