TS取参数类型
前端科代表张继科 人气:0正文
挑战
我们先来做一个ts的挑战。
你知道如何为下面的app.get方法定义TypeScript类型吗?
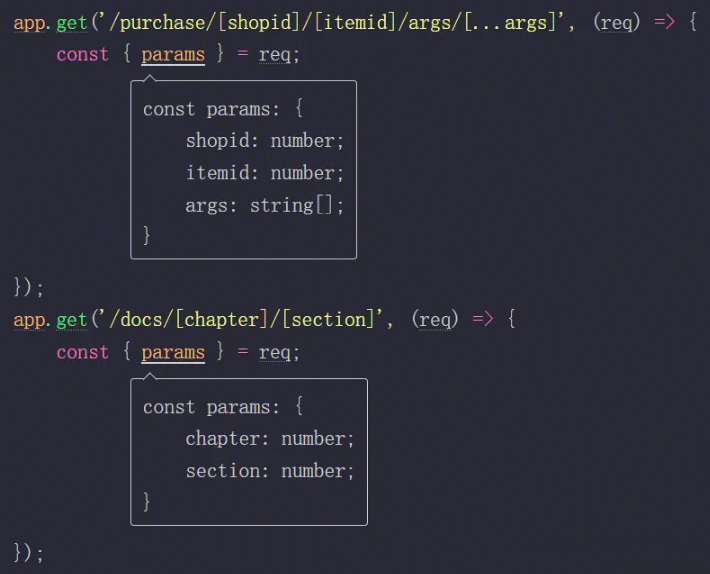
req.params是从传入的第一个参数字符串中提取出来的。
当你想对一个类似路由的函数定义一个类型时,这显得很有用,你可以传入一个带路径模式的路由,你可以使用自定义语法格式去定义动态参数片段(例如:[shopid]、:shopid),以及一个回调函数,它的参数类型来源于你刚刚传入的路由。
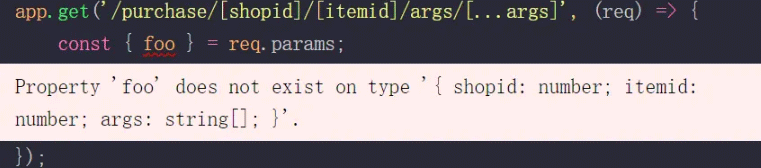
所以,如果你尝试访问没有定义的参数,将会报错!
举一个真实案例,如果你对React Router很熟悉,应该知道render函数中的RouteProps的类型是从path参数派生出来的。

本文将探讨如何定义这样一个类型,通过各种ts技术,从字符串字面量类型中提取类型。
需要掌握的内容
首先,在我们探讨之前,需要先讲下一些基本的知识要求。
字符串字面量类型
ts的字符串类型是一个可以有任何值的字符串
let str: string = 'abc'; str = 'def'; // no errors, string type can have any value
而字符串字面量类型是一个具有特定值的字符串类型。
let str: 'abc' = 'abc'; str = 'def'; // Type '"def"' is not assignable to type '"abc"'.
通常情况下,我们将它与联合类型一起使用,用来确定你可以传递给函数、数组、对象的字符串取值的列表。
function eatSomething(food: 'sushi' | 'ramen') {}
eatSomething('sushi');
eatSomething('ramen');
eatSomething('pencil'); // Argument of type '"pencil"' is not assignable to parameter of type '"sushi" | "ramen"'.
let food: Array<'sushi' | 'ramen'> = ['sushi'];
food.push('pencil'); // Argument of type '"pencil"' is not assignable to parameter of type '"sushi" | "ramen"'.
let object: { food: 'sushi' | 'ramen' };
object = { food: 'sushi' };
object = { food: 'pencil' }; // Type '"pencil"' is not assignable to type '"sushi" | "ramen"'.你是如何创建字符串字面量类型的呢?
当你使用const定义一个字符串变量时,它就是一个字符串字面量类型。然而,如果你用let去定义它,ts识别出变量的值可能会改变,所以它把变量分配给一个更通用的类型:

同样的情况对对象和数组也一样,你可以在以后去修改对象、数组的值,因此ts分配给了一个更通用的类型。

不过,你可以通过使用const断言向ts提示,你将只从对象、数组中读取值,而不会去改变它。

模板字面量类型和字符串字面量类型
从ts4.1开始,ts支持一种新的方式来定义新的字符串字面量类型,就是大家熟悉的字符串模板的语法:
const a = 'a';
const b = 'b';
// In JavaScript, you can build a new string
// with template literals
const c = `${a} ${b}`; // 'a b'
type A = 'a';
type B = 'b';
// In TypeScript, you can build a new string literal type
// with template literals too!
type C = `${A} ${B}`; // 'a b'条件类型
条件类型允许你基于另一个类型来定义一个类型。在这个例子中,Collection<X>可以是number[]或者Set<number>,这取决于X的类型:
type Collection<X> = X extends 'arr' ? number[] : Set<number>; type A = Collection<'arr'>; // number[] // If you pass in something other than 'arr' type B = Collection<'foo'>; // Set<number>
你使用extends关键字用来测试X的类型是否可以被分配给arr类型,并使用条件运算符(condition ? a : b)来确定测试成立的类型。
如果你想测试一个更复杂的类型,你可以使用infer关键字来推断该类型的一部分,并根据推断的部分定义一个新类型。
// Here you are testing whether X extends `() => ???` // and let TypeScript to infer the `???` part // TypeScript will define a new type called // `Value` for the inferred type type GetReturnValue<X> = X extends () => infer Value ? Value : never; // Here we inferred that `Value` is type `string` type A = GetReturnValue<() => string>; // Here we inferred that `Value` is type `number` type B = GetReturnValue<() => number>;
函数重载和通用函数
当你想在ts中定义一个参数类型和返回值类型相互依赖的函数类型时,可以使用函数重载或者通用函数。
function firstElement(arr) {
return arr[0];
}
const string = firstElement(['a', 'b', 'c']);
const number = firstElement([1, 2, 3]);// return string when passed string[]
function firstElement(arr: string[]): string;
// return number when passed number[]
function firstElement(arr: number[]): number;
// then the actual implementation
function firstElement(arr) {
return arr[0];
}
const string = firstElement(['a', 'b', 'c']);// Define type parameter `Item` and describe argument and return type in terms of `Item`
function firstElement<Item>(arr: Item[]): Item | undefined {
return arr[0];
}
// `Item` can only be of `string` or `number`
function firstElement<Item extends string | number>(arr: Item[]): Item | undefined {
return arr[0];
}
const number = firstElement([1, 3, 5]);
const obj = firstElement([{ a: 1 }]); // Type '{ a: number; }' is not assignable to type 'string | number'.着手解决问题
了解了以上知识,我们对于问题的解决方案可能可以采取这样的形式:
function get<Path extends string>(path: Path, callback: CallbackFn<Path>): void {
// impplementation
}
get('/docs/[chapter]/[section]/args/[...args]', (req) => {
const { params } = req;
});我们使用了一个类型参数Path(必须是一个字符串)。path参数的类型是Path,回调函数的类型是CallbackFn<Path>,而挑战的关键之处就是要弄清楚CallbackFn<Path>。
我们计划是这样子的:
- 给出
path的类型是Path,是一个字符串字面量类型。
type Path = '/purchase/[shopid]/[itemid]/args/[...args]';
- 我们派生出一个新的类型,这个类型将字符串分解成它的各个部分。
type Parts<Path> = 'purchase' | '[shopid]' | '[itemid]' | 'args' | '[...args]';
- 筛选出只包含参数的部分
type FilteredParts<Path> = '[shopid]' | '[itemid]' | '[...args]';
- 删除不需要的括号
type FilteredParts<Path> = 'shopid' | 'itemid' | '...args';
- 将参数映射到一个对象类型中
type Params<Path> = {
shopid: any;
itemid: any;
'...args': any;
};- 使用条件类型来定义map的值部分
type Params<Path> = {
shopid: number;
itemid: number;
'...args': string[];
};- 重置键名,删除
...args中的...
type Params<Path> = {
shopid: number;
itemid: number;
args: string[];
};最后
type CallbackFn<Path> = (req: { params: Params<Path> }) => void;分割字符串字面量类型
为了分割一个字符串字面量类型,我们可以使用条件类型来检查字符串字面量的取值:
type Parts<Path> = Path extends `a/b` ? 'a' | 'b' : never; type AB = Parts<'a/b'>; // type AB = "a" | "b"
但是要接收任意字符串字面量,我们无法提前知道是什么值
type CD = Parts<'c/d'>; type EF = Parts<'e/f'>;
我们必须在条件测试中推断出数值,并使用推断出来的数值类型:
type Parts<Path> = Path extends `${infer PartA}/${infer PartB}` ? PartA | PartB : never;
type AB = Parts<'a/b'>; // type AB = "a" | "b"
type CD = Parts<'c/d'>; // type CD = "c" | "d"
type EFGH = Parts<'ef/gh'>; // type EFGH = "ef" | "gh"而如果你传入一个不匹配模式的字符串字面量,我们希望直接返回:
type Parts<Path> = Path extends `${infer PartA}/${infer PartB}` ? PartA | PartB : Path;
type A = Parts<'a'>; // type A = "a"有一点需要注意,PartA的推断是'non-greedily'的,即:它将尽可能地进行推断,但不包含一个/字符串。
type ABCD = Parts<'a/b/c/d'>; // type ABCD = "a" | "b/c/d"
因此,为了递归地分割Path字符串字面量,我们可以返回Parts<PathB>类型替代原有的PathB类型:
type Parts<Path> = Path extends `${infer PartA}/${infer PartB}` ? PartA | Parts<PartB> : Path;
type ABCD = Parts<'a/b/c/d'>; // type ABCD = "a" | "b" | "c" | "d"以下是所发生的详细复盘:
type Parts<'a/b/c/d'> = 'a' | Parts<'b/c/d'>; type Parts<'a/b/c/d'> = 'a' | 'b' | Parts<'c/d'>; type Parts<'a/b/c/d'> = 'a' | 'b' | 'c' | Parts<'d'>; type Parts<'a/b/c/d'> = 'a' | 'b' | 'c' | 'd';
参数语法部分的过滤
这一步的关键是观察到,任何类型与never类型联合都不会产生类型
type A = 'a' | never; // type A = "a"
type Obj = { a: 1 } | never; // type Obj = { a: 1; }如果我们可以转换
'purchase' | '[shopid]' | '[itemid]' | 'args' | '[...args]'
成
never | '[shopid]' | '[itemid]' | never | '[...args]'
那我们就可以得到:
'[shopid]' | '[itemid]' | '[...args]'
所以,要怎么实现呢?
我们得再次向条件类型寻求帮助,我们可以有一个条件类型,如果它以[开始,以]结尾,则返回字符串字面量本身,如果不是,则返回never:
type IsParameter<Part> = Part extends `[${infer Anything}]` ? Part : never;
type Purchase = IsParameter<'purchase'>; // type Purchase = never
type ShopId = IsParameter<'[shopid]'>; // type ShopId = "[shopid]"type IsParameter<Part> = Part extends `[${infer Anything}]` ? Part : never;
type FilteredParts<Path> = Path extends `${infer PartA}/${infer PartB}` ? IsParameter<PartA> | FilteredParts<PartB> : IsParameter<Path>;
type Params = FilteredParts<'/purchase/[shopid]/[itemid]/args/[...args]'>; // type Params = "[shopid]" | "[itemid]" | "[...args]"删除括号:
type IsParameter<Part> = Part extends `[${infer ParamName}]` ? ParamName : never;
type FilteredParts<Path> = Path extends `${infer PartA}/${infer PartB}` ? IsParameter<PartA> | FilteredParts<PartB> : IsParameter<Path>;
type ParamsWithoutBracket = FilteredParts<'/purchase/[shopid]/[itemid]/args/[...args]'>;在对象类型里做一个映射
在这一步中,我们将使用上一步的结果作为键名来创建一个对象类型。
type Params<Keys extends string> = {
[Key in Keys]: any;
};
const params: Params<'shopid' | 'itemid' | '...args'> = {
shopid: 2,
itemid: 3,
'...args': 4,
};type IsParameter<Part> = Part extends `[${infer ParamName}]` ? ParamName : never;
type FilteredParts<Path> = Path extends `${infer PartA}/${infer PartB}` ? IsParameter<PartA> | FilteredParts<PartB> : IsParameter<Path>;
type Params<Path> = {
[Key in FilteredParts<Path>]: any;
};
type ParamObject = Params<'/purchase/[shopid]/[itemid]/args/[...args]'>;最终版:
type IsParameter<Part> = Part extends `[${infer ParamName}]` ? ParamName : never;
type FilteredParts<Path> = Path extends `${infer PartA}/${infer PartB}` ? IsParameter<PartA> | FilteredParts<PartB> : IsParameter<Path>;
type ParamValue<Key> = Key extends `...${infer Anything}` ? string[] : number;
type RemovePrefixDots<Key> = Key extends `...${infer Name}` ? Name : Key;
type Params<Path> = {
[Key in FilteredParts<Path> as RemovePrefixDots<Key>]: ParamValue<Key>;
};
type CallbackFn<Path> = (req: { params: Params<Path> }) => void;
function get<Path extends string>(path: Path, callback: CallbackFn<Path>) {
// TODO: implement
}加载全部内容