React跨窗口通信方式
jie19100 人气:0iframe
跨窗口通信就是在嵌套了iframe的时候,实现iframe与父窗口的通信。
什么是iframe
- 它是一个
html标签,它可以将一个网站作为一个dom元素,嵌入到另一个网站中。 iframe具有自己的window与document对象。
使用场景
- 比如公司开发了一个完整的网站,需要在另一个项目中去使用。比如直播功能,一些插件,这时候就可以使用
iframe嵌入的方式。减少了重复开发的时间,需要修改界面的时候,也只需要修改一份代码即可。 - 微应用,微应用也有很多是使用
iframe来实现。
同源策略
当两个网站同时满足:同协议+同域名+同端口的时候。
当iframe与父窗口同源时
- 父窗口可以对
iframe进行完全访问,如window,document,location等对象的访问。 - 父窗口可以调用
iframe的全局函数。 - 父窗口可以修改
iframe的元素内容
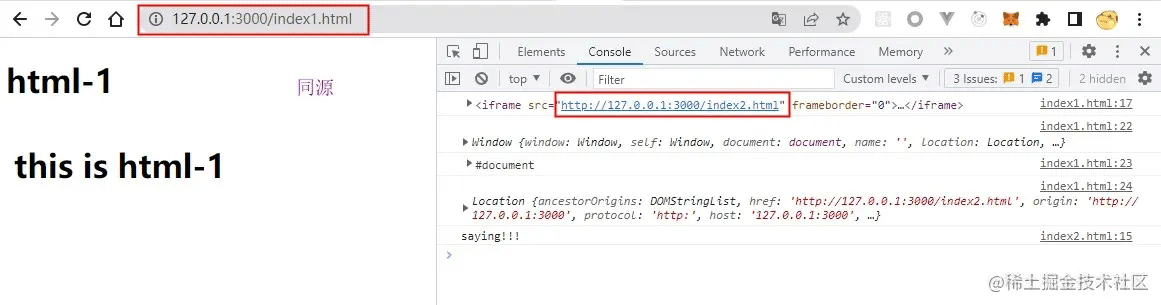
效果图
index1.html嵌套同源的index2.html
html1
<body>
<h1>html-1</h1>
<iframe src="http://127.0.0.1:3000/index2.html" frameborder="0"></iframe>
<script>
const iframe = document.querySelector("iframe");
iframe.onload = function () {
console.log(iframe)
// 获取iframe的window对象
const iWindow = iframe.contentWindow;
// 获取iframe的document对象
const iDocument = iframe.contentDocument;
console.log(iWindow)
console.log(iWindow.location)
iWindow.say()
iDocument.body.innerHTML = "<h1>this is html-1</h1>"
}
</script>
</body>
html2
<body>
<h1>html-2</h1>
<script>
function say() {
console.log("saying!!!")
}
</script>
</body>
效果图
index1.html嵌套同源的index2.html
发现子iframe的window,document,location对象,以及子iframe的全局方法都可以访问。
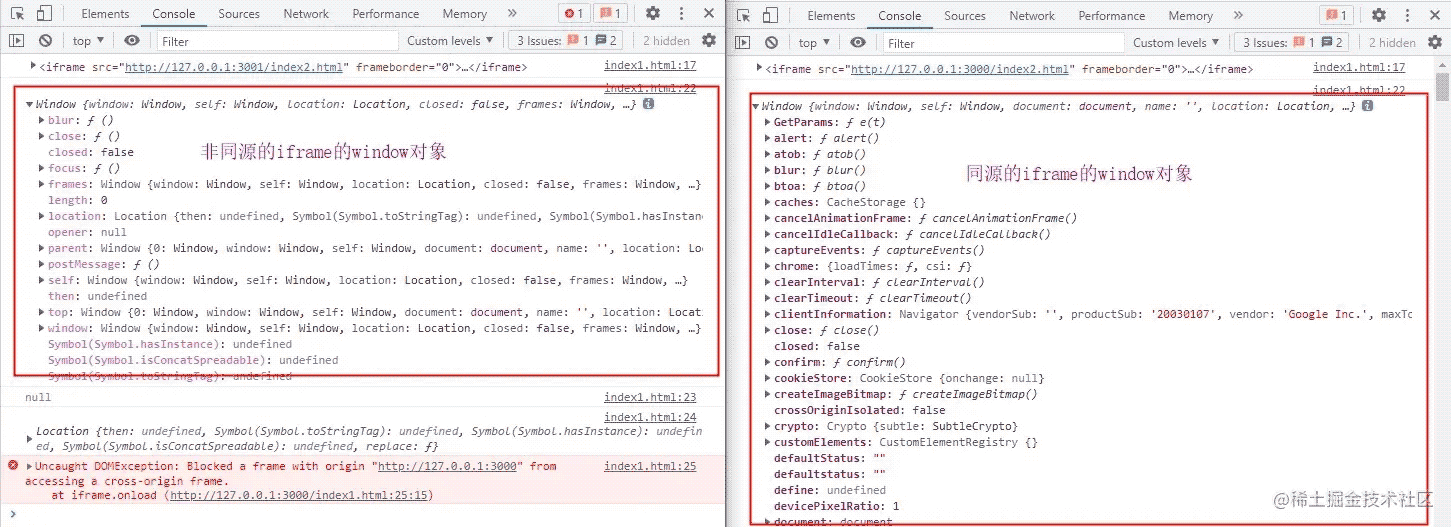
当iframe与父窗口不同源时
- 父窗口无法访问
iframe的window的所有属性与方法。 - 父窗口无法访问
iframe的document。 - 无法调用
iframe的全局方法。
效果图
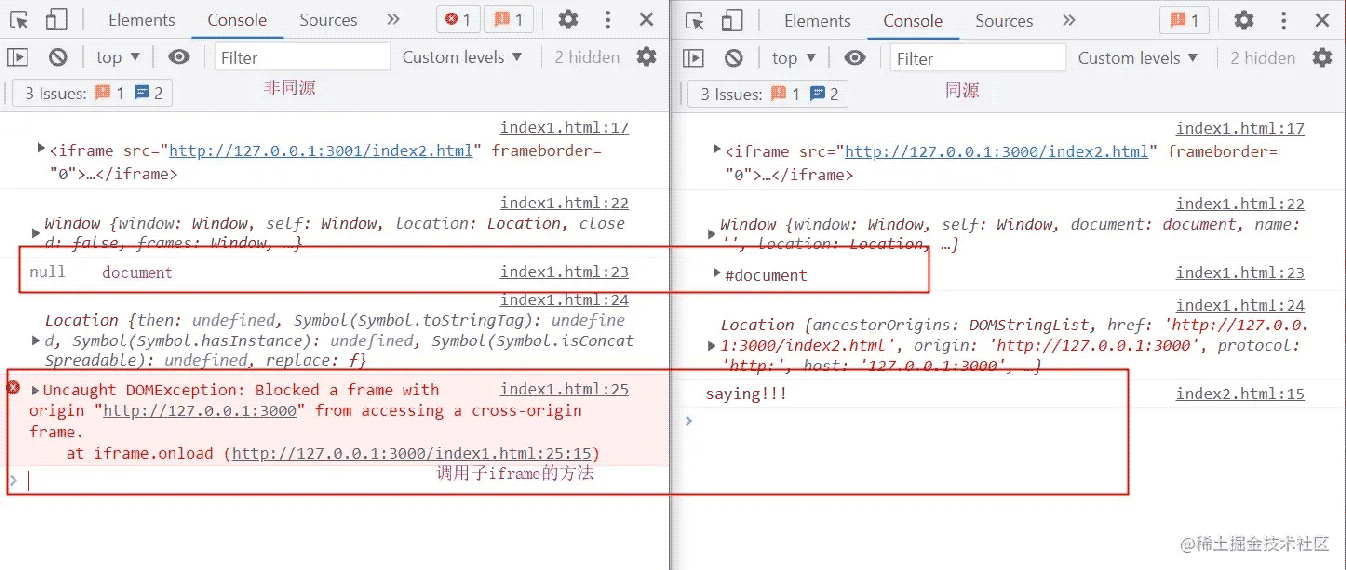
跨窗口通信
一:通过window.parent、frames、top
window.frames:获取子iframe的列表,与document.querySelector("iframe")一样
window.parent:获取父window的引用
window.top:获取最顶层窗口的window引用
上一节我们讲到,当iframe同源时,不同窗口可以拿到对方的window对象,以及全局方法,那么我们可以利用全局方法来实现不同window窗口的通信。
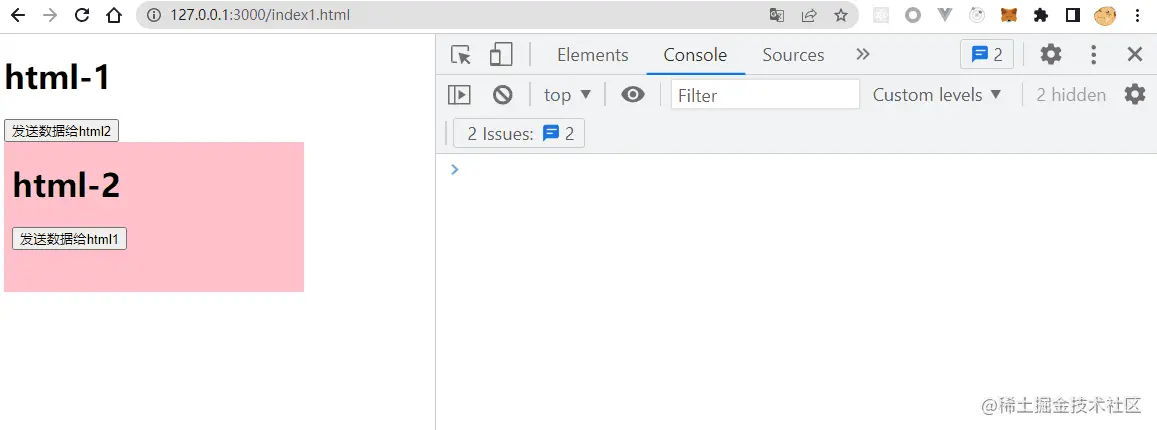
html1
<body>
<h1>html-1</h1>
<div>
<button onclick="send(Math.random(1))">发送数据给html2</button>
</div>
<iframe src="http://127.0.0.1:3000/index2.html" frameborder="0"></iframe>
<script>
const iframe = document.querySelector("iframe");
let send;
iframe.onload = function () {
// 获取iframe的window对象
const iWindow = iframe.contentWindow;
// 获取iframe的document对象
const iDocument = iframe.contentDocument;
function receive(value) {
console.log("这是html1,来了一条数据:", value)
}
send = function (value) {
iWindow.receive(value)
}
}
</script>
</body>
html2
<body>
<h1>html-2</h1>
<div>
<button onclick="send(Math.random(1))">发送数据给html1</button>
</div>
<script>
function receive(value) {
console.log("当前是html2,收到一条数据:", value)
}
function send(value) {
window.parent.receive(value)
}
</script>
</body>
效果图
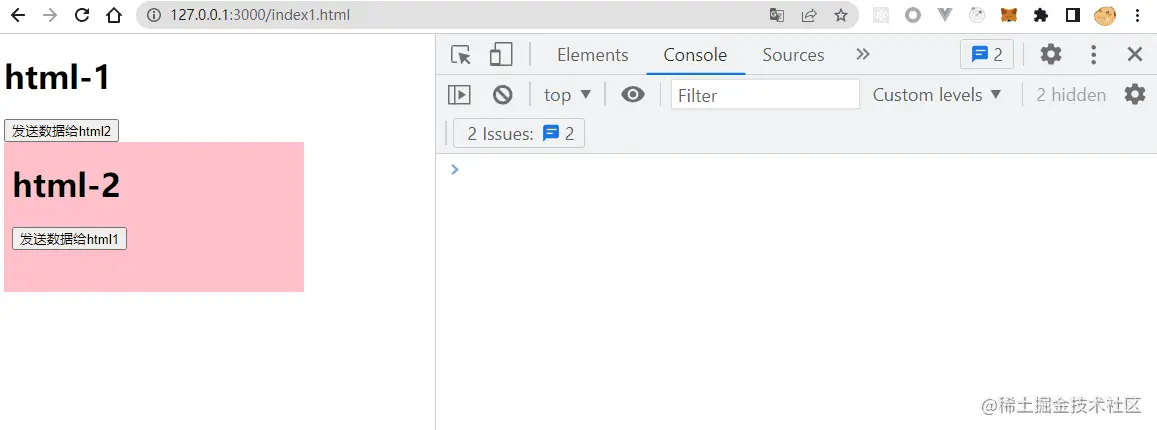
同理,window.top也可以这样通信
二:window.postMessage
postMessage支持不同窗口之间的通信,即使是非同源的情况。
发送数据
当需要使用给其他窗口(window)发送数据时,需要调用对方window的postMessage方法。
该方法接收两个参数
- 参数一:需要发送的数据,数据最后为字符串形式,因为IE只支持字符串数据。
- 参数二:接收方的地址(协议+域名+端口)
接收数据
监听message事件
该事件对象包含接收的数据,以及发送方的地址等信息。
html1
<body>
<h1>html-1</h1>
<div>
<button onclick="send(Math.random(1))">发送数据给html2</button>
</div>
<iframe src="http://127.0.0.1:3001/index2.html" frameborder="0"></iframe>
<script>
const iframe = document.querySelector("iframe");
let send;
iframe.onload = function () {
// 获取iframe的window对象
const iWindow = iframe.contentWindow;
send = function (value) {
iWindow.postMessage("wuwuwuw", "http://127.0.0.1:3001")
}
}
window.addEventListener("message", function (event) {
if (event.origin != 'http://127.0.0.1:3001') {
// 过滤指定地址的信息
return;
}
if (window == event.source) {
// 页面初始化的时候会被浏览器触发一次message,在这里根据发送方地址进行过滤
return
}
console.log("html1收到的数据 " + event.data);
})
</script>
</body>
html2
<body>
<h1>html-2</h1>
<div>
<button onclick="send(Math.random(1))">发送数据给html1</button>
</div>
<script>
function receive(value) {
console.log("当前是html2,收到一条数据:", value)
}
function send(value) {
window.parent.postMessage(value, "http://127.0.0.1:3000")
}
window.addEventListener("message", function (event) {
if (event.origin != 'http://127.0.0.1:3000') {
// 过滤指定地址的信息
return;
}
if (window == event.source) {
// 页面初始化的时候会被浏览器触发一次message,在这里根据发送方地址进行过滤
return;
}
console.log("html2收到的数据 " + event.data);
})
</script>
</body>
效果图
其他通信方法
- 使用soket,需要后端支持
- 使用本地存储,监听本地存储的数据变化
加载全部内容