scrapy实现增量式爬取
冯子玉 人气:0实现爬虫的增量式爬取有两种方法,一是在获得页面解析的内容后判断该内容是否已经被爬取过,二是在发送请求之前判断要被请求的url是否已经被爬取过,前一种方法可以感知每个页面的内容是否发生变化,能获取页面新增或者变化的内容,但是由于要对每个url发送请求,所以速度比较慢,而对网站服务器的压力也比较大,后一种无法获得页面变化的内容,但是因为不用对已经爬取过的url发送请求,所以对服务器压力比较小,速度比较快,适用于爬取新增网页
下面用一个小说网站爬虫的例子来介绍在scrapy中这两种方式的实现
1.要爬取的信息
在scrapy中,信息通过item来封装,这里我定义两个item,一个用于封装每本小说的信息,一个用于封装每个章节的信息
1.BookItem
class BookItem(scrapy.Item):
_id = scrapy.Field() #小说id,用于定位章节信息,章节唯一
novel_Name = scrapy.Field() #小说名称
novel_Writer = scrapy.Field()#小说作者
novel_Type = scrapy.Field()#小说类型
novel_Status = scrapy.Field()#小说状态,连载或者完结
novel_UpdateTime = scrapy.Field()#最后更新时间
novel_Words = scrapy.Field() #总字数
novel_ImageUrl = scrapy.Field()#封面图片
novel_AllClick = scrapy.Field()#总点击
novel_MonthClick = scrapy.Field()#月点击
novel_WeekClick = scrapy.Field()#周点击
novel_AllComm = scrapy.Field()#总推荐
novel_MonthComm = scrapy.Field()#月推荐
novel_WeekComm = scrapy.Field()#周推荐
novel_Url = scrapy.Field()#小说url
novel_Introduction = scrapy.Field()#小说简介2.ChapterItem
class ChapterItem(scrapy.Item):
chapter_Url = scrapy.Field()#章节url
_id = scrapy.Field()#章节id
novel_Name = scrapy.Field()#小说名称
chapter_Name = scrapy.Field()#章节名称
chapter_Content = scrapy.Field()#内容
novel_ID = scrapy.Field()#小说id
is_Error = scrapy.Field()#是否异常2.解析信息
这里我是用的是scrapy自带的通用爬虫模块,只需要指定信息解析方式,需要跟进的url就够了
1.指定需要跟进的url和回调函数
allowed_domains = ["23us.so"] #允许爬取的域名
start_urls = ["http://www.23us.so/xiaoshuo/414.html"]#种子url
#跟进的url
rules=(
Rule(LinkExtractor(allow=("xiaoshuo/\d*\.html")),callback="parse_book_message",follow=True),
Rule(LinkExtractor(allow=("files/article/html/\d*?/\d*?.index.html")),callback="parse_book_chapter",follow=True),
Rule(LinkExtractor(allow=("files/article/html/\d*?/\d*?/\d*?.html")),callback="parse_chapter_content",follow=True),
Rule(LinkExtractor(allow=(".*")),follow=True),
)2.解析方法
1.解析书籍信息方法
#解析小说信息页面
def parse_book_message(self,response):
if not response.body:
print(response.url+"已经被爬取过了,跳过")
return;
ht = response.body.decode("utf-8")
text = html.fromstring(ht)
novel_Url = response.url
novel_Name = text.xpath(".//dl[@id='content']/dd[1]/h1/text()")[0].split(" ")[0] if response.xpath(".//dl[@id='content']/dd[1]/h1/text()") else "None"
novel_ImageUrl = text.xpath(".//a[@class='hst']/img/@src")[0] if response.xpath(".//a[@class='hst']/img/@src") else "None"
novel_ID = int(response.url.split("/")[-1].split(".")[0]) if response.url.split("/")[-1].split(".") else "None"
novel_Type = text.xpath(".//table[@id='at']/tr[1]/td[1]/a/text()") if response.xpath(".//table[@id='at']/tr[1]/td[1]/a/text()") else "None"
novel_Writer = "".join(text.xpath(".//table[@id='at']/tr[1]/td[2]/text()")) if response.xpath(".//table[@id='at']/tr[1]/td[2]/text()") else "None"
novel_Status = "".join(text.xpath(".//table[@id='at']/tr[1]/td[3]/text()")) if response.xpath(".//table[@id='at']/tr[1]/td[3]/text()") else "None"
novel_Words = self.getNumber("".join(text.xpath(".//table[@id='at']/tr[2]/td[2]/text()"))) if response.xpath(".//table[@id='at']/tr[2]/td[2]/text()") else "None"
novel_UpdateTime = "".join(text.xpath(".//table[@id='at']/tr[2]/td[3]/text()")) if response.xpath(".//table[@id='at']/tr[2]/td[3]/text()") else "None"
novel_AllClick = int("".join(text.xpath(".//table[@id='at']/tr[3]/td[1]/text()"))) if response.xpath(".//table[@id='at']/tr[3]/td[1]/text()") else "None"
novel_MonthClick = int("".join(text.xpath(".//table[@id='at']/tr[3]/td[2]/text()"))) if response.xpath(".//table[@id='at']/tr[3]/td[2]/text()") else "None"
novel_WeekClick = int("".join(text.xpath(".//table[@id='at']/tr[3]/td[3]/text()"))) if response.xpath(".//table[@id='at']/tr[3]/td[3]/text()") else "None"
novel_AllComm = int("".join(text.xpath(".//table[@id='at']/tr[4]/td[1]/text()"))) if response.xpath(".//table[@id='at']/tr[4]/td[1]/text()") else "None"
novel_MonthComm = int("".join(text.xpath(".//table[@id='at']/tr[4]/td[3]/text()"))) if response.xpath(".//table[@id='at']/tr[4]/td[2]/text()") else "None"
novel_WeekComm = int("".join(text.xpath(".//table[@id='at']/tr[4]/td[3]/text()"))) if response.xpath(".//table[@id='at']/tr[4]/td[3]/text()") else "None"
pattern = re.compile('<p>(.*)<br')
match = pattern.search(ht)
novel_Introduction = "".join(match.group(1).replace(" ","")) if match else "None"
#封装小说信息类
bookitem = BookItem(
novel_Type = novel_Type[0],
novel_Name = novel_Name,
novel_ImageUrl = novel_ImageUrl,
_id = novel_ID, #小说id作为唯一标识符
novel_Writer = novel_Writer,
novel_Status = novel_Status,
novel_Words = novel_Words,
novel_UpdateTime = novel_UpdateTime,
novel_AllClick = novel_AllClick,
novel_MonthClick = novel_MonthClick,
novel_WeekClick = novel_WeekClick,
novel_AllComm = novel_AllComm,
novel_MonthComm = novel_MonthComm,
novel_WeekComm = novel_WeekComm,
novel_Url = novel_Url,
novel_Introduction = novel_Introduction,
)
return bookitem
2.解析章节信息
def parse_chapter_content(self,response):
if not response.body:
print(response.url+"已经被爬取过了,跳过")
return;
ht = response.body.decode('utf-8')
text = html.fromstring(ht)
soup = BeautifulSoup(ht)
novel_ID = response.url.split("/")[-2]
novel_Name = text.xpath(".//p[@class='fr']/following-sibling::a[3]/text()")[0]
chapter_Name = text.xpath(".//h1[1]/text()")[0]
'''
chapter_Content = "".join("".join(text.xpath(".//dd[@id='contents']/text()")).split())
if len(chapter_Content) < 25:
chapter_Content = "".join("".join(text.xpath(".//dd[@id='contents']//*/text()")))
pattern = re.compile('dd id="contents".*?>(.*?)</dd>')
match = pattern.search(ht)
chapter_Content = "".join(match.group(1).replace(" ","").split()) if match else "爬取错误"
'''
result,number = re.subn("<.*?>","",str(soup.find("dd",id='contents')))
chapter_Content = "".join(result.split())
print(len(chapter_Content))
novel_ID = response.url.split("/")[-2]
return ChapterItem(
chapter_Url = response.url,
_id=int(response.url.split("/")[-1].split(".")[0]),
novel_Name=novel_Name,
chapter_Name=chapter_Name,
chapter_Content= chapter_Content,
novel_ID = novel_ID,
is_Error = len(chapter_Content) < 3000
)
3.scrapy中实现增量式爬取的几种方式
1.缓存
通过开启缓存,将每个请求缓存至本地,下次爬取时,scrapy会优先从本地缓存中获得response,这种模式下,再次请求已爬取的网页不用从网络中获得响应,所以不受带宽影响,对服务器也不会造成额外的压力,但是无法获取网页变化的内容,速度也没有第二种方式快,而且缓存的文件会占用比较大的内存,在setting.py的以下注释用于设置缓存
#HTTPCACHE_ENABLED = True #HTTPCACHE_EXPIRATION_SECS = 0 #HTTPCACHE_DIR = 'httpcache' #HTTPCACHE_IGNORE_HTTP_CODES = [] #HTTPCACHE_STORAGE = 'scrapy.extensions.httpcache.FilesystemCacheStorage'
这种方式比较适合内存比较大的主机使用,我的阿里云是最低配的,在爬取半个晚上接近27W个章节信息后,内存就用完了
2.对item实现去重
本文开头的第一种方式,实现方法是在pipelines.py中进行设置,即在持久化数据之前判断数据是否已经存在,这里我用的是mongodb持久化数据,逻辑如下
#处理书信息
def process_BookItem(self,item):
bookItemDick = dict(item)
try:
self.bookColl.insert(bookItemDick)
print("插入小说《%s》的所有信息"%item["novel_Name"])
except Exception:
print("小说《%s》已经存在"%item["novel_Name"])
#处理每个章节
def process_ChapterItem(self,item):
try:
self.contentColl.insert(dict(item))
print('插入小说《%s》的章节"%s"'%(item['novel_Name'],item['chapter_Name']))
except Exception:
print("%s存在了,跳过"%item["chapter_Name"])
def process_item(self, item, spider):
'''
if isinstance(item,ChaptersItem):
self.process_ChaptersItem(item)
'''
if isinstance(item,BookItem):
self.process_BookItem(item)
if isinstance(item,ChapterItem):
self.process_ChapterItem(item)
return item
两种方法判断mongodb中是否存在已有的数据,一是先查询后插入,二是先设置唯一索引或者主键再直接插入,由于mongodb的特点是插入块,查询慢,所以这里直接插入,需要将唯一信息设置为”_id”列,或者设置为唯一索引,在mongodb中设置方法如下
db.集合名.ensureIndex({"要设置索引的列名":1},{"unique":1})需要用什么信息实现去重,就将什么信息设置为唯一索引即可(小说章节信息由于数据量比较大,用于查询的列最好设置索引,要不然会非常慢),这种方法对于服务器的压力太大,而且速度比较慢,我用的是第二种方法,即对已爬取的url进行去重
3.对url实现去重
对我而言,这种方法是最好的方法,因为速度快,对网站服务器的压力也比较小,不过网上的资料比较少,后来在文档中发现scrapy可以自定义下载中间件,才解决了这个问题
文档原文如下
class scrapy.downloadermiddlewares.DownloaderMiddleware
process_request(request, spider) 当每个request通过下载中间件时,该方法被调用。
process_request() 必须返回其中之一: 返回 None 、返回一个 Response 对象、返回一个 Request对象或raise IgnoreRequest 。
如果其返回 None ,Scrapy将继续处理该request,执行其他的中间件的相应方法,直到合适的下载器处理函数(downloadhandler)被调用, 该request被执行(其response被下载)。
如果其返回 Response 对象,Scrapy将不会调用 任何 其他的 process_request() 或process_exception() 方法,或相应地下载函数; 其将返回该response。 已安装的中间件的process_response() 方法则会在每个response返回时被调用。
如果其返回 Request 对象,Scrapy则停止调用process_request方法并重新调度返回的request。当新返回的request被执行后,相应地中间件链将会根据下载的response被调用。
如果其raise一个 IgnoreRequest 异常,则安装的下载中间件的 process_exception()方法会被调用。如果没有任何一个方法处理该异常,则request的errback(Request.errback)方法会被调用。如果没有代码处理抛出的异常,则该异常被忽略且不记录(不同于其他异常那样)。
所以只需要在process_request中实现去重的逻辑就可以了,代码如下
class UrlFilter(object):
#初始化过滤器(使用mongodb过滤)
def __init__(self):
self.settings = get_project_settings()
self.client = pymongo.MongoClient(
host = self.settings['MONGO_HOST'],
port = self.settings['MONGO_PORT'])
self.db = self.client[self.settings['MONGO_DB']]
self.bookColl = self.db[self.settings['MONGO_BOOK_COLL']]
#self.chapterColl = self.db[self.settings['MONGO_CHAPTER_COLL']]
self.contentColl = self.db[self.settings['MONGO_CONTENT_COLL']]
def process_request(self,request,spider):
if (self.bookColl.count({"novel_Url":request.url}) > 0) or (self.contentColl.count({"chapter_Url":request.url}) > 0):
return http.Response(url=request.url,body=None)
但是又会有一个问题,就是有可能下次开启时,种子url已经被爬取过了,爬虫会直接关闭,后来想到一个笨方法解决了这个问题,即在pipeline.py里的open_spider方法中再爬虫开启时删除对种子url的缓存
def open_spider(self,spider):
self.bookColl.remove({"novel_Url":"http://www.23us.so/xiaoshuo/414.html"})4.结果
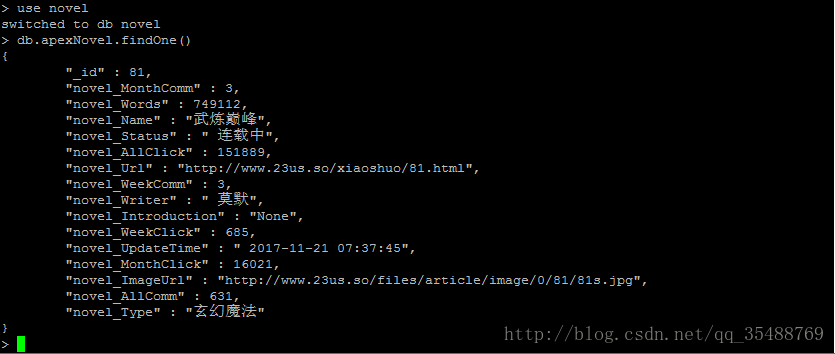
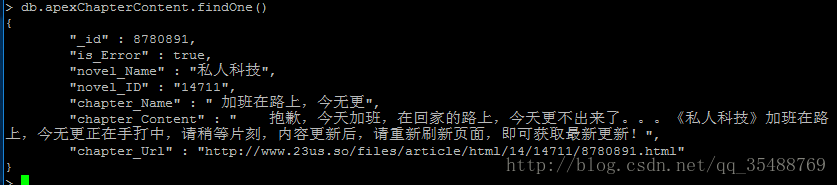
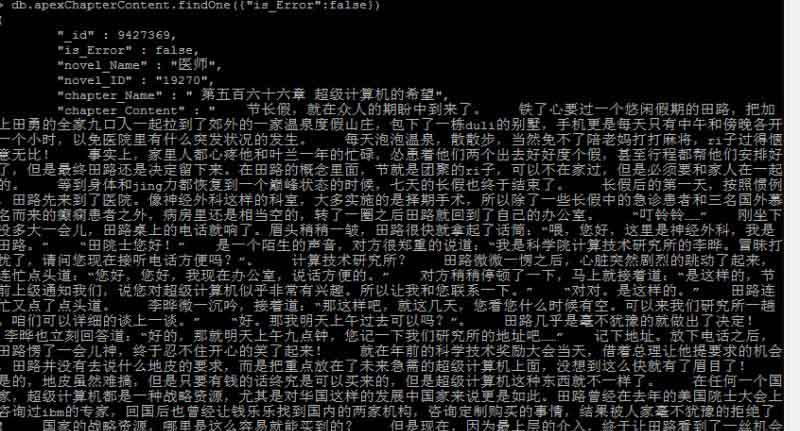

目前一个晚上爬取了大约1000部小说35W个章节的信息,还在继续爬取中
以上为个人经验,希望能给大家一个参考,也希望大家多多支持。
加载全部内容