Spring AOP增强方式
wl_Honest 人气:0什么是AOP
AOP (Aspect Orient Programming),直译过来就是 面向切面编程。AOP 是一种编程思想,是面向对象编程(OOP)的一种补充。面向对象编程将程序抽象成各个层次的对象,而面向切面编程是将程序抽象成各个切面。从《Spring实战(第4版)》图书中扒了一张图:
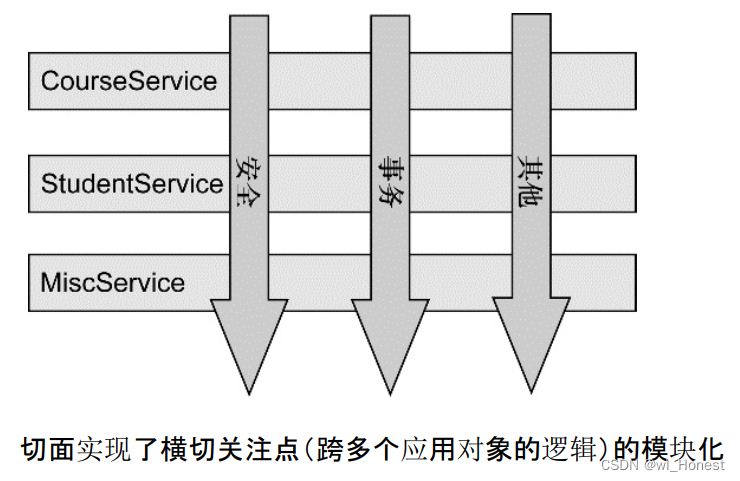
从该图可以很形象地看出,所谓切面,相当于应用对象间的横切点,我们可以将其单独抽象为单独的模块。
为什么需要AOP
想象下面的场景,开发中在多个模块间有某段重复的代码,我们通常是怎么处理的?显然,没有人会靠“复制粘贴”吧。在传统的面向过程编程中,我们也会将这段代码,抽象成一个方法,然后在需要的地方分别调用这个方法,这样当这段代码需要修改时,我们只需要改变这个方法就可以了。然而需求总是变化的,有一天,新增了一个需求,需要再多出做修改,我们需要再抽象出一个方法,然后再在需要的地方分别调用这个方法,又或者我们不需要这个方法了,我们还是得删除掉每一处调用该方法的地方。实际上涉及到多个地方具有相同的修改的问题我们都可以通过 AOP 来解决。
AOP术语
AOP 领域中的特性术语:
- 通知(Advice): AOP 框架中的增强处理。通知描述了切面何时执行以及如何执行增强处理。
- 连接点(join point): 连接点表示应用执行过程中能够插入切面的一个点,这个点可以是方法的调用、异常的抛出。在 Spring AOP 中,连接点总是方法的调用。
- 切点(PointCut): 可以插入增强处理的连接点。
- 切面(Aspect): 切面是通知和切点的结合。
- 引入(Introduction):引入允许我们向现有的类添加新的方法或者属性。
- 织入(Weaving): 将增强处理添加到目标对象中,并创建一个被增强的对象,这个过程就是织入。
通过注解声明5种通知类型
Spring AOP 中有 5 中通知类型,分别如下:
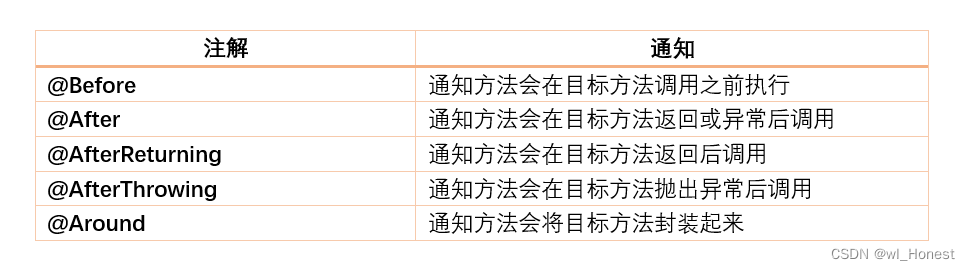
本章中主要以@Before、@After和@Around为例展示AOP的增强方式。
首先引入依赖,这里只放aop的依赖,其它的依赖请根据自己的实际情况引入:
<!-- aop -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-aop</artifactId>
<version>5.1.18.RELEASE</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-aspects</artifactId>
<version>5.1.18.RELEASE</version>
</dependency>
接着新建一个切面类TesstAspect,并且定义3个切点,就是后面要测试的3个切点:
package com.wl.standard.aop.aspect;
import com.wl.standard.util.JoinPointUtils;
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
import org.apache.commons.lang.ArrayUtils;
import org.aspectj.lang.JoinPoint;
import org.aspectj.lang.ProceedingJoinPoint;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.*;
import org.aspectj.lang.reflect.MethodSignature;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
/**
* @author wl
* @date 2022/7/2 16:08
*/
@Slf4j
@Component
@Aspect
public class TestAspect {
@Pointcut("execution(public * com.wl.standard.service.TravelRecordService.getAllRecord(..))")
public void pointCut1(){};
@Pointcut("execution(public * com.wl.standard.service.CityRailService.getTopRail(..))")
public void pointCut2(){};
@Pointcut("execution(public * com.wl.standard.service.CityGdpService.compareGDP(..))")
public void pointCut3(){};
}备注:execution():用于匹配方法执行的连接点,第一个*表示匹配任意的方法返回值
@Before
先测试第一个增强方法,在切点方法之前执行,因为是简单测试,就只打印一下日志就好了:
package com.wl.standard.aop.aspect;
import com.wl.standard.util.JoinPointUtils;
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
import org.apache.commons.lang.ArrayUtils;
import org.aspectj.lang.JoinPoint;
import org.aspectj.lang.ProceedingJoinPoint;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.*;
import org.aspectj.lang.reflect.MethodSignature;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
/**
* @author wl
* @date 2022/7/2 16:08
*/
@Slf4j
@Component
@Aspect
public class TestAspect {
@Pointcut("execution(public * com.wl.standard.service.TravelRecordService.getAllRecord(..))")
public void pointCut1(){};
@Pointcut("execution(public * com.wl.standard.service.CityRailService.getTopRail(..))")
public void pointCut2(){};
@Pointcut("execution(public * com.wl.standard.service.CityGdpService.compareGDP(..))")
public void pointCut3(){};
@Before("pointCut1()")
public void doBefore(JoinPoint joinPoint) {
log.info("当前线程: {} 开始执行查询前任务...", Thread.currentThread().getName());
}
}启动项目,进入swagger的页面调用接口测试:
调用接口后,在控制台可以看到日志打印的先后顺序,先执行的@Before里的增强方法再执行的service里的方法:

@After
接着测试@After,为了更好的展示增强方式,这次利用JoinPoint获取参数。
说明:Joinpoint是AOP的连接点。一个连接点代表一个被代理的方法。
为了获取参数的方法能够复用,这里新建一个工具类JoinPointUtils:
package com.wl.standard.util;
import org.apache.commons.lang.ArrayUtils;
import org.aspectj.lang.JoinPoint;
import org.aspectj.lang.Signature;
import org.aspectj.lang.reflect.MethodSignature;
/**
* JoinPoint 工具类
* @author wl
* @date 2022/7/2 21:55
*/
public class JoinPointUtils {
public static <T> T getParamByName(JoinPoint joinPoint, String paramName, Class<T> clazz) {
// 获取所有参数的值
Object[] args = joinPoint.getArgs();
// 获取方法签名
Signature signature = joinPoint.getSignature();
MethodSignature methodSignature = (MethodSignature) signature;
// 在方法签名中获取所有参数的名称
String[] parameterNames = methodSignature.getParameterNames();
// 根据参数名称拿到下标, 参数值的数组和参数名称的数组下标是一一对应的
int index = ArrayUtils.indexOf(parameterNames, paramName);
// 在参数数组中取出下标对应参数值
Object obj = args[index];
if (obj == null) {
return null;
}
// 将object对象转为Class返回
if (clazz.isInstance(obj)) {
return clazz.cast(obj);
}
return (T) obj;
}
}接着编写@After的增强方法,在切点方法之后执行:
package com.wl.standard.aop.aspect;
import com.wl.standard.util.JoinPointUtils;
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
import org.apache.commons.lang.ArrayUtils;
import org.aspectj.lang.JoinPoint;
import org.aspectj.lang.ProceedingJoinPoint;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.*;
import org.aspectj.lang.reflect.MethodSignature;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
/**
* @author wl
* @date 2022/7/2 16:08
*/
@Slf4j
@Component
@Aspect
public class TestAspect {
@Pointcut("execution(public * com.wl.standard.service.TravelRecordService.getAllRecord(..))")
public void pointCut1(){};
@Pointcut("execution(public * com.wl.standard.service.CityRailService.getTopRail(..))")
public void pointCut2(){};
@Pointcut("execution(public * com.wl.standard.service.CityGdpService.compareGDP(..))")
public void pointCut3(){};
@Before("pointCut1()")
public void doBefore(JoinPoint joinPoint) {
log.info("当前线程: {} 开始执行查询前任务...", Thread.currentThread().getName());
}
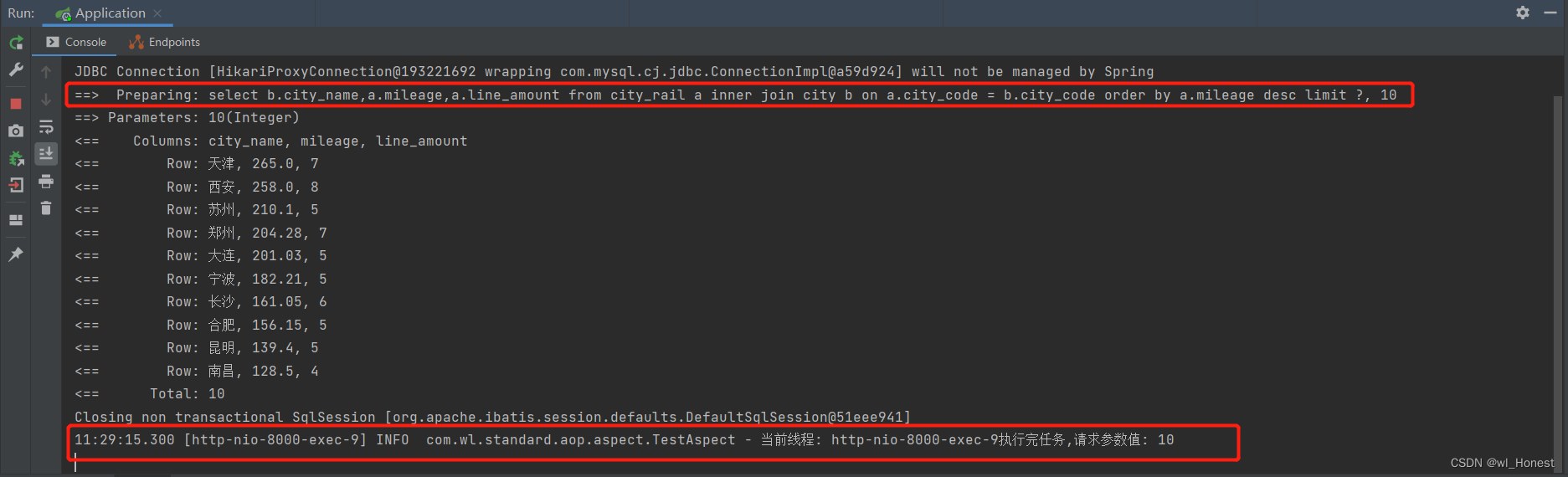
@After("pointCut2()")
public void doAfter(JoinPoint joinPoint) {
Integer index = JoinPointUtils.getParamByName(joinPoint, "index", Integer.class);
log.info("当前线程: {}执行完任务,请求参数值: {}", Thread.currentThread().getName(), index);
}
}为了方便理解这里获取的参数,下面放一下这里切入的方法:
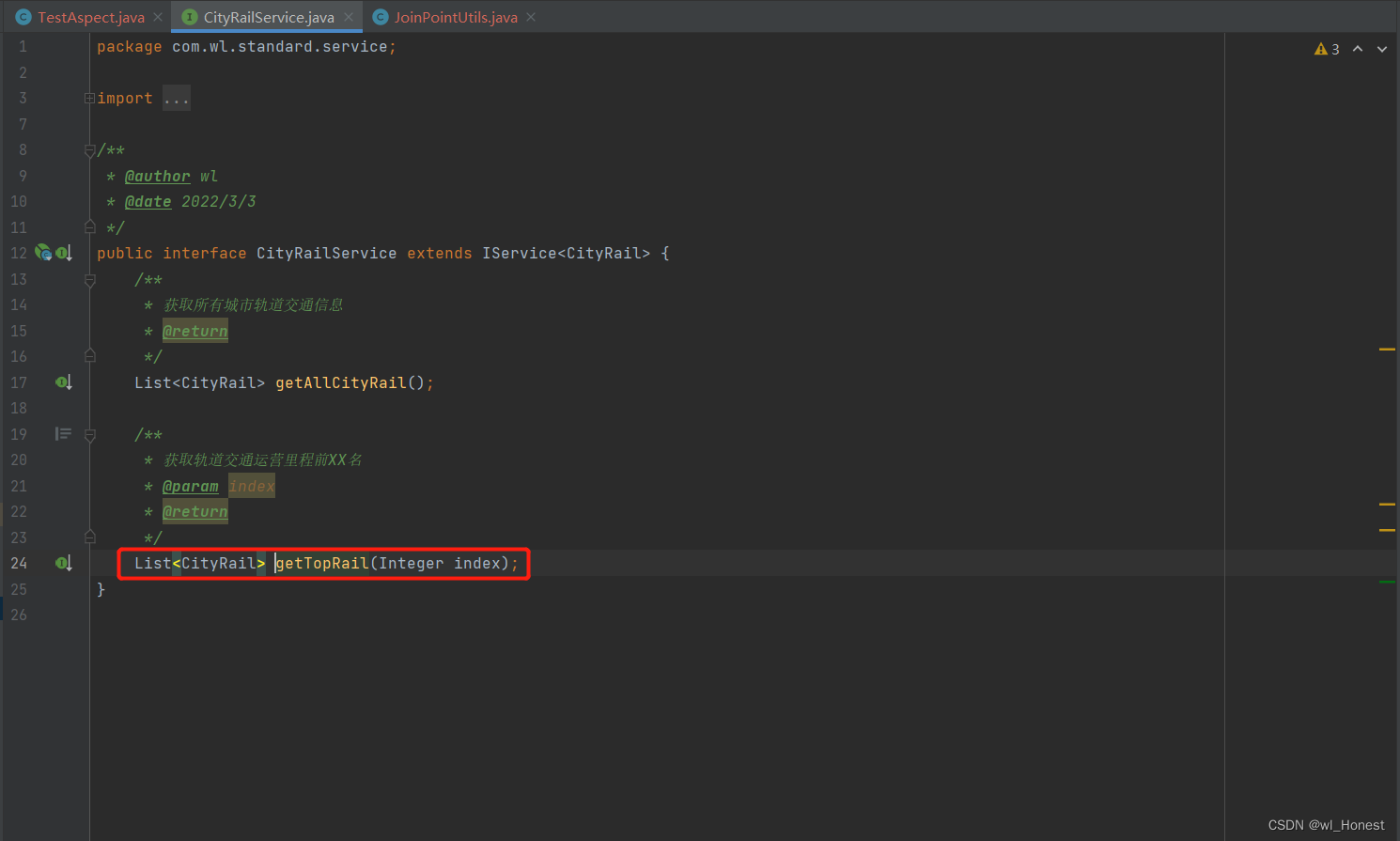
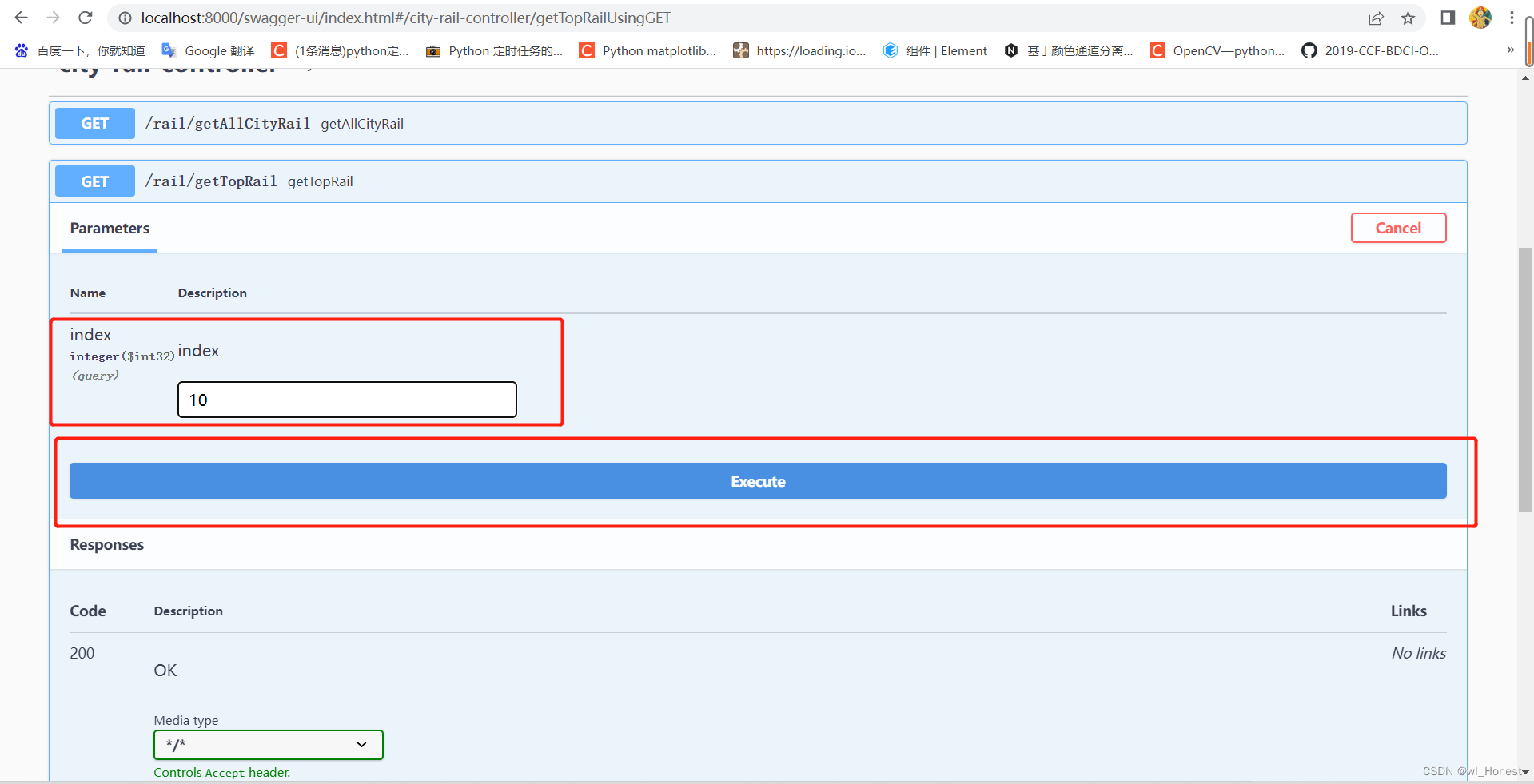
然后一样的流程,启动项目,在swagger页面里调用接口:
@Around
前面2个例子一个是在切点之前执行,一个是在切点之后执行,如果项目中我们想要记录一个sql执行的耗时时间,应该怎么做?
@Around环绕通知:它集成了@Before、@AfterReturing、@AfterThrowing、@After四大通知。需要注意的是,它和其他四大通知注解最大的不同是需要手动进行接口内方法的反射后才能执行接口中的方法,换言之,@Around其实就是一个动态代理。
利用@Around的话,就可以编写一个方法,切入多个切点记录耗时了:
package com.wl.standard.aop.aspect;
import com.wl.standard.util.JoinPointUtils;
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
import org.apache.commons.lang.ArrayUtils;
import org.aspectj.lang.JoinPoint;
import org.aspectj.lang.ProceedingJoinPoint;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.*;
import org.aspectj.lang.reflect.MethodSignature;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
/**
* @author wl
* @date 2022/7/2 16:08
*/
@Slf4j
@Component
@Aspect
public class TestAspect {
@Pointcut("execution(public * com.wl.standard.service.TravelRecordService.getAllRecord(..))")
public void pointCut1(){};
@Pointcut("execution(public * com.wl.standard.service.CityRailService.getTopRail(..))")
public void pointCut2(){};
@Pointcut("execution(public * com.wl.standard.service.CityGdpService.compareGDP(..))")
public void pointCut3(){};
@Before("pointCut1()")
public void doBefore(JoinPoint joinPoint) {
log.info("当前线程: {} 开始执行查询前任务...", Thread.currentThread().getName());
}
@After("pointCut2()")
public void doAfter(JoinPoint joinPoint) {
Integer index = JoinPointUtils.getParamByName(joinPoint, "index", Integer.class);
log.info("当前线程: {}执行完任务,请求参数值: {}", Thread.currentThread().getName(), index);
}
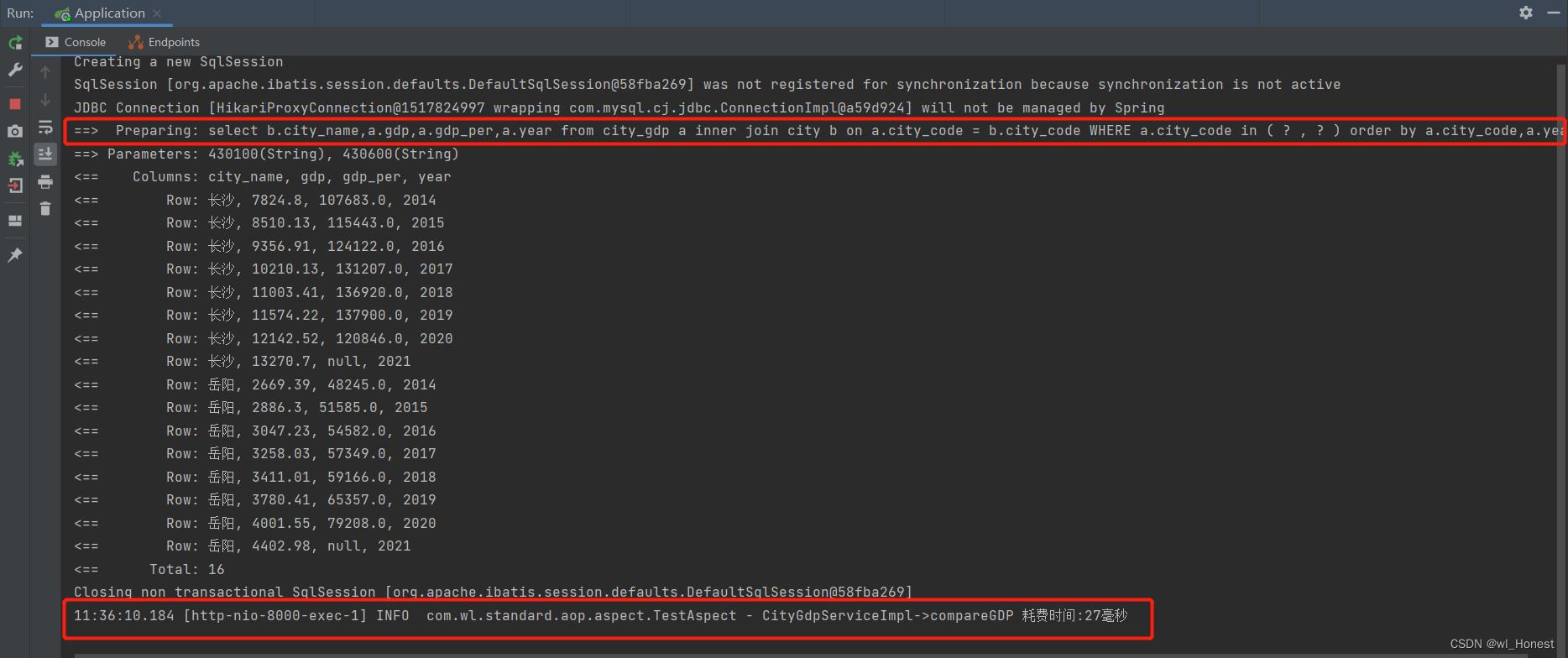
@Around("pointCut3()")
public Object doAround(ProceedingJoinPoint pjp) throws Throwable {
long start = System.currentTimeMillis();
// 调用执行目标方法(result为目标方法执行结果),必须有此行代码才会执行目标调用的方法(等价于@befor+@after),否则只会执行一次之前的(等价于@before)
Object result = pjp.proceed();
long end = System.currentTimeMillis();
log.info(pjp.getTarget().getClass().getSimpleName() + "->" + pjp.getSignature().getName() + " 耗费时间:" + (end - start) + "毫秒");
return result;
}
}启动项目,调用接口,看控制台输出:
加载全部内容