C++ OpenCV图像拼接
猿力猪 人气:0前言
本文以实现图像拼接为目标,把分割开的图像进行拼接还原,核心的内容包括:OpenCV图像拼接相关原理以及OpenCV图像拼接案例的实现
一、图像拼接相关原理

图像特征采集
一幅图中总存在着一些独特的像素点,这些点我们可以认为就是这幅图的特征,即为特征点
如何确定左边的是狼,右边的是猪?
获取一幅图中存在的一些独特的像素点,需要解决两个问题:
- 解决尺度不变性问题,不同大小的图片获取到的特征是一样的
- 提取到的特征点要稳定,能被精确定位
特征提取算法
| 名称 | 支持尺寸不变性 | 速度 |
| SURF | 支持 | 快 |
| SIFT | 支持 | 比SURF慢 |
| ORB | 不支持 | SURF算法快10倍 |
| FAST | 没有尺度不变性 | 比ORB快 |
透视变换
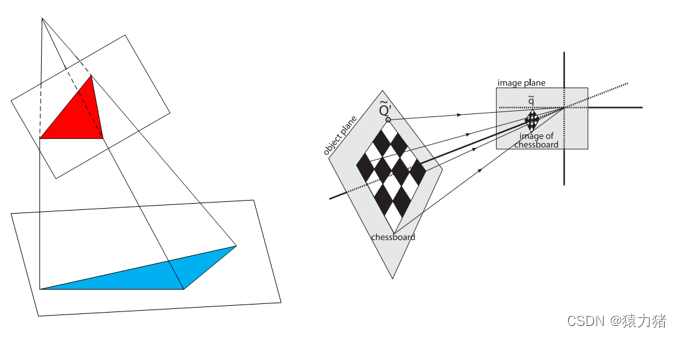
透视变换是按照物体成像投影规律进行变换,即将物体重新投影到新的成像平面
透视变换常用于机器人视觉导航研究中,由于相机视场与地面存在倾斜角使得物体成像产生畸变,通常通过透视变换实现对物体图像的校正
透视矩阵
[u,v,w] 表示当前平面坐标的x,y,z,如果是平面,那么z=1
[x',y',z'] 表示目标平面坐标的x,y,z,如果是平面,那么z=1
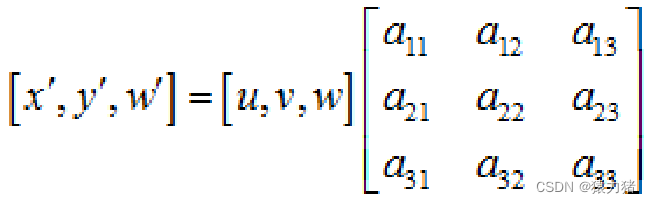

以上公式,我们可以理解为,透视矩阵是原始平面可目标平面之间的一种转换关系
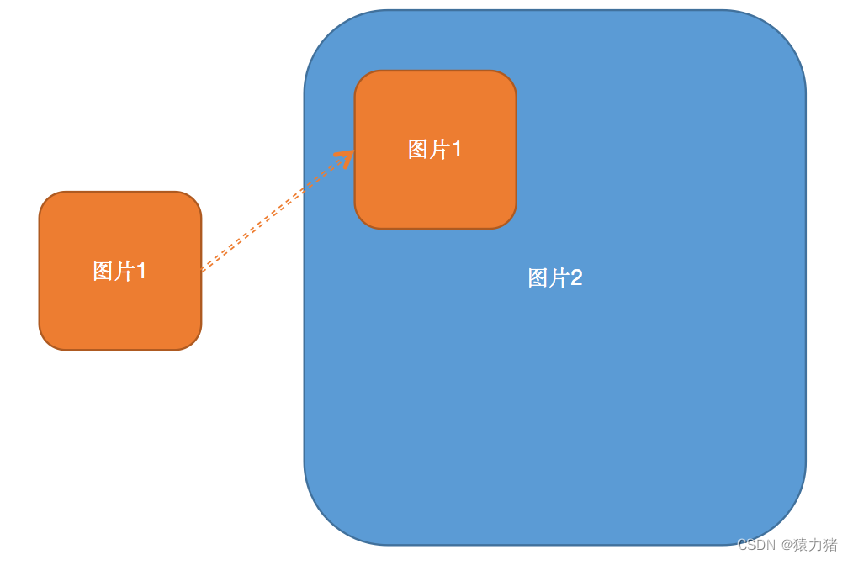
图像拷贝
将一副图像拷贝到另一副图像上的过程
二、案例实现
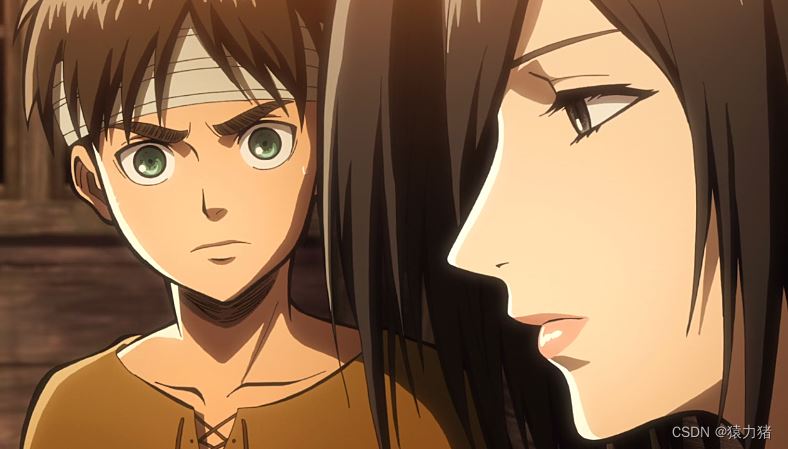
这是本案例所用到的素材,如下图所示:

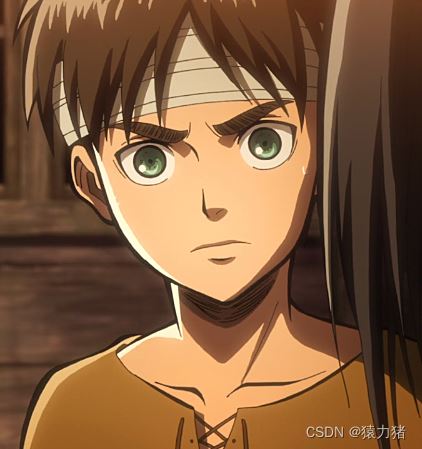
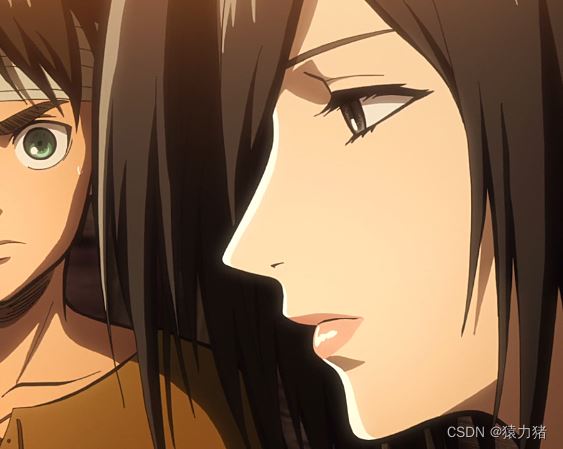
我们将上图进行分割,用于实现拼接还原,如下图所示:


Step1:导入目标图片
设置需要处理的两张图片,进行拼接准备工作
Mat left=imread("C:/Users/86177/Desktop/image/a11.png");//左侧:图片路径
Mat right=imread("C:/Users/86177/Desktop/image/a22.png");//右侧:图片路径
imshow("left",left);
imshow("right",right);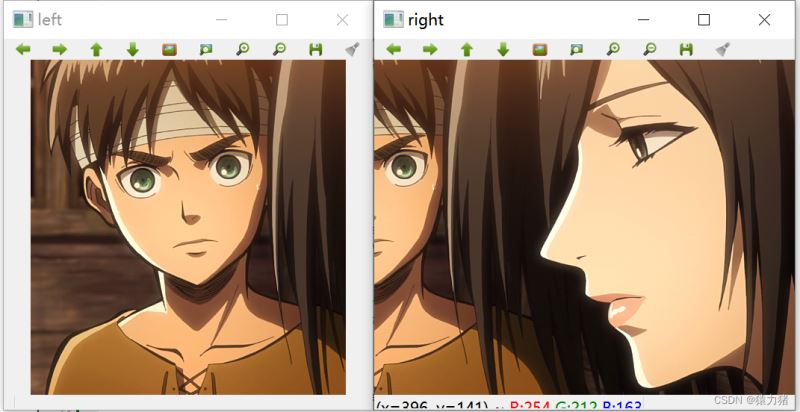
Step2:特征点提取和匹配
用SIFT算法来实现图像拼接是很常用的方法,虽说SURF精确度和稳定性不及SIFT,但是其综合能力还是优越一些
//创建SURF对象
Ptr<SURF>surf; //可以容纳800个特征点
surf = SURF::create(800);//参数 查找的海森矩阵 create 海森矩阵阀值
//暴力匹配器
BFMatcher matcher;
vector<KeyPoint>key1,key2;
Mat c,d;
//寻找特征点
surf->detectAndCompute(left,Mat(),key2,d);
surf->detectAndCompute(right,Mat(),key1,c);
//特征点对比,保存下来
vector<DMatch>matches;//DMatch 点和点之间的关系
//使用暴力匹配器匹配特征点,找到存来
matcher.match(d,c,matches);
//排序 从小到大
sort(matches.begin(),matches.end());
//保留最优的特征点对象
vector<DMatch>good_matches;//最优
//设置比例
int ptrPoint = std::min(50,(int)(matches.size()*0.15));
for(int i = 0;i < ptrPoint;i++)
{
good_matches.push_back(matches[i]);
}
//最佳匹配的特征点连成线
Mat outimg;
drawMatches(left,key2,right,key1,good_matches,outimg,
Scalar::all(-1),Scalar::all(-1),
vector<char>(),DrawMatchesFlags::NOT_DRAW_SINGLE_POINTS);
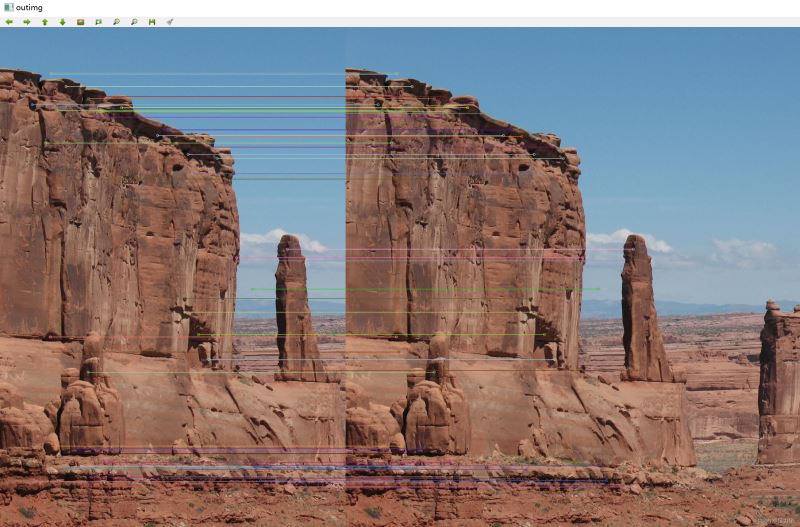
imshow("outimg",outimg);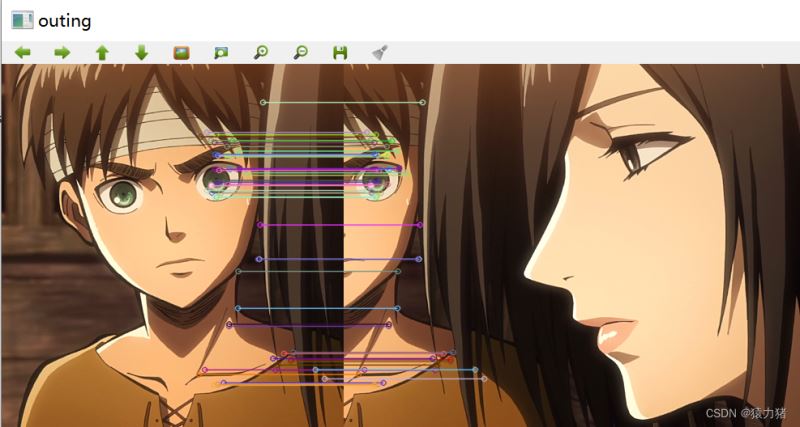
Step3:图像配准
我们就可以得到了两幅待拼接图的匹配点集,接下来我们进行图像的配准,即将两张图像转换为同一坐标下
//特征点配准
vector<Point2f>imagepoint1,imagepoint2;
for(int i = 0;i<good_matches.size();i++)
{
imagepoint1.push_back(key1[good_matches[i].trainIdx].pt);
imagepoint2.push_back(key2[good_matches[i].queryIdx].pt);
}
//透视转换
Mat homo = findHomography(imagepoint1,imagepoint2,CV_RANSAC);
imshow("homo",homo);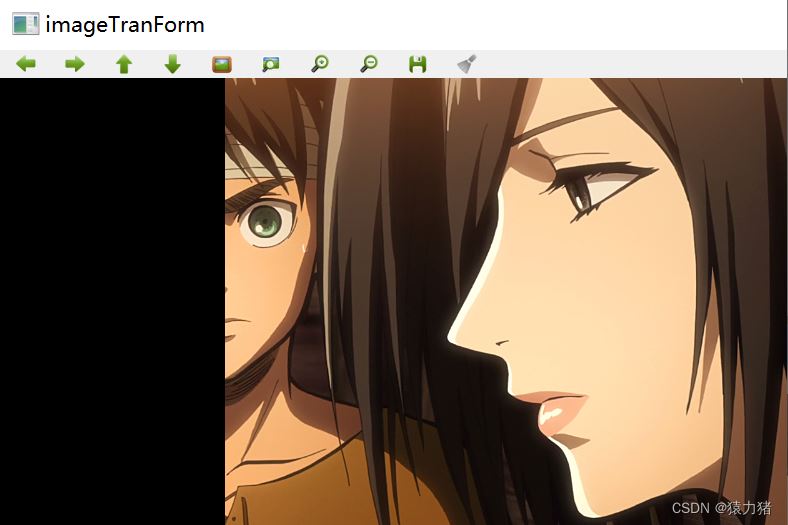
Step4:图像拷贝
将我们的左图拷贝到设置好的配准图(右图)上
//创建拼接后的图,计算图的大小
int dst_width = imageTranForm.cols;//获取最右点为拼接图长度
int dst_height = left.rows;
Mat dst(dst_height,dst_width,CV_8UC3);
dst.setTo(0);
imageTranForm.copyTo(dst(Rect(0,0,imageTranForm.cols,imageTranForm.rows)));
left.copyTo(dst(Rect(0,0,left.cols,left.rows)));
imshow("dst",dst);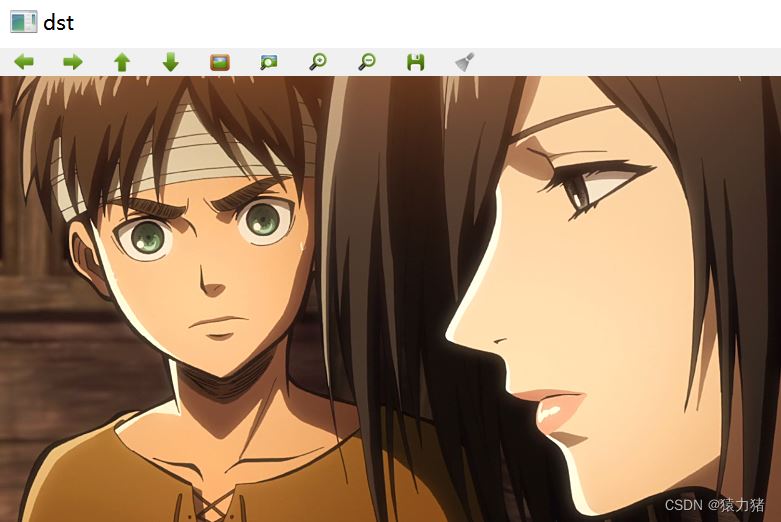
Step5:图像融合
去裂缝处理,让我们的优化两图的连接处,使得拼接自然
PS:上面拼接完的图片看不太出来,拼接处理中,还是建议用上
//优化两图的连接处,使得拼接自然
void OptimizeSeam(Mat& img1, Mat& trans, Mat& dst)
{
int start = MIN(corners.left_top.x, corners.left_bottom.x);//开始位置,即重叠区域的左边界
double processWidth = img1.cols - start;//重叠区域的宽度
int rows = dst.rows;
int cols = img1.cols; //注意,是列数*通道数
double alpha = 1;//img1中像素的权重
for (int i = 0; i < rows; i++)
{
uchar* p = img1.ptr<uchar>(i); //获取第i行的首地址
uchar* t = trans.ptr<uchar>(i);
uchar* d = dst.ptr<uchar>(i);
for (int j = start; j < cols; j++)
{
//如果遇到图像trans中无像素的黑点,则完全拷贝img1中的数据
if (t[j * 3] == 0 && t[j * 3 + 1] == 0 && t[j * 3 + 2] == 0)
{
alpha = 1;
}
else
{
//img1中像素的权重,与当前处理点距重叠区域左边界的距离成正比,实验证明,这种方法确实好
alpha = (processWidth - (j - start)) / processWidth;
}
d[j * 3] = p[j * 3] * alpha + t[j * 3] * (1 - alpha);
d[j * 3 + 1] = p[j * 3 + 1] * alpha + t[j * 3 + 1] * (1 - alpha);
d[j * 3 + 2] = p[j * 3 + 2] * alpha + t[j * 3 + 2] * (1 - alpha);
}
}
}
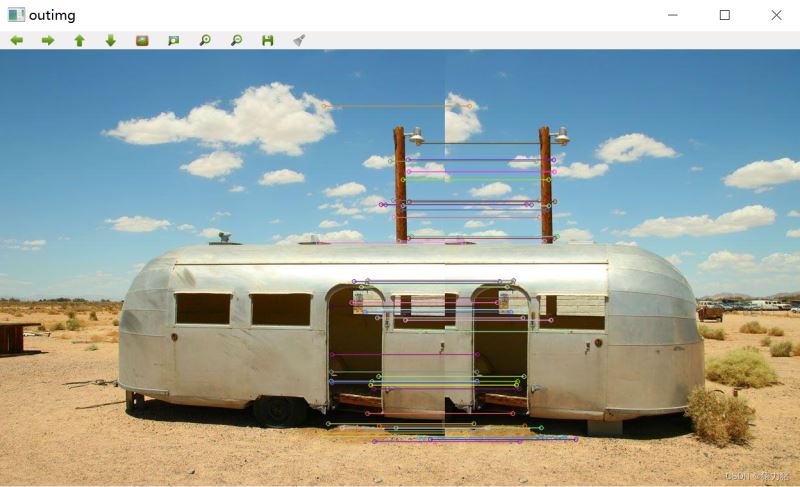
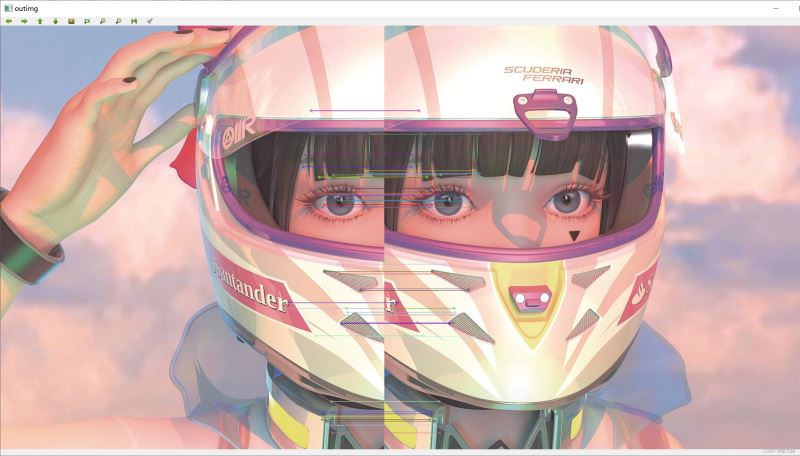
其他图片拼接效果,如下图所示:





完整代码
#include <iostream>
#include <opencv2/opencv.hpp>
#include <opencv2/highgui.hpp>
#include <opencv2/xfeatures2d.hpp>
#include <opencv2/calib3d.hpp>
#include <opencv2/imgproc.hpp>
using namespace std;
using namespace cv;
using namespace cv::xfeatures2d;
typedef struct
{
//四个顶点
Point2f left_top;
Point2f left_bottom;
Point2f right_top;
Point2f right_bottom;
}four_corners_t;
four_corners_t corners;
//计算配准图的四个顶点坐标
void CalcCorners(const Mat& H, const Mat& src)
{
double v2[] = { 0, 0, 1 };//左上角
double v1[3];//变换后的坐标值
Mat V2 = Mat(3, 1, CV_64FC1, v2); //列向量
Mat V1 = Mat(3, 1, CV_64FC1, v1); //列向量
V1 = H * V2;
//左上角(0,0,1)
cout << "V2: " << V2 << endl;
cout << "V1: " << V1 << endl;
corners.left_top.x = v1[0] / v1[2];
corners.left_top.y = v1[1] / v1[2];
//左下角(0,src.rows,1)
v2[0] = 0;
v2[1] = src.rows;
v2[2] = 1;
V2 = Mat(3, 1, CV_64FC1, v2); //列向量
V1 = Mat(3, 1, CV_64FC1, v1); //列向量
V1 = H * V2;
corners.left_bottom.x = v1[0] / v1[2];
corners.left_bottom.y = v1[1] / v1[2];
//右上角(src.cols,0,1)
v2[0] = src.cols;
v2[1] = 0;
v2[2] = 1;
V2 = Mat(3, 1, CV_64FC1, v2); //列向量
V1 = Mat(3, 1, CV_64FC1, v1); //列向量
V1 = H * V2;
corners.right_top.x = v1[0] / v1[2];
corners.right_top.y = v1[1] / v1[2];
//右下角(src.cols,src.rows,1)
v2[0] = src.cols;
v2[1] = src.rows;
v2[2] = 1;
V2 = Mat(3, 1, CV_64FC1, v2); //列向量
V1 = Mat(3, 1, CV_64FC1, v1); //列向量
V1 = H * V2;
corners.right_bottom.x = v1[0] / v1[2];
corners.right_bottom.y = v1[1] / v1[2];
}
//优化两图的连接处,使得拼接自然
void OptimizeSeam(Mat& img1, Mat& trans, Mat& dst)
{
int start = MIN(corners.left_top.x, corners.left_bottom.x);//开始位置,即重叠区域的左边界
double processWidth = img1.cols - start;//重叠区域的宽度
int rows = dst.rows;
int cols = img1.cols; //注意,是列数*通道数
double alpha = 1;//img1中像素的权重
for (int i = 0; i < rows; i++)
{
uchar* p = img1.ptr<uchar>(i); //获取第i行的首地址
uchar* t = trans.ptr<uchar>(i);
uchar* d = dst.ptr<uchar>(i);
for (int j = start; j < cols; j++)
{
//如果遇到图像trans中无像素的黑点,则完全拷贝img1中的数据
if (t[j * 3] == 0 && t[j * 3 + 1] == 0 && t[j * 3 + 2] == 0)
{
alpha = 1;
}
else
{
//img1中像素的权重,与当前处理点距重叠区域左边界的距离成正比,实验证明,这种方法确实好
alpha = (processWidth - (j - start)) / processWidth;
}
d[j * 3] = p[j * 3] * alpha + t[j * 3] * (1 - alpha);
d[j * 3 + 1] = p[j * 3 + 1] * alpha + t[j * 3 + 1] * (1 - alpha);
d[j * 3 + 2] = p[j * 3 + 2] * alpha + t[j * 3 + 2] * (1 - alpha);
}
}
}
int main(int argc, char *argv[])
{
Mat left=imread("C:/Users/86177/Desktop/image/test(1).png");//左侧:图片路径
Mat right=imread("C:/Users/86177/Desktop/image/test(2).png");//右侧:图片路径
imshow("left",left);
imshow("right",right);
//创建SURF对象
Ptr<SURF>surf; //可以容纳800个特征点
surf = SURF::create(800);//参数 查找的海森矩阵 create 海森矩阵阀值
//暴力匹配器
BFMatcher matcher;
vector<KeyPoint>key1,key2;
Mat c,d;
//寻找特征点
surf->detectAndCompute(left,Mat(),key2,d);
surf->detectAndCompute(right,Mat(),key1,c);
//特征点对比,保存下来
vector<DMatch>matches;//DMatch 点和点之间的关系
//使用暴力匹配器匹配特征点,找到存来
matcher.match(d,c,matches);
//排序 从小到大
sort(matches.begin(),matches.end());
//保留最优的特征点对象
vector<DMatch>good_matches;//最优
//设置比例
int ptrPoint = std::min(50,(int)(matches.size()*0.15));
for(int i = 0;i < ptrPoint;i++)
{
good_matches.push_back(matches[i]);
}
//最佳匹配的特征点连成线
Mat outimg;
drawMatches(left,key2,right,key1,good_matches,outimg,
Scalar::all(-1),Scalar::all(-1),
vector<char>(),DrawMatchesFlags::NOT_DRAW_SINGLE_POINTS);
imshow("outimg",outimg);
//特征点配准
vector<Point2f>imagepoint1,imagepoint2;
for(int i = 0;i<good_matches.size();i++)
{
imagepoint1.push_back(key1[good_matches[i].trainIdx].pt);
imagepoint2.push_back(key2[good_matches[i].queryIdx].pt);
}
//透视转换
Mat homo = findHomography(imagepoint1,imagepoint2,CV_RANSAC);
imshow("homo",homo);
//四个顶点坐标的转换计算
CalcCorners(homo,right);
Mat imageTranForm;
warpPerspective(right,imageTranForm,homo,
Size(MAX(corners.right_top.x,
corners.right_bottom.x),
left.rows));
imshow("imageTranForm",imageTranForm);
//创建拼接后的图,计算图的大小
int dst_width = imageTranForm.cols;//获取最右点为拼接图长度
int dst_height = left.rows;
Mat dst(dst_height,dst_width,CV_8UC3);
dst.setTo(0);
imageTranForm.copyTo(dst(Rect(0,0,imageTranForm.cols,imageTranForm.rows)));
left.copyTo(dst(Rect(0,0,left.cols,left.rows)));
//优化拼接,主要目的去除黑边
OptimizeSeam(left,imageTranForm, dst);
imshow("dst",dst);
waitKey(0);
return 0;
}
三、总结
本文的核心内容包括:OpenCV图像拼接相关原理以及OpenCV图像拼接案例的实现
图像拼接在我们日常生活中运用其实算是非常广了,比如说我们现在经常见到的无人机航拍,以及我们手机相机的全景拍摄
图像拼接是我们对图像进行其他处理的基础条件,图像拼接的好坏,将会直接影响了咱们出图的效果!所以学会拼接算法对图像进行拼接处理,很重要!
加载全部内容