MyBatis SqlSource源码示例解析
念念清晰 人气:0正文
MyBatis版本:3.5.12。
本篇讲从mybatis的角度分析SqlSource。在xml中sql可能是带?的预处理语句,也可能是带$或者动态标签的动态语句,也可能是这两者的混合语句。
SqlSource设计的目标就是封装xml的crud节点,使得mybatis运行过程中可以直接通过SqlSource获取xml节点中解析后的SQL。
简单的示意图就是

接下来我们先来介绍几个基础的组件,正是这些组件构成的SqlSource
SqlNode
mybatis提供了这么9种动态节点:
- trim
- where
- set
- foreach
- if
- choose
- when
- otherwise
- bind
每一种节点是一个SqlNode,并且每个动态节点都分别对应了一个XxxSqlNode的实现类。SqlNode是一个接口,该接口就代表mybatis的动态节点。

接下来我们来用一个案例分析mybatis是如何把一个<select>节点解析为一个SqlNode对象的(update/insert/delete原理一样)。示例如下
<select id="selectById">
select * from user
<where>
<if test="id != null">
and id = #{id}
</if>
<if test="age != null">
and age > ${age}
</if>
</where>
</select>
它会被解析成如下这样一颗SqlNode树
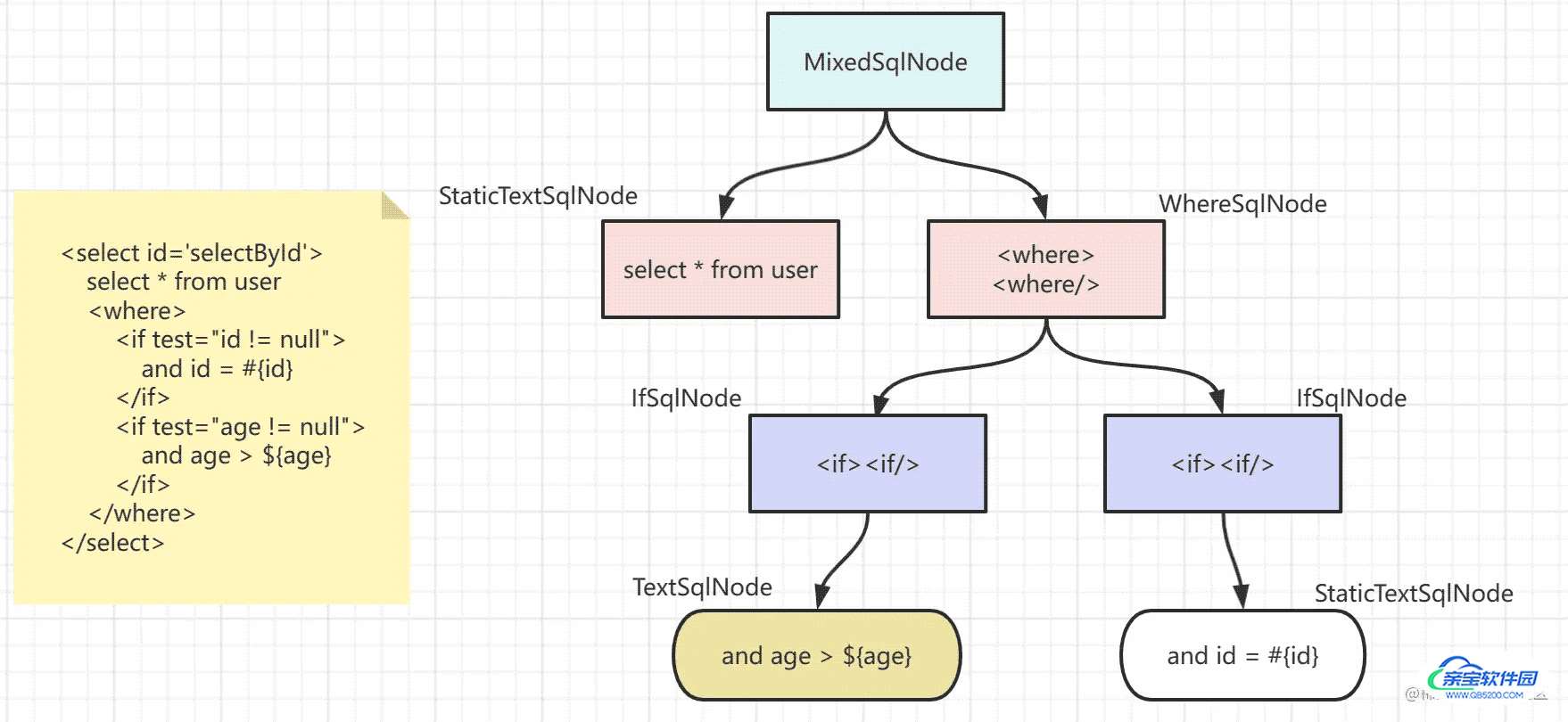
树的根节点都是MixedSqlNode,MixedSqlNode类其中有一个属性private final List<SqlNode> contents;专门存放标签下所有的子节点解析成的SqlNode
该标签的的第一部分就是select * from user;这段文本既不包含标签,也不包含$等表达式,它就属于静态文本,会被解析成StaticTextSqlNode
- 然后与接下来是一个wehre标签,它会被解析为
WhereSqlNode - whhre标签中有两个if标签,这两个if标签会被解析为两个
IfSqlNode加入到WhereSqlNode中 - 第一个if标签中的文本不包含
$会被解析成StaticTextSqlNode(没错,即使它有#符,它不属于静态文本哦。只有包含$才算动态节点) - 而第二个if标签中的文本包含
$会被解析成TextSqlNode
看明白了xml文件中一个标签是如何由这些SqlNode是组成的。接下来我们唠一唠SqlNode接口的定义
SqlNode接口定义
public interface SqlNode {
boolean apply(DynamicContext context);
}
SqlNode接口定义非常简单,只有一个apply方法,方法的参数是DynamicContext,DynamicContext可以看作是一个sql上下文,它其中维护了一个StringBuilder sql字段。这个字段就是用来记录整个<select>节点解析过后的SQL语句的。
mybatis会在解析过程中把select标签解析为如上分析的一棵树MixedSqlNode然后就会递归遍历这些SqlNode并调用他们的apply方法,调用apply方法实际上就是把标签解析后的sql片段拼接到了context中的sql字段。最后只需要调用context.getSql方法就可以获得可执行SQL了。而一切都从根节点的apply方法说起,MixedSqlNode的源码如下
public class MixedSqlNode implements SqlNode {
private final List<SqlNode> contents;
public MixedSqlNode(List<SqlNode> contents) {
this.contents = contents;
}
@Override
public boolean apply(DynamicContext context) {
contents.forEach(node -> node.apply(context));
return true;
}
}
可以发现MixedSqlNode中有一个List字段,该字段存储的是树的叶子节点,在这个示例中,List字段中应该由两个SqlNode
- 第一个是标识静态文本的
StaticTextSqlNode,它其中封装的select * from user文本。 - 第二个SqlNode是
WhereSqlNode它其中封装的文本是
<where>
<if test="id != null">
and id = #{id}
</if>
<if test="age != null">
and age > ${age}
</if>
</where>
而WhereSqlNode类中也还有一个List属性,封装了两个if节点,这里就不展开说了,我们只需要知道,所有的SqlNode都会递归执行apply方法,而apply方法只做了一件事——那就是把SqlNode节点中的文本经过一系列规则解析过后(通常就是删除标签,删除无用的and|or,删除无用的,等),返回可执行SQL的片段,这些SQL片段最终都会以如下方法把sql片段拼接,
context.appendSql(text);
最终形成一个完整的SQL:select * from user where id = 1 (age条件没成立)
BoundSql
知道了什么是SqlNode之后,我们再来看BoundSql,BoundSql内部封装了可执行SQL,先来看下BoundSql的重要字段
public class BoundSql {
private final String sql;
private final List<ParameterMapping> parameterMappings;
private final Object parameterObject;
private final Map<String, Object> additionalParameters;
private final MetaObject metaParameters;
}
- sql:上小节说到的
SqlNode调用完apply方法后存储在DynamicContext中的sql就会被赋值给该字段。sql字段其实就是类似于select * from user where id = ?这样的字符串, - parameterObject:用户传入的属性,用于给sql字段的
?赋值 - additionalParameters: bind标签中绑定的值会存储在此
- metaParameters:additionalParameters的元类型
还记得开篇我们说的目标吗?我贴过来再看一遍
SqlSource设计的目标就是封装xml的crud节点,使得mybatis运行过程中可以直接通过SqlSource获取xml节点中解析后的SQL。
简单的示意图就是
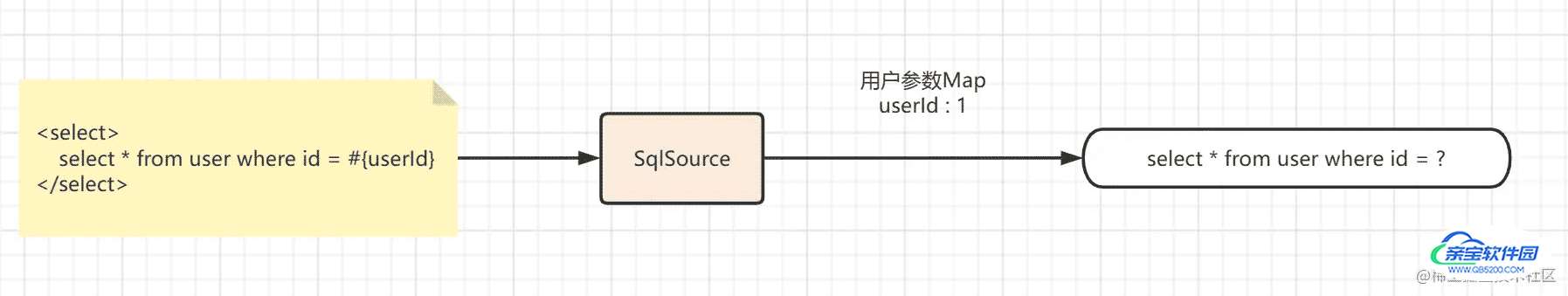
那么有了BoundSql,实现这个目标是不是就很容易了。我们只需要获取BoundSql对象,然后再调用BoundSql#getSql方法就能获取到可执行Sql了。
SqlSource
为了完成开篇说的SqlSource的目标,我们现在迫切想要做的就是获取BoundSql对象。刚好SqlSource接口的定义如下
public interface SqlSource {
BoundSql getBoundSql(Object parameterObject);
}
SqlSource是一个接口,其中只提供了一个方法 getBoundSql 。该方法只有一个参数Object parameterObject,这个参数就是用户传入的查询参数。SqlSource的继承体系如下
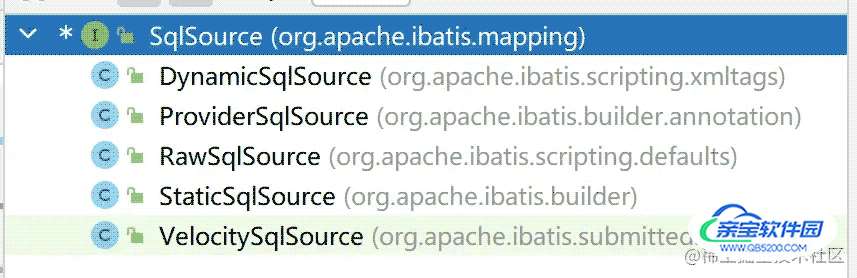
- DynamicSqlSource:动态SQL节点会被解析为该对象,那怎么判断xml文件中的节点是否是动态的呢?满足如下两个条件的任何一个就算是动态节点。一是包含
$占位符的表达式,比如select * from user where id = ${id}。二是包含9种动态标签中的任何一个(trim set wehre if foreach等9个。前文有说)。注意只包含#占位符表达式的语句不会被解析成动态标签。 - ProviderSqlSource:注解定义的SQL
- RawSqlSource:不是DynamicSqlSource,就会被解析为RawSqlSource
- . StaticSqlSource:静态文本SQL其中不包含任何
$和动态标签。DynamicSqlSource和RawSqlSource最终都会被解析为StaticSqlSource - . VelocitySqlSource:暂且忽略(不在本文讨论范围)
SqlSource解析时机
至此SqlSource的组成部分我们都已经清楚了,那么XML的节点在何时被解析为SqlSource的呢?
答案是在mybatis启动时,会加载xml文件并进行解析。相关流程如下
- XMLMapperBuilder#configurationElement,
private void configurationElement(XNode context) {
try {
String namespace = context.getStringAttribute("namespace");
if (namespace == null || namespace.isEmpty()) {
throw new BuilderException("Mapper's namespace cannot be empty");
}
builderAssistant.setCurrentNamespace(namespace);
cacheRefElement(context.evalNode("cache-ref"));
cacheElement(context.evalNode("cache"));
parameterMapElement(context.evalNodes("/mapper/parameterMap"));
resultMapElements(context.evalNodes("/mapper/resultMap"));
sqlElement(context.evalNodes("/mapper/sql"));
buildStatementFromContext(context.evalNodes("select|insert|update|delete"));
} catch (Exception e) {
throw new BuilderException("Error parsing Mapper XML. The XML location is '" + resource + "'. Cause: " + e, e);
}
}
该方法解析一个xml文件中所有的节点:namespace、cache-ref、cache等,其中解析select|insert|update|delete节点的方法是buildStatementFromContext
- XMLMapperBuilder#buildStatementFromContext
private void buildStatementFromContext(List<XNode> list, String requiredDatabaseId) {
for (XNode context : list) {
final XMLStatementBuilder statementParser = new XMLStatementBuilder(configuration, builderAssistant, context, requiredDatabaseId);
try {
statementParser.parseStatementNode();
} catch (IncompleteElementException e) {
configuration.addIncompleteStatement(statementParser);
}
}
}
该方法会遍历xml中的所有select|insert|update|delete节点并解析。其中list标识所有select|insert|update|delete节点的结合。接下来来看parseStatementNode这个方法,它用来解析单个select|insert|update|delete节点
- XMLStatementBuilder#parseStatementNode
public void parseStatementNode() {
// 省略解析 id flushCache useCache SelectKey resultType等属性的过程
// 创建SqlSource对象,也就是解析xml的crud标签,封装成SqlSource对象,然后再把SqlSource对象存入MS对象中
SqlSource sqlSource = langDriver.createSqlSource(configuration, context, parameterTypeClass);
builderAssistant.addMappedStatement(id, sqlSource, statementType, sqlCommandType,
fetchSize, timeout, parameterMap, parameterTypeClass, resultMap, resultTypeClass,
resultSetTypeEnum, flushCache, useCache, resultOrdered,
keyGenerator, keyProperty, keyColumn, databaseId, langDriver, resultSets, dirtySelect);
}
可以看到SqlSource在此被创建了,并且最后作为MappedStatement的属性存储在MappedStatement对象中。这里我们着重关心SqlSource的创建过程,它是在createSqlSource方法完成的
- XMLLanguageDriver#createSqlSource
public SqlSource createSqlSource(Configuration configuration, XNode script, Class<?> parameterType) {
XMLScriptBuilder builder = new XMLScriptBuilder(configuration, script, parameterType);
return builder.parseScriptNode();
}
XMLLanguageDriver又委托XMLScriptBuilder解析,接下来我们看XMLScriptBuilder#parseScriptNode方法
- XMLScriptBuilder#parseScriptNode
public SqlSource parseScriptNode() {
MixedSqlNode rootSqlNode = parseDynamicTags(context);
SqlSource sqlSource;
if (isDynamic) {
sqlSource = new DynamicSqlSource(configuration, rootSqlNode);
} else {
sqlSource = new RawSqlSource(configuration, rootSqlNode, parameterType);
}
return sqlSource;
}
mybatis就是在这个方法中创建SqlSource对象,他首先会调用parseDynamicTags方法来解析下节点是否是动态节点,它的解析过程就是看节点是否包含动态标签或包含$占位符,如果满足任意一个条件它就会被解析为动态标签,并创建DynamicSqlSource对象,否则创建RawSqlSource对象
SqlSource调用时机
mybatis需要的是可以执行的SQL,而通过SqlSource我们可以获取BoundSql进而获取BoundSql中的sql字段(该字段就是可执行语句)。所以其调用时机是在mybatis进行查询数据库的时候——调用SqlSource#getBoundSql
具体代码处是Executor执行query方法的时候调用,源码在BaseExecutor中,BaseExecutor#query代码如下
public <E> List<E> query(MappedStatement ms, Object parameter, RowBounds rowBounds, ResultHandler resultHandler) throws SQLException {
BoundSql boundSql = ms.getBoundSql(parameter);
CacheKey key = createCacheKey(ms, parameter, rowBounds, boundSql);
return query(ms, parameter, rowBounds, resultHandler, key, boundSql);
}
public BoundSql getBoundSql(Object parameterObject) {
BoundSql boundSql = sqlSource.getBoundSql(parameterObject);
return boundSql;
}
我们前文说过,SqlSource生成时会被存储在MappedStatement对象当中,所以这里自然也是通过MappedStatement对象来使用SqlSource获取BoundSql。这样在mybatis真正调用JDBC查询数据库的时候就可以通过BoundSql拿到可执行语句啦
总结
- SqlSource封装了XML中的
select|insert|update|delete节点,每个节点都会被解析为MixedSqlNode,可以看作是一棵树,其中包含许多子节点嵌套 - 只包含
#的sql不算动态节点,只有包含动态标签或者$占位符才算是动态节点 - BoundSql中包含了可执行sql
本文只是粗略的介绍了SqlSource,只能带你粗略的了解下mybatis的组件结构。其中SqlSource如何获取BoundSql对象,以及节点到底是如何被解析的,比如if标签是如何进行判断的 等。读者在理解了这些概念后再阅读源码会容易很多。
加载全部内容