iOS的UITableview的用法及优化 iOS开发中UITableview控件的基本使用及性能优化方法
文顶顶 人气:0UITableview控件基本使用
一、一个简单的英雄展示程序
NJHero.h文件代码(字典转模型)
#import <Foundation/Foundation.h>
@interface NJHero : NSObject
/**
* 头像
*/
@property (nonatomic, copy) NSString *icon;
/**
* 名称
*/
@property (nonatomic, copy) NSString *name;
/**
* 描述
*/
@property (nonatomic, copy) NSString *intro;
- (instancetype)initWithDict:(NSDictionary *)dict;
+ (instancetype)heroWithDict:(NSDictionary *)dict;
@end
NJViewController.m文件代码
#import "NJViewController.h"
#import "NJHero.h"
@interface NJViewController ()<UITableViewDataSource, UITableViewDelegate>
/**
* 保存所有的英雄数据
*/
@property (nonatomic, strong) NSArray *heros;
@property (weak, nonatomic) IBOutlet UITableView *tableView;
@end
@implementation NJViewController
#pragma mark - 懒加载
- (NSArray *)heros
{
if (_heros == nil) {
// 1.获得全路径
NSString *fullPath = [[NSBundle mainBundle] pathForResource:@"heros" ofType:@"plist"];
// 2.更具全路径加载数据
NSArray *dictArray = [NSArray arrayWithContentsOfFile:fullPath];
// 3.字典转模型
NSMutableArray *models = [NSMutableArray arrayWithCapacity:dictArray.count];
for (NSDictionary *dict in dictArray) {
NJHero *hero = [NJHero heroWithDict:dict];
[models addObject:hero];
}
// 4.赋值数据
_heros = [models copy];
}
// 4.返回数据
return _heros;
}
- (void)viewDidLoad
{
[super viewDidLoad];
// 设置Cell的高度
// 当每一行的cell高度一致的时候使用属性设置cell的高度
self.tableView.rowHeight = 60;
self.tableView.delegate = self;
}
#pragma mark - UITableViewDataSource
// 返回多少组
- (NSInteger)numberOfSectionsInTableView:(UITableView *)tableView
{
return 1;
}
// 返回每一组有多少行
- (NSInteger) tableView:(UITableView *)tableView numberOfRowsInSection:(NSInteger)section
{
return self.heros.count;
}
// 返回哪一组的哪一行显示什么内容
- (UITableViewCell *)tableView:(UITableView *)tableView cellForRowAtIndexPath:(NSIndexPath *)indexPath
{
// 1.创建CELL
UITableViewCell *cell = [[UITableViewCell alloc] initWithStyle:UITableViewCellStyleSubtitle reuseIdentifier:nil];
// 2.设置数据
// 2.1取出对应行的模型
NJHero *hero = self.heros[indexPath.row];
// 2.2赋值对应的数据
cell.textLabel.text = hero.name;
cell.detailTextLabel.text = hero.intro;
cell.imageView.image = [UIImage imageNamed:hero.icon];
// 3.返回cell
return cell;
}
#pragma mark - UITableViewDelegate
/*
// 当每一行的cell的高度不一致的时候就使用代理方法设置cell的高度
- (CGFloat)tableView:(UITableView *)tableView heightForRowAtIndexPath:(NSIndexPath *)indexPath
{
if (1 == indexPath.row) {
return 180;
}
return 44;
}
*/
#pragma mark - 控制状态栏是否显示
/**
* 返回YES代表隐藏状态栏, NO相反
*/
- (BOOL)prefersStatusBarHidden
{
return YES;
}
@end
实现效果:

代码注意点:
(1)在字典转模型的代码处用下面的代码,为可变数组分配dictArray.count个存储空间,可以提高程序的性能
NSMutableArray *models = [NSMutableArrayarrayWithCapacity:dictArray.count];
(2)设置cell的高度
有三种办法可以设置cell的高度
1) 可以在初始加载方法中设置,self.tableView.rowHeight = 60;这适用于当每一行的cell高度一致的时候,使用属性设置cell的高度。
2)在storyboard中设置,适用于高度一致
3)当每一行的cell的高度不一致的时候就使用代理方法设置cell的高度
- (CGFloat)tableView:(UITableView *)tableView heightForRowAtIndexPath:(NSIndexPath *)indexPath
{
if (1 == indexPath.row) {
return 180;
}
return 44;
}
二、cell的一些属性
代码示例:
#import "NJViewController.h"
#import "NJHero.h"
@interface NJViewController ()<UITableViewDataSource, UITableViewDelegate>
/**
* 保存所有的英雄数据
*/
@property (nonatomic, strong) NSArray *heros;
@property (weak, nonatomic) IBOutlet UITableView *tableView;
@end
@implementation NJViewController
#pragma mark - 懒加载
- (NSArray *)heros
{
if (_heros == nil) {
// 1.获得全路径
NSString *fullPath = [[NSBundle mainBundle] pathForResource:@"heros" ofType:@"plist"];
// 2.更具全路径加载数据
NSArray *dictArray = [NSArray arrayWithContentsOfFile:fullPath];
// 3.字典转模型
NSMutableArray *models = [NSMutableArray arrayWithCapacity:dictArray.count];
for (NSDictionary *dict in dictArray) {
NJHero *hero = [NJHero heroWithDict:dict];
[models addObject:hero];
}
// 4.赋值数据
_heros = [models copy];
}
// 4.返回数据
return _heros;
}
- (void)viewDidLoad
{
[super viewDidLoad];
// 设置Cell的高度
// 当每一行的cell高度一致的时候使用属性设置cell的高度
self.tableView.rowHeight = 60;
self.tableView.delegate = self;
}
#pragma mark - UITableViewDataSource
// 返回多少组
- (NSInteger)numberOfSectionsInTableView:(UITableView *)tableView
{
return 1;
}
// 返回每一组有多少行
- (NSInteger) tableView:(UITableView *)tableView numberOfRowsInSection:(NSInteger)section
{
return self.heros.count;
}
// 返回哪一组的哪一行显示什么内容
- (UITableViewCell *)tableView:(UITableView *)tableView cellForRowAtIndexPath:(NSIndexPath *)indexPath
{
// 1.创建CELL
UITableViewCell *cell = [[UITableViewCell alloc] initWithStyle:UITableViewCellStyleSubtitle reuseIdentifier:nil];
// 2.设置数据
// 2.1取出对应行的模型
NJHero *hero = self.heros[indexPath.row];
// 2.2赋值对应的数据
cell.textLabel.text = hero.name;
cell.detailTextLabel.text = hero.intro;
cell.imageView.image = [UIImage imageNamed:hero.icon];
// 2.3设置cell的辅助视图
// cell.accessoryType = UITableViewCellAccessoryDisclosureIndicator;
if (0 == indexPath.row) {
cell.accessoryView = [UIButton buttonWithType:UIButtonTypeContactAdd];
}else
{
cell.accessoryView = [[UISwitch alloc] init];
}
// UIButton *btn = [[UIButton alloc] init];
// btn.backgroundColor = [UIColor redColor];
// cell.accessoryView = btn;
// 2.4设置cell的背景颜色
cell.backgroundColor = [UIColor blueColor];
// 设置默认状态的背景
// UIView *view = [[UIView alloc] init];
// view.backgroundColor = [UIColor blueColor];
// cell.backgroundView = view;
UIImageView *iv = [[UIImageView alloc] initWithImage:[UIImage imageNamed:@"buttondelete"]];
cell.backgroundView = iv;
// 设置选中状态的背景
UIView *view2 = [[UIView alloc] init];
view2.backgroundColor = [UIColor purpleColor];
cell.selectedBackgroundView = view2;
// 3.返回cell
return cell;
}
#pragma mark - 控制状态栏是否显示
/**
* 返回YES代表隐藏状态栏, NO相反
*/
- (BOOL)prefersStatusBarHidden
{
return YES;
}
@end
实现效果:

cell的一些属性:
(1)设置cell的辅助视图,设置cell.accessoryView(系统提供了枚举型,也可以自定义@父类指针指向子类对象);
(2)设置cell的背景颜色,有两种方式可以设置cell的背景颜色:
通过backgroundColor 和 backgroundView都可以设置cell的背景。但是backgroundView 的优先级比 backgroundColor的高,所以如果同时设置了backgroundColor和backgroundView, 那么backgroundView会盖住backgroundColor
示例:cell.backgroundColor = [UIColorblueColor];
(3)设置cell默认状态的背景
示例1:
UIView *view = [[UIView alloc] init];
view.backgroundColor = [UIColor blueColor];
cell.backgroundView = view;
示例2:
UIImageView *iv = [[UIImageViewalloc] initWithImage:[UIImageimageNamed:@"buttondelete"]];
cell.backgroundView = iv;(父类指针指向子类对象,可以使用图片用简单的操作设置绚丽的效果)
(4)设置cell选中状态的背景
示例:
UIView *view2 = [[UIView alloc] init];
view2.backgroundColor = [UIColorpurpleColor];
cell.selectedBackgroundView = view2;
三、tableview的一些属性
代码示例:
#import "NJViewController.h"
@interface NJViewController ()<UITableViewDataSource>
@end
@implementation NJViewController
- (void)viewDidLoad
{
[super viewDidLoad];
// 1.创建tableview
UITableView *tableview = [[UITableView alloc] init];
tableview.frame = self.view.bounds;
// 2.设置数据源
tableview.dataSource =self;
// 3.添加tableview到view
[self.view addSubview:tableview];
// 4.设置分割线样式
// tableview.separatorStyle = UITableViewCellSeparatorStyleNone;
// 5.设置分割线颜色
接收的参数是颜色的比例值
tableview.separatorColor = [UIColor colorWithRed:0/255.0 green:255/255.0 blue:0/255.0 alpha:255/255.0];
// 设置tableview的头部视图
tableview.tableHeaderView = [UIButton buttonWithType:UIButtonTypeContactAdd];
tableview.tableFooterView = [[UISwitch alloc] init];
}
- (NSInteger)numberOfSectionsInTableView:(UITableView *)tableView
{
return 1;
}
- (NSInteger)tableView:(UITableView *)tableView numberOfRowsInSection:(NSInteger)section
{
return 10;
}
- (UITableViewCell *)tableView:(UITableView *)tableView cellForRowAtIndexPath:(NSIndexPath *)indexPath
{
// 1.创建cell
UITableViewCell *cell = [[UITableViewCell alloc] initWithStyle:UITableViewCellStyleDefault reuseIdentifier:nil];
// 2.设置cell的数据
cell.textLabel.text = [NSString stringWithFormat:@"%d", indexPath.row ];
// 3.返回cell
return cell;
}
- (BOOL)prefersStatusBarHidden
{
return YES;
}
@end
实现效果:

tableview的一些属性:
(1)设置分割样式(tableview.separatorStyle),这是个枚举类型
(2)设置分割线的颜色,可以直接使用系统给出的颜色,如果系统给定的颜色不能满足需求时,也可以自定义。
补充:颜色分为24位和32位的,如下
24bit颜色
R 8bit 0 ~ 255
G 8bit 0 ~ 255
B 8bit 0 ~ 255
32bit颜色
A 8bit 0 ~ 255(tou)
R 8bit
G 8bit
B 8bit
#ff ff ff 白色
#00 00 00 黑色
#ff 00 00 红色
#255 00 00
设置为自定义颜色的实例:
//接收的参数是颜色的比例值
(3)设置顶部和底部视图
tableview.tableHeaderView //顶部
tableview.tableFooterView //底部
UITableviewcell的性能问题
一、UITableviewcell的一些介绍
UITableView的每一行都是一个UITableViewCell,通过dataSource的 tableView:cellForRowAtIndexPath:方法来初始化每⼀行
UITableViewCell内部有个默认的子视图:contentView,contentView是UITableViewCell所显示内容的父视图,可显示一些辅助指示视图
辅助指示视图的作⽤是显示一个表示动作的图标,可以通过设置UITableViewCell的 accessoryType来显示,默认是UITableViewCellAccessoryNone(不显⽰示辅助指⽰示视图), 其他值如下:
UITableViewCellAccessoryDisclosureIndicator
UITableViewCellAccessoryDetailDisclosureButton
UITableViewCellAccessoryCheckmark
还可以通过cell的accessoryView属性来自定义辅助指示视图(⽐如往右边放一个开关)
二、问题
cell的工作:在程序执行的时候,能看到多少条,它就创建多少条数据,如果视图滚动那么再创建新显示的内容。(系统自动调用)。即当一个cell出现在视野范围内的时候,就会调用创建一个cell。这样的逻辑看上去没有什么问题,但是真的没有任何问题吗?
当创建调用的时候,我们使用nslog打印消息,并打印创建的cell的地址。我们发现如果数据量非常大,用户在短时间内来回滚动的话,那么会创建大量的cell,一直开辟空间,且如果是往回滚,通过打印地址,我们会发现它并没有重用之前已经创建的cell,而是重新创建,开辟新的存储空间。
那有没有什么好的解决办法呢?
三、cell的重用原理
(1) iOS设备的内存有限,如果用UITableView显示成千上万条数据,就需要成千上万 个UITableViewCell对象的话,那将会耗尽iOS设备的内存。要解决该问题,需要重用UITableViewCell对象
(2)重⽤原理:当滚动列表时,部分UITableViewCell会移出窗口,UITableView会将窗口外的UITableViewCell放入一个对象池中,等待重用。当UITableView要求dataSource返回 UITableViewCell时,dataSource会先查看这个对象池,如果池中有未使用的 UITableViewCell,dataSource则会用新的数据来配置这个UITableViewCell,然后返回给 UITableView,重新显示到窗口中,从而避免创建新对象 。这样可以让创建的cell的数量维持在很低的水平,如果一个窗口中只能显示5个cell,那么cell重用之后,只需要创建6个cell就够了。
(3)注意点:还有⼀个非常重要的问题:有时候需要自定义UITableViewCell(用⼀个子类继 承UITableViewCell),而且每⼀行⽤的不一定是同一种UITableViewCell,所以一 个UITableView可能拥有不同类型的UITableViewCell,对象池中也会有很多不同类型的 UITableViewCell,那么UITableView在重⽤用UITableViewCell时可能会得到错误类型的 UITableViewCell
解决⽅方案:UITableViewCell有个NSString *reuseIdentifier属性,可以在初始化UITableViewCell的时候传入一个特定的字符串标识来设置reuseIdentifier(一般用UITableViewCell的类名)。当UITableView要求dataSource返回UITableViewCell时,先 通过一个字符串标识到对象池中查找对应类型的UITableViewCell对象,如果有,就重用,如果没有,就传入这个字符串标识来初始化⼀一个UITableViewCell对象。
图片示例:
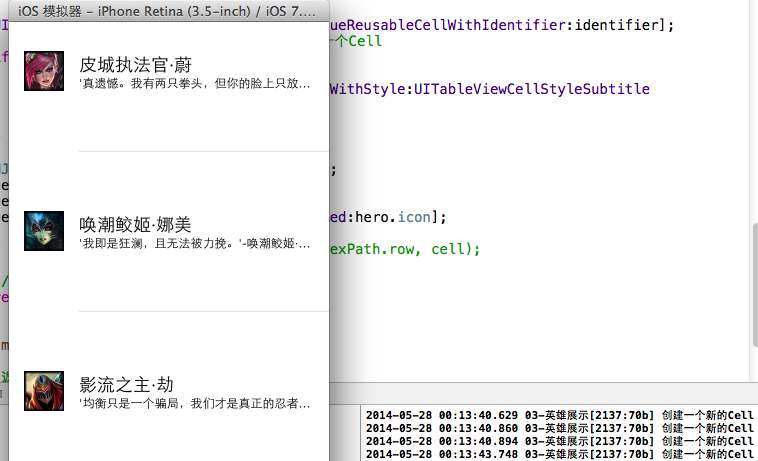
说明:一个窗口放得下(可视)三个cell,整个程序只需要创建4个该类型的cell即可。
四、cell的优化代码
代码示例:
#import "NJViewController.h"
#import "NJHero.h"
// #define ID @"ABC"
@interface NJViewController ()<UITableViewDataSource, UITableViewDelegate>
/**
* 保存所有的英雄数据
*/
@property (nonatomic, strong) NSArray *heros;
@property (weak, nonatomic) IBOutlet UITableView *tableView;
@end
@implementation NJViewController
#pragma mark - 懒加载
- (NSArray *)heros
{
if (_heros == nil) {
// 1.获得全路径
NSString *fullPath = [[NSBundle mainBundle] pathForResource:@"heros" ofType:@"plist"];
// 2.更具全路径加载数据
NSArray *dictArray = [NSArray arrayWithContentsOfFile:fullPath];
// 3.字典转模型
NSMutableArray *models = [NSMutableArray arrayWithCapacity:dictArray.count];
for (NSDictionary *dict in dictArray) {
NJHero *hero = [NJHero heroWithDict:dict];
[models addObject:hero];
}
// 4.赋值数据
_heros = [models copy];
}
// 4.返回数据
return _heros;
}
- (void)viewDidLoad
{
[super viewDidLoad];
// 设置Cell的高度
// 当每一行的cell高度一致的时候使用属性设置cell的高度
self.tableView.rowHeight = 160;
}
#pragma mark - UITableViewDataSource
// 返回多少组
- (NSInteger)numberOfSectionsInTableView:(UITableView *)tableView
{
return 1;
}
// 返回每一组有多少行
- (NSInteger) tableView:(UITableView *)tableView numberOfRowsInSection:(NSInteger)section
{
return self.heros.count;
}
// 当一个cell出现视野范围内的时候就会调用
// 返回哪一组的哪一行显示什么内容
- (UITableViewCell *)tableView:(UITableView *)tableView cellForRowAtIndexPath:(NSIndexPath *)indexPath
{
// 定义变量保存重用标记的值
static NSString *identifier = @"hero";
// 1.先去缓存池中查找是否有满足条件的Cell
UITableViewCell *cell = [tableView dequeueReusableCellWithIdentifier:identifier];
// 2.如果缓存池中没有符合条件的cell,就自己创建一个Cell
if (cell == nil) {
// 3.创建Cell, 并且设置一个唯一的标记
cell = [[UITableViewCell alloc] initWithStyle:UITableViewCellStyleSubtitle reuseIdentifier:identifier];
NSLog(@"创建一个新的Cell");
}
// 4.给cell设置数据
NJHero *hero = self.heros[indexPath.row];
cell.textLabel.text = hero.name;
cell.detailTextLabel.text = hero.intro;
cell.imageView.image = [UIImage imageNamed:hero.icon];
// NSLog(@"%@ - %d - %p", hero.name, indexPath.row, cell);
// 3.返回cell
return cell;
}
#pragma mark - 控制状态栏是否显示
/**
* 返回YES代表隐藏状态栏, NO相反
*/
- (BOOL)prefersStatusBarHidden
{
return YES;
}
@end
缓存优化的思路:
(1)先去缓存池中查找是否有满足条件的cell,若有那就直接拿来
(2)若没有,就自己创建一个cell
(3)创建cell,并且设置一个唯一的标记(把属于“”的给盖个章)
(4)给cell设置数据
注意点:
定义变量用来保存重用标记的值,这里不推荐使用宏(#define来处理),因为该变量只在这个作用域的内部使用,且如果使用宏定义的话,定义和使用位置太分散,不利于阅读程序。由于其值不变,没有必要每次都开辟一次,所以用static定义为一个静态变量。
加载全部内容