Python实现随机漫步的详细过程
Aperion 人气:0本篇博客将使用 Python 来 生成随机漫步数据,再使用 Matplotlib 库,将以引人注目的方式将这些数据呈现出来。
随机漫步 顾名思义就是随机走出的步伐,它是这样行走得到的路径:每次行走都是完全随机的、没有明确的方向,结果是由一系列随机决策决定的。我们可以将随机漫步看作是 蚂蚁在晕头转向 的情况下,每次都沿随机的方向前行所经过的路径。
1. 创建 RandomWalk 类
为模拟随机漫步,首先创建一个名为 RandomWalk 的类,其作用是 随机的选择前进方向。这个类需要三个属性:一个是 存储随机漫步次数的变量,其他两个是 列表,分别存储随机漫步经过的每个点的 x 坐标 和 y 坐标。
RandomWalk 类只包含两个方法:
- 方法 __init__ () ,初始化属性
- 方法 fill_walk () ,计算随机漫步经过的所有点
from random import choice
class RandomWalk:
'''一个生成随机漫步数据的类'''
def __init__(self, num_points = 500):
'''初始化随机漫步的属性'''
self.num_points = num_points
# 所有随机漫步都使于(0,0)
self.x_values = [0]
self.y_values = [0]- 为做出 随机决策,将 所有可能的选择 都存储在一个列表中,并在每次决策时,都使用模块 random 中的 choice () 来决定使用哪种选择 。
- 将随机漫步包含的默认点数设置为 5000,这个数大到 足以生成有趣的模式,又小到可确保能够 快速地模拟随机漫步。
- 创建两个用于存储 x 值和 y 值的列表,并让每次漫步都从 点(0,0)出发。
2. 选择方向
我们将使用方法 fill_walk() 来生成 漫步包含的点,并 决定每次漫步的方向。
import random
def fill_walk(self):
'''计算随机漫步包含的所有点'''
# 不断漫步,直到列表达到指定的长度
while len(self.x_values) < self.num_points:
# 决定前进方向以及沿这个方向前进的距离
x_direction = random.choice([1,-1])
x_distance = random.choice([0,1,2,3,4])
x_step = x_direction * x_distance
y_direction = random.choice([1,-1])
y_distance = random.choice([0,1,2,3,4])
y_step = y_direction * y_distance
# 拒绝原地踏步
if x_step == 0 and y_step == 0:
continue
# 计算下一个点的 x 值和 y 的值
x = self.x_values[-1] + x_step
y = self.y_values[-1] + y_step
self.x_values.append(x)
self.y_values.append(y)- 先建立一个循环,它不断运行,直到漫步包含所需的点数。方法 fill_walk()的主要部分告诉 Python 如何模拟四种漫步决定:向右走还是向左走?沿指定的方向走多远?向上走还是向下走?沿指定的方向走多远?
- 使用 choice([-1,-1]) 给 x_direction 选择一个值,结果要么是表示向右走的 1,要么是表示向左走的 -1。接下来,choice([0,1,2,3,4]) 随机的选择一个 0~4 的整数,告诉 Python 沿指定方向走多远(x_distance)。通过包含 0 ,不仅能够同时沿两个轴移动,还能够只沿一个轴移动。
- 将 移动方向乘以移动距离,确定沿 x 轴和 y 轴移动的距离。如果 x_step 为正将向右移动,为负将向左移动,为零将垂直移动;如果 y_step 为正将向上移动,为负将向下移动,为零将水平移动。如果 x_step 和 y_step 都为零,则意味着原地踏步。我们拒绝这样的情况,接着执行下一次循环。
- 为获取漫步中下一个点的 x 的值,将 x_step 和 x_values 中的最后一个值相加,对 y 值也做相同的处理。获得下一个点的 x 值和 y 值后,将它们分别附件到列表 x_values 和 y_values 的末尾。
3. 绘制随机漫步图
下面的代码将随机漫步的所有点都绘制出来:
from random import choice
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
class RandomWalk:
'''一个生成随机漫步数据的类'''
def __init__(self, num_points = 5000):
'''初始化随机漫步的属性'''
self.num_points = num_points
# 所有随机漫步都使于(0,0)
self.x_values = [0]
self.y_values = [0]
def fill_walk(self):
'''计算随机漫步包含所有的点'''
# 不断漫步,直到列表达到指定的长度
while len(self.x_values) < self.num_points:
# 决定前进的方向以及沿着这个方向前进的距离
x_direction = choice([1,-1])
x_distance = choice([0,1,2,3,4])
x_step = x_direction * x_distance
y_direction = choice([1,-1])
y_distance = choice([0,1,2,3,4])
y_step = y_direction * y_distance
# 拒绝原地踏步
if x_step == 0 and y_step == 0:
continue
# 计算下一个点的 x 值和 y 值
x = self.x_values[-1] + x_step
y = self.y_values[-1] + y_step
self.x_values.append(x)
self.y_values.append(y)
# 创建一个 RandomWalk 实例
random_wander = RandomWalk()
random_wander.fill_walk()
# 将所有的点都绘制出来
plt.style.use('classic')
(fig,ax) = plt.subplots()
ax.scatter(random_wander.x_values, random_wander.y_values, s = 15)
plt.show()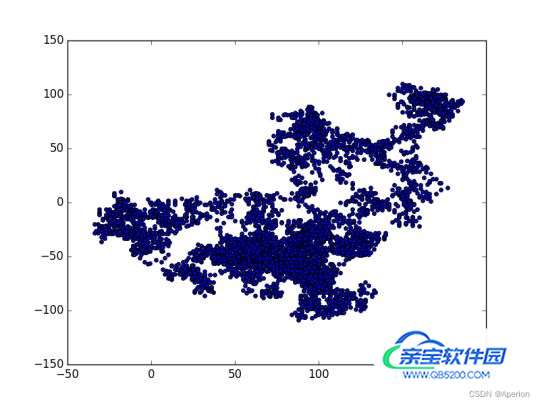
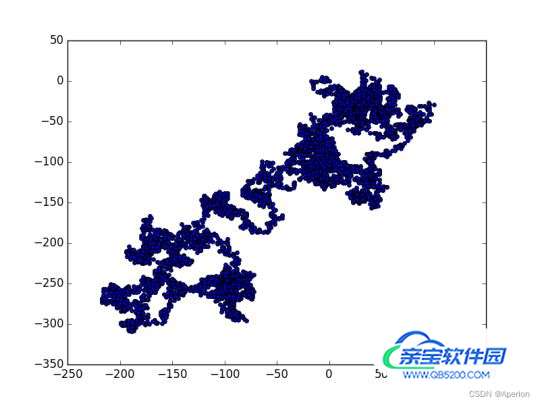
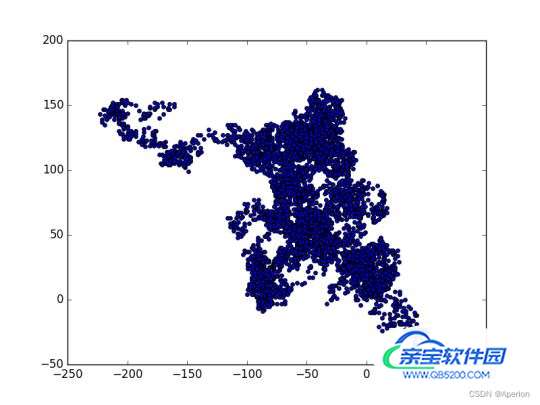
4. 总结
这篇文章主要讲解了随机漫步相关知识点。
加载全部内容