JavaScript中六种面试常考继承方式总结
mick 人气:0js的几种继承方式在我们面试的时候经常会被问到,所以深入理解js几种继承方式以及它们的优缺点是非常有必要的。
原型链继承
之前我们介绍过原型和实例的关系:每一个构造函数都有一个原型prototype,原型对象中的constructor又指回构造函数,实例中有一个内部指针__proto__指向构造函数的prototype。不清楚的可以看这篇 下面看个代码
function Parent() {
this.name = "mick";
}
Parent.prototype.getName = function () {
console.log(this.name);
};
function Child() {}
Child.prototype = new Parent();
var child1 = new Child();
console.log(child1.getName());
我们将构造函数Parent的实例赋值给了构造函数Child的原型,实现了Child能够继承Parent的属性和方法。
优点
1.父类的方法可以被复用
缺点
1.父类的所有属性都会被子类共享,只要修改了一个子类的引用类型的属性,其他的子类也会受影响
function Parent() {
this.names = ["mick", "randy"];
}
function Child() {}
Child.prototype = new Parent();
var child1 = new Child();
child1.names.push("qr");
console.log(child1.names); // ["mick", "randy", "qr"]
var child2 = new Child();
console.log(child2.names); // ["mick", "randy", "qr"]
2.子类实例不能给父类构造函数传参
盗用构造函数
盗用构造函数的思路其实就是在子类构造函数中通过call或者apply方法调用父类构造函数
function Parent() {
this.names = ["mick", "randy"];
}
function Child() {
Parent.call(this);
}
var child1 = new Child();
child1.names.push("qr");
console.log(child1.names); // ["mick", "randy", "qr"]
var child2 = new Child();
console.log(child2.names); // ["mick", "randy"]
这里我们通过在构造函数Child中通过call调用Parent,此时this就是构造函数Child,其实就是Child的实例被创建的时候都会对Parent进行初始化,相当于每一个实例都拥有了names属性。
我们也可以给父构造函数传参了
function Parent(name) {
this.name = name;
}
function Child(name, age) {
Parent.call(this, name);
this.age = age;
}
var child1 = new Child("randy", 18);
console.log(child1.name); // randy
优点
- 可以在子类构造函数向父类构造函数传参
- 父类的实例的引用属性不会被共享
缺点
子类不能访问父类原型上的方法,所以所有方法和属性都写在构造函数中,每次实例创建都会被初始化。
组合继承
组合继承就是综合原型链继承和盗用构造函数继承的优点,从何又对这两种方法的缺点互补。使用原型链继承可以访问父类原型上的属性和方法,通过构造函数继承可以访父类实例的属性和方法。
function Parent(name) {
this.name = name;
this.colors = ["red", "blue", "green"];
}
Parent.prototype.getName = function () {
console.log(this.name);
};
function Child(name, age) {
Parent.call(this, name); // 第一次
this.age = age;
}
Child.prototype = new Parent(); // 第二次
Child.prototype.constructor = Child;
var child1 = new Child("mick", "18");
child1.colors.push("black");
console.log(child1.name); // mick
console.log(child1.age); // 18
console.log(child1.colors); // ["red", "blue", "green", "black"]
var child2 = new Child("randy", "20");
console.log(child2.name); // randy
console.log(child2.age); // 20
console.log(child2.colors); // ["red", "blue", "green"]
优点
- 父类的方法可以复用
- 可以在子类构造函数向父类传参
- 父类构造函数中的引用属性不会共享
缺点
父类构造函数被调用了两次(文章中的注释已经标出)
原型式继承
创建一个临时的构造函数,将传入的对象赋值给这个构造函数的原型,然后返回这个临时类型的一个实例。其实就是对传入对应进行一次浅复制。
function createObj(o) {
function F() {}
F.prototype = o;
return new F();
}其实就是Object.create的模拟实现,将传入的对象作为创建的对象的原型 缺点
1.引用类型的属性值始终都会共享相应的值,这点跟原型链继承一样
function createObj(o) {
function F() {}
F.prototype = o;
return new F();
}
let person = {
name: "mick",
colors: ["red", "blue", "green"],
};
let anotherPerson = createObj(person);
anotherPerson.name = "randy";
anotherPerson.colors.push("black");
console.log(anotherPerson.colors); // ['red', 'blue', 'green', 'black']
let yetAnotherPerson = createObj(person);
yetAnotherPerson.colors.push("yellow");
console.log(yetAnotherPerson.name); // mick
console.log(yetAnotherPerson.colors); // ['red', 'blue', 'green', 'black', 'yellow']
修改了anotherPerson.name的值,yetAnotherPerson.name没有发生变化,这是因为anotherPerson.name给anotherPerson添加了name的值,并不是修改了原型上的值。
寄生式继承
寄生式继承背后类似于寄生构造函数和工厂模式:创建一个实现继承的函数,以某种方式增强对象,然后返回这个对象。我们继续使用原型式继承创建的方法
function createObj(o) {
function F() {}
F.prototype = o;
return new F();
}
function createAnother(original) {
let clone = createObj(original);
clone.sayHi = function () {
console.log("hi");
};
return clone;
}缺点
跟盗用构造函数一样的,方法在每次创建对象都会重新创建一遍
寄生式组合继承
我们首先回看下组合继承有个缺点就是父类构造函数会调用两次,那如何优化这个缺点呢?
寄生式组合继承通过盗用构造函数继承属性,但使用混合式原型链继承方法。基本思路是不通过调用父类构造函数给子类原型赋值,而是取得父类原型的一个副本。也就是使用寄生式继承来继承父类原型,然后将返回的新对象赋值给子类原型
function Parent(name) {
this.name = name;
this.colors = ["red", "blue", "green"];
}
Parent.prototype.getName = function () {
console.log(this.name);
};
function Child(name, age) {
Parent.call(this, name);
this.age = age;
}
var F = function () {};
F.prototype = Parent.prototype;
Child.prototype = new F();
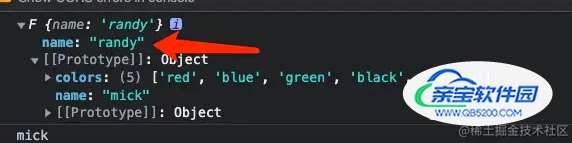
var child1 = new Child("mick", "18");
console.log(child1);
封装一下
function createObj(o) {
function F() {}
F.prototype = o;
return new F();
}
function prototype(child, Parent) {
var prototype = createObj(parent.prototype);
prototype.constructor = child;
child.prototype = prototype;
}
function Parent(name) {
this.name = name;
this.colors = ["red", "blue", "green"];
}
Parent.prototype.getName = function () {
console.log(this.name);
};
function Child(name, age) {
Parent.call(this, name);
this.age = age;
}
prototype(Child, Parent)
var child1 = new Child("mick", "18");
console.log(child1);
这种方式的高效率体现它只调用了一次Parent构造函数,并且因此避免了在Parent.prototype上面创建不必要的、多余的属性。与此同时,原型链还能保持不变;因此,还能够正常使用instanceof和isPrototypeOf。开发人员普遍认为寄生组合式继承是引用类型最理想的继承范式。
加载全部内容