python如何寻找主串中所有指定子串下标
头秃头凉凉 人气:0python寻找主串中所有指定子串下标
该函数可实现显示字符串中指定子串所有下标(首字下标)
def subStrIndex(substr,str): result = [] index = 0 while str.find(substr,index,len(str)) != -1: temIndex = str.find(substr,index,len(str)) result.append(temIndex) index = temIndex + 1 return result
其中substr中传入需要的寻找子串,str为主串。
使用示例:
str = "我们去了天安门,天安门附近有很多人"
list = subStrIndex('天安门',str)
print(list)输出结果:[4,8]
其中4表示第一次出现“天安门”的下标,8表示第二次出现的下标。(由0开始)
python字符串常用操作
查找
1、find():检测某个⼦串是否包含在这个字符串中,如果在,返回这个串开始的位置下标,否则则返回-1。
语法:字符串串序列列.find(⼦子串串, 开始位置下标, 结束位置下标)
mystr = "hello world and itcast and itheima and Python"
print(mystr.find('and')) # 12
print(mystr.find('and', 15, 30)) # 23
print(mystr.find('ands')) # -1
2、index():检测某个⼦串是否包含在这个字符串中,如果在返回这个子串开始的位置下标,否则报异常。
语法:字符串串序列列.index(⼦子串串, 开始位置下标, 结束位置下标)
mystr = "hello world and itcast and itheima and Python"
print(mystr.index('and')) # 12
print(mystr.index('and', 15, 30)) # 23
print(mystr.index('ands')) # 报错
rfind(): 和find()功能相同,但查找⽅方向为右侧开始。rindex():和index()功能相同,但查找⽅方向为右侧开始。
3、count():返回某个⼦子串串在字符串串中出现的次数
语法:字符串串序列列.count(⼦子串串, 开始位置下标, 结束位置下标)
mystr = "hello world and itcast and itheima and Python"
print(mystr.count('and')) # 3
print(mystr.count('ands')) # 0
print(mystr.count('and', 0, 20)) # 1
修改
1、replace():替换
语法:字符串序列.replace(旧⼦串, 新⼦串, 替换次数)
mystr = "hello world and itcast and itheima and Python"
# 结果:hello world he itcast he itheima he Python
print(mystr.replace('and', 'he'))
# 结果:hello world he itcast he itheima he Python
print(mystr.replace('and', 'he', 10))
# 结果:hello world and itcast and itheima and Python
print(mystr)
字符串类型的数据修改的时候不能改变原有字符串,属于不能直接修改数据的类型即是不可变类型。
2、split():按照指定字符分割字符串。
语法:字符串序列.split(分割字符, num)
num表示的是分割字符出现的次数,即将来返回数据个数为num+1个。
mystr = "hello world and itcast and itheima and Python"
# 结果:['hello world ', ' itcast ', ' itheima ', ' Python']
print(mystr.split('and'))
# 结果:['hello world ', ' itcast ', ' itheima and Python']
print(mystr.split('and', 2))
3、join():用一个字符或⼦串合并字符串,即是将多个字符串合并为个新的字符串。
语法:字符或⼦串.join(多字符串组成的序列)
list1 = ['chuan', 'zhi', 'bo', 'ke']
# 结果:chuan_zhi_bo_ke
print('_'.join(list1))
4、字符转换
capitalize():将字符串第一个字符转换成大写title():将字符串每个单词首字母转换成大写lower():将字符串中大写转小写upper():将字符串中⼩写转大写
mystr = "hello world and itcast and itheima and Python" # 结果:Hello world and itcast and itheima and python print(mystr.capitalize()) # 结果:Hello World And Itcast And Itheima And Python print(mystr.title()) # 结果:hello world and itcast and itheima and python print(mystr.lower()) # 结果:HELLO WORLD AND ITCAST AND ITHEIMA AND PYTHON print(mystr.upper())
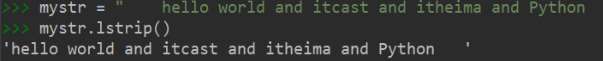
lstrip():删除字符串左侧空白字符rstrip():删除字符串右侧空⽩字符strip():删除字符串两侧空白字符
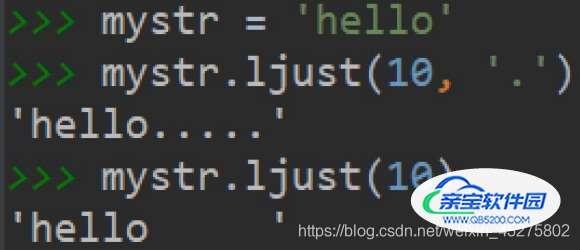
ljust():返回一个原字符串左对齐,并使用指定字符(默认空格)填充⾄至对应⻓度的新字符串。
语法:字符串序列.ljust(⻓度, 填充字符)
rjust():返回⼀个原字符串右对⻬,并使⽤指定字符(默认空格)填充⾄至对应⻓度的新字符串,语法和ljust()相同。center():返回⼀个原字符串居中对齐,并使⽤指定字符(默认空格)填充⾄对应长度的新字符串,语法和ljust()相同。
判断
startswith():检查字符串是否是以指定⼦串开头,是则返回 True,否则返回 False。如果设置开始和结束位置下标,则在指定范围内检查。
mystr = "hello world and itcast and itheima and Python "
# 结果:True
print(mystr.startswith('hello'))
# 结果False
print(mystr.startswith('hello', 5, 20))
endswith():检查字符串是否是以指定⼦串结尾,是则返回 True,否则返回 False。如果设置开始和结束位置下标,则在指定范围内检查。
mystr = "hello world and itcast and itheima and Python"
# 结果:True
print(mystr.endswith('Python'))
# 结果:False
print(mystr.endswith('python'))
# 结果:False
print(mystr.endswith('Python', 2, 20))
isalpha():如果字符串至少有⼀个字符并且所有字符都是字母则返回 True, 否则返回 False。isdigit():如果字符串只包含数字则返回 True 否则返回 False。isalnum():如果字符串至少有一个字符并且所有字符都是字母或数字则返回 True,否则返回False。isspace():如果字符串中只包含空白,则返回 True,否则返回False。
mystr1 = 'hello' mystr2 = 'hello12345' # 结果:True print(mystr1.isalpha()) # 结果:False print(mystr2.isalpha()) ----------------------------- mystr1 = 'aaa12345' mystr2 = '12345' # 结果: False print(mystr1.isdigit()) # 结果:False print(mystr2.isdigit()) ----------------------------- mystr1 = 'aaa12345' mystr2 = '12345-' # 结果:True print(mystr1.isalnum()) # 结果:False print(mystr2.isalnum()) ----------------------------- mystr1 = '1 2 3 4 5' mystr2 = ' ' # 结果:False print(mystr1.isspace()) # 结果:True print(mystr2.isspace())
总结
以上为个人经验,希望能给大家一个参考,也希望大家多多支持。
加载全部内容