JS数组方法reduce的妙用分享
CUGGZ 人气:01. 基本用法
reduce() 是 JavaScript 中一个很有用的数组方法,MDN 对其解释如下:
reduce() 方法对数组中的每个元素按序执行一个 reducer 函数,每一次运行 reducer 会将先前元素的计算结果作为参数传入,最后将其结果汇总为单个返回值。
reduce() 方法的语法如下:
array.reduce(reducer, initialValue)
其中有两个参数:(1)reducer 函数,包含四个参数:
previousValue:上一次调用 callbackFn 时的返回值。在第一次调用时,若指定了初始值 initialValue,其值则为 initialValue,否则为数组索引为 0 的元素 array[0]。currentValue:数组中正在处理的元素。在第一次调用时,若指定了初始值 initialValue,其值则为数组索引为 0 的元素 array[0],否则为 array[1]。currentIndex:数组中正在处理的元素的索引。若指定了初始值 initialValue,则起始索引号为 0,否则从索引 1 起始。array:用于遍历的数组。
(2)initialValue 可选 作为第一次调用 callback 函数时参数 previousValue 的值。若指定了初始值 initialValue,则 currentValue 则将使用数组第一个元素;否则 previousValue 将使用数组第一个元素,而 currentValue 将使用数组第二个元素。
下面是一个使用reduce() 求数组元素之和的例子:
const arr = [0, 1, 2, 3, 4];
const calculateSum = (previousValue, currentValue) => {
console.log('previousValue: ', previousValue);
console.log('currentValue:', currentValue);
return previousValue + currentValue;
};
arr.reduce(calculateSum)
reducer 会逐个遍历数组元素,每一步都将当前元素的值与上一步的计算结果相加(上一步的计算结果是当前元素之前所有元素的总和),直到没有更多的元素被相加。
这段代码的输出如下:
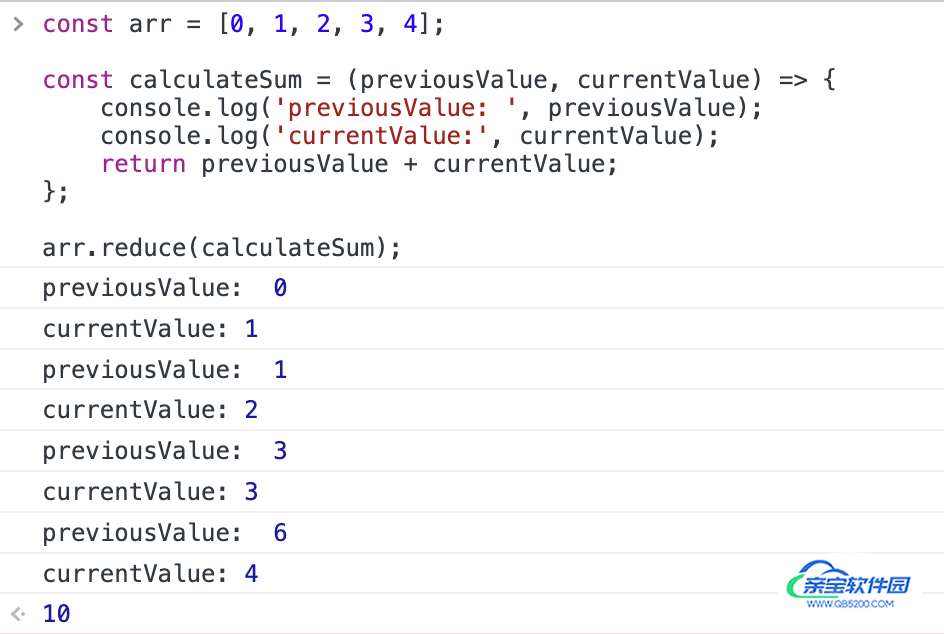
其执行过程如下:
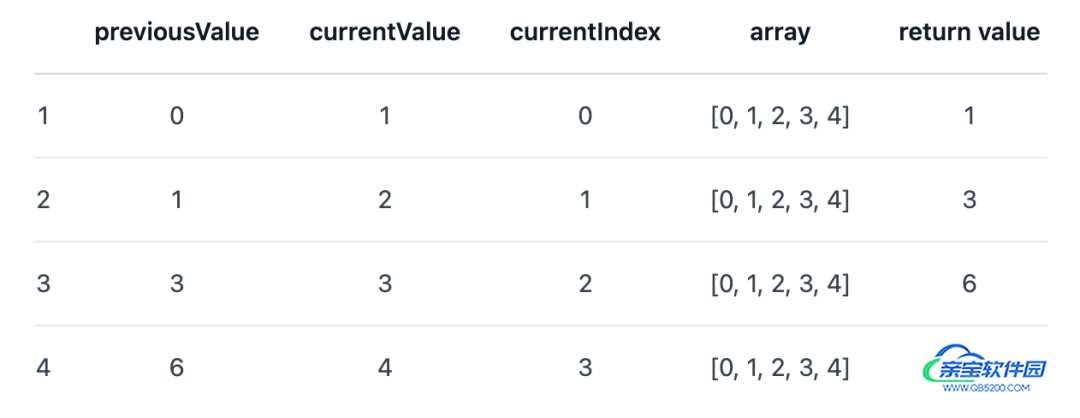
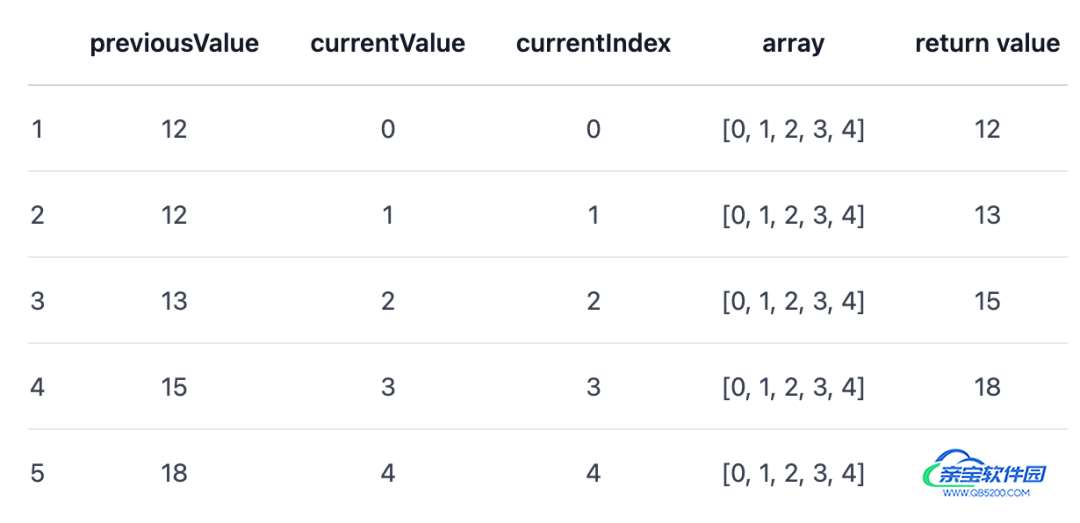
当我们给reduce()方法一个初始值12时:
arr.reduce(calculateSum, 12);
其执行过程如下:
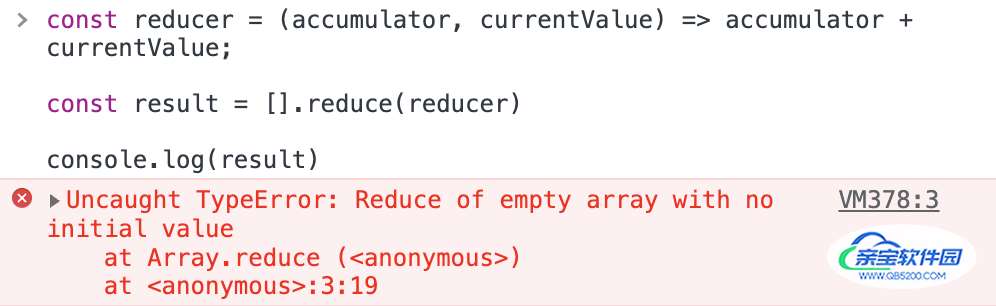
如果数组为空且未提供初始值,reduce() 方法就会抛出 TypeError:
const reducer = (accumulator, currentValue) => accumulator + currentValue; const result = [].reduce(reducer) console.log(result)
输出结果如下:
2. 使用技巧
(1)数组求和
reduce()方法最直接的用法就是对数组元素求和:
const total = [34, 12, 143, 13, 76].reduce( (previousValue, currentValue) => previousValue + currentValue, 0 ); console.log(total);
其输出结果如下:
278
(2)扁平数组
reduce()方法还可以用来扁平化数组:
const array = [[0, 1], [2, 3], [4, 5], [5, 6]]; const flattenedArray = array.reduce( (previousValue, currentValue) => previousValue.concat(currentValue), [] ); console.log(flattenedArray);
输出结果如下:
[0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 5, 6]
如果数组有不止一层嵌套数组,可以递归调用 reduce 函数来扁平化,然后将它们与最终的数组连接起来即可。
const nestedArray = [[1, [2, 3]], [4, 5], [[6, 7], [8, 9]]];
function flattenArray(nestedArray) {
return nestedArray.reduce(
(accumulator, currentValue) =>
accumulator.concat(
Array.isArray(currentValue) ? flattenArray(currentValue) : currentValue
),
[]);
}
const flattenedArray = flattenArray(nestedArray);
console.log(flattenedArray)
输出结果如下:
[1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9]
(3)数组分组
假设有一个国家对象数组,根据国家所在洲对数组中的每个国家进行分组。可以使用 reduce 方法来完成:
cosnt countries = [
{name: "Germany", continent: "Europe"},
{name: "Brazil", continent: "South America"},
{name: "India", continent: "Asia"},
{name: "France", continent: "Europe"},
{name: "South Korea", continent: "Asia"},
]
const groupedCountries = countries.reduce(
(groupedCountries, country) => {
if (!groupedCountries[country.continent]){
groupedCountries[country.continent] = []
}
groupedCountries[country.continent].push(country)
return groupedCountries
},
{}
);
console.log(groupedCountries)
输出结果如下:

(4)使用 reduce() 代替 filter().map()
在 Javascript 中,数组的 filter 方法可以通过回调过滤数组中的元素,map 方法可以通过回调内部传递的逻辑使用旧数组创建一个新数组。有时我们必须同时使用这两种方法,对某些条件过滤的结果创建一个新数组。
可以使用 reduce 方法来完成相同的工作,这样就只需要遍历数组一次。例如,要创建一个大于 30 的数字的平方根数组,使用 filter().map() 可能会这么写:
const numbers = [3, 21, 34, 121, 553, 12, 53, 5, 42, 11]; const newArray = numbers.filter(number => number > 30).map(number => Math.sqrt(number));
使用 reduce 实现:
const numbers = [3, 21, 34, 121, 553, 12, 53, 5, 42, 11];
const newArray = numbers.reduce((previousValue, currentValue) => {
if (currentValue > 30) {
previousValue.push(Math.sqrt(currentValue))
}
return previousValue
}, []);
console.log(newArray);
输出结果如下:
[5.830951894845301, 11, 23.515952032609693, 7.280109889280518, 6.48074069840786]
(5)统计数组元素出现次数
可以使用reduce来统计数组中每个元素出现的次数:
const colors = ['green', 'red', 'red', 'yellow', 'red', 'yellow', 'green', 'green'];
const colorMap = colors.reduce((previousValue, currentValue) => {
previousValue[currentValue] >= 1 ? previousValue[currentValue]++ : previousValue[currentValue] = 1;
return previousValue;
},
{}
);
console.log(colorMap);
输出结果如下:
{green: 3, red: 3, yellow: 2}
(6)串行执行异步函数
有一组需要串行执行的异步函数,可以使用reduce()来调用执行:
const functions = [
async function() { return 1; },
async function() { return 2; },
async function() { return 3; }
];
const res = await functions.reduce((promise, fn) => promise.then(fn), Promise.resolve());
console.log(res); // 输出结果:3
这里的 res 就相当于执行了:
Promise.resolve().then(fn1).then(fn2).then(fn3);
(7)创建管道
假设有一组简单的数学函数,这些函数允许我们增加、减少、加倍和减半:
function increment(input) { return input + 1;}
function decrement(input) { return input — 1; }
function double(input) { return input * 2; }
function halve(input) { return input / 2; }
如果想对一个值进行多次上述操作,就可以使用reduce()。管道是用于将某些初始值转换为最终值的函数列表的术语。我们只需将执行过程中每一步用到函数写在管道数组中即可。
const pipeline = [increment, double, decrement];
const result = pipeline.reduce((total, func) => {
return func(total);
}, 5);
console.log(result) // 输出结果:11
(8)反转字符串
可以使用reduce()实现字符串的反转:
const str = 'hello world'; [...str].reduce((a,v) => v + a); // 输出结果:'dlrow olleh'
(9)数组去重
有一个包含重复项的数组,可以使用 reduce() 来对数组进行去重:
const arr = ["
加载全部内容
- 用户评论
 爱之家商城
爱之家商城 氢松练
氢松练 Face甜美相机
Face甜美相机 花汇通
花汇通 走路宝正式版
走路宝正式版 天天运动有宝
天天运动有宝 深圳plus
深圳plus 热门免费小说
热门免费小说