Java链表数据结构
行百里er 人气:1认识链表结构
单向链表
单链表在内存中的表示:
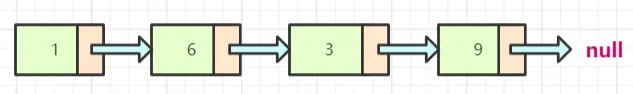
可以看到,一个链表的节点包含数据域和指向下一个节点的引用,链表最后一个节点指向null(空区域)。
我们可以根据这一定义,用Java语言表示一下单向链表的结构:
public class Node {
public int value;
public Node next;
public Node(int value) {
this.value = value;
}
}在链表的结构中,有数据域value,以及一个指向下一个节点的引用next。
TIP:这里的value还可以定义成泛型的。
双向链表
我们再来看一下双向链表的结构:
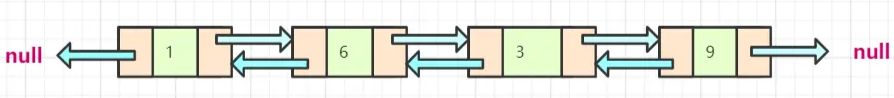
双向链表中的节点有数值域,和指向它前一个节点的引用以及指向它后一个节点的引用,据此我们可以定义出
双向链表的结构:
public class DoubleNode {
public int value;
public DoubleNode pre;
public DoubleNode next;
public DoubleNode(int value) {
this.value = value;
}
}加深对链表结构的理解
实现单向和双向链表的反转
说明:
对于一个链表如图所示:
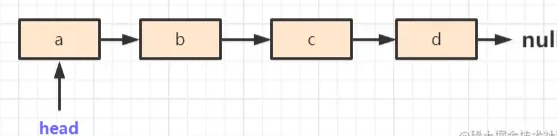
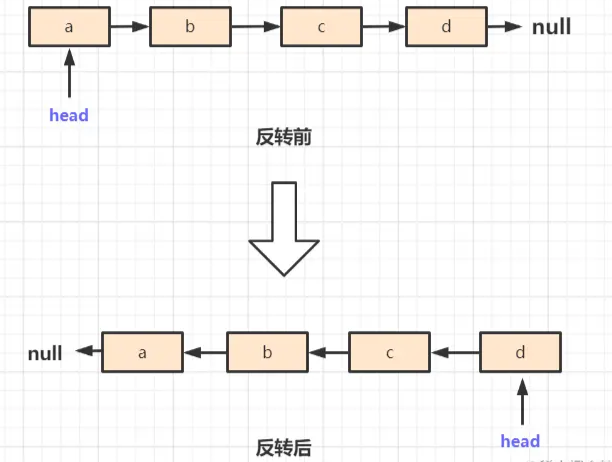
反转的意思是,将原来链表上的节点指针指向反转,原来的指向是:a -> b -> c -> d -> null,变成现在的指向:d -> c -> b -> a -> null,
即反转后的结构如图所示:
这个题目不难,我们转换一下指针的指向就行了。
设计这样一个函数,函数的过程是调整链表各节点的指针指向,那么这个函数的要素有:
- 返回值是链表的新的头结点,这样能保证函数执行完,原链表变成一个有新的头结点的链表
- 需要传入一个链表,用头结点表示
解题技巧:定义两个Node引用辅助我们反转指针指向。
代码实现:
public static Node reverseNode(Node head) {
Node pre = null;
Node next = null;
//最终让head指向null
while (head != null) {
next = head.next;
head.next = pre;
pre = head;
head = next;
}
return pre;
}我们来模拟一下这个函数的执行过程。
链表原始状态:
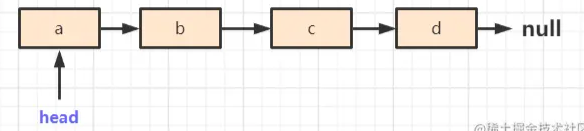
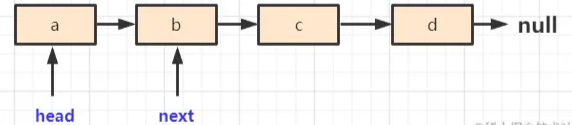
方法开始执行,此时 head.next 不为空,所以,执行如下步骤:
next = head.next:让next指向head(当前节点)的下一个节点,即b
head.next = pre:让当前节点的下一个节点指向pre,即null
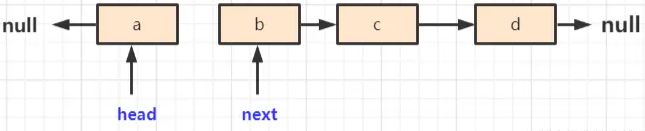
此时当前节点从原来指向b,改为指向null。
- pre = head:让pre指向当前节点
- head = next:让当前节点指向next,相当于移动head节点,直到将head节点移动到原来tail节点的位置
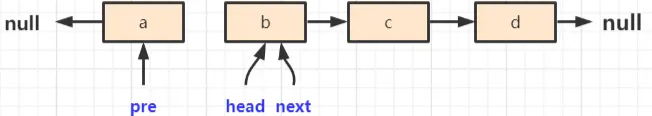
第一次循环执行结束,此时 head 为b,不是null,所以继续循环,执行流程:

此时 head 为c,不是null,所以继续循环,执行流程如下:

同理,此时 head 为d,不是null,继续循环:
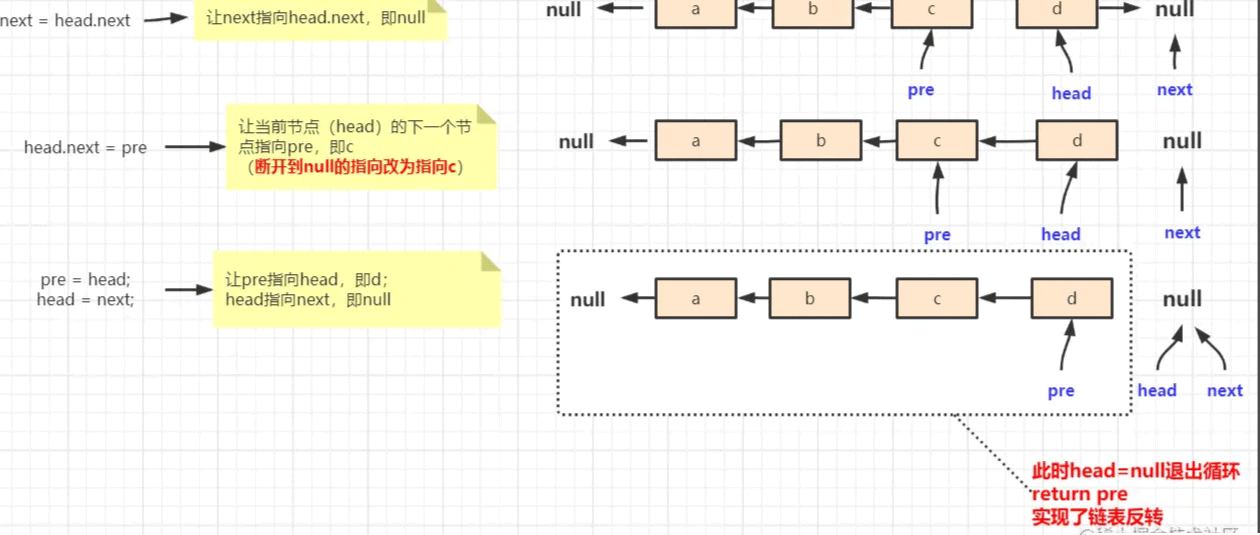
这是就完成了单链表的反转步骤。
有了单链表反转的经验,我们很容易就能实现双向链表的反转,代码如下:
public DoubleNode reverseDoubleNode(DoubleNode head) {
DoubleNode pre = null;
DoubleNode next = null;
while (head != null) {
next = head.next;
//操作(移动)当前节点
head.next = pre;
head.pre = next;
pre = head;
head = next;
}
return pre;
}实现把链表中给定的值都删除
题如:给定一个单链表头节点head,以及一个整数,要求把链表中值为给定整数的节点都删除。

实现思路:
- 要实现的函数需要给我传一个头节点以及给定的数值,头节点确定链表。func(Node head, int num)。
- 函数给不给返回值,返回值是什么?试想,针对链表
3 -> 5 -> 4 -> 3 -> 4 -> 5,假如要删除4,那么新链表就是3 -> 5-> 3 -> 5,头节点仍然是原来的节点3;而如果要删除值为3的节点呢,删除后就是5 -> 4 -> 4 -> 5,头节点变了。因此,我们要设计的这个函数需要返回新链表的头节点。 - 上述分析得知,需要返回新链表的头节点,因此也就是要返回第一个不是给定值的节点(因为给定值的节点都要被删除掉)。
//head移动到第一个不需要删除的位置:边界条件
while (head != null) {
if (head.value != num) {
break;
}
//head右移
head = head.next;
}
//跳出循环之后,head的情况:
//1. head = null,这种情况是链表中的值全部是给定值,全删了
//2. head != null
// 中间操作
//最终返回head:第一个不是给定值的节点
return head;head移动到第一个不需要删除的位置后,head若为null,表示所有节点都删除了,直接返回就可以了;若head不为null,借助两个辅助变量Node pre和cur,从head处开始往next走,遇到给定值就跳过。
Node pre = head;
Node cur = head;
while (cur != null) {
if (cur.value == num) {
pre.next = cur.next;
} else {
pre = cur;
}
cur = cur.next;
}
这一执行过程图解如下:
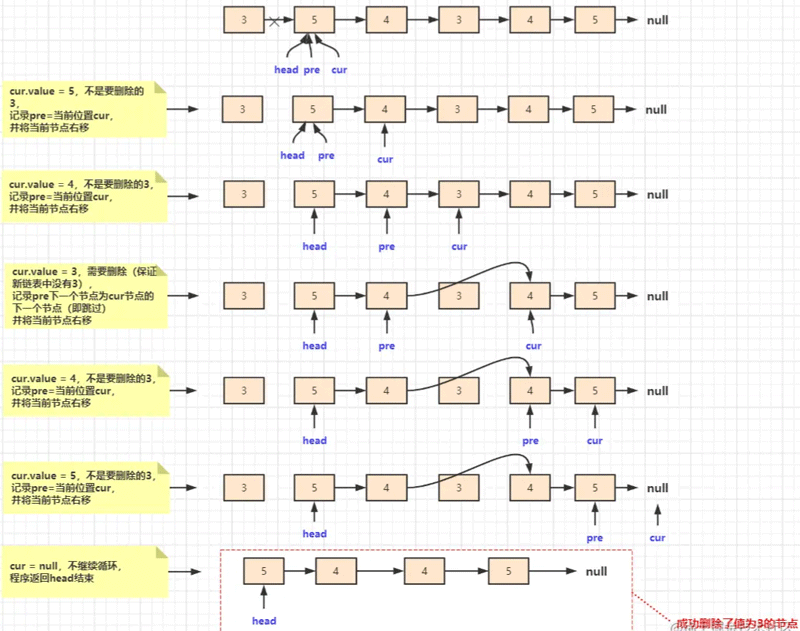
通过上述分析,写出完整实现代码:
public static Node remove (Node head, int num) {
while (head != null) {
if (head.value != num) {
break;
}
head = head.next;
}
Node pre = head;
Node cur = head;
while (cur != null) {
if (cur.value == num) {
pre.next = cur.next;
} else {
pre = cur;
}
cur = cur.next;
}
return head;
}小结
针对链表这种数据结构进行了一些简单的分析,通过两个例子熟悉了链表的结构。
针对链表的操作,需要注意的就是指针指向以及边界问题,后续关于链表的算法还会遇到。
加载全部内容