分布式医疗挂号系统数据字典模块前后端
Hudie. 人气:0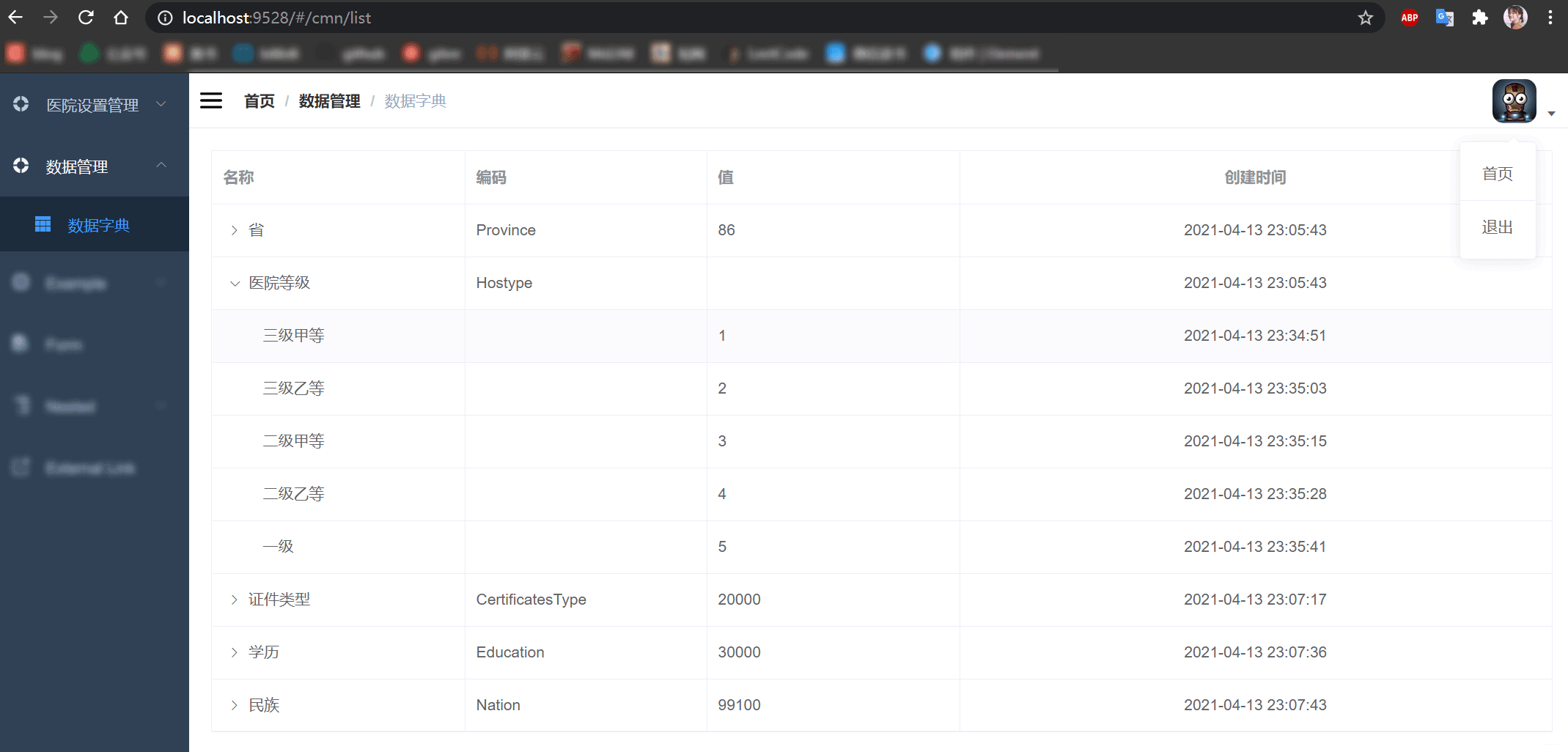
数据字典可以管理系统常用的分类数据或 固定数据,例如:省市区三级联动数据、民族数据、行业数据、学历数据等。由于我们的 分布式医疗挂号系统 大量使用这种数据,所有我们要做一个数据管理,方便管理系统数据,并且在一般的系统中基本都会做数据管理。
数据字典主要功能:使系统中的各项数据变的更加的严格,这样有利于降低因为数据问题而导致的bug。
一、后端接口
1.数据库表设计
数据字典的数据库表字段和对应的实体类的属性应该是一一对应的,但要注意下面两个地方:
添加上@TableLogic表示为逻辑删除,后续删除操作会自动变为修改操作。为了实现页面上单击展开子节点的功能,额外使用@TableField(exist = false)加入ha’s’Children属性。

2.编写三层调用
根据下图总结的三层调用关系,我们需要分别编写好Controlller层、Service层、Mapper层的代码。
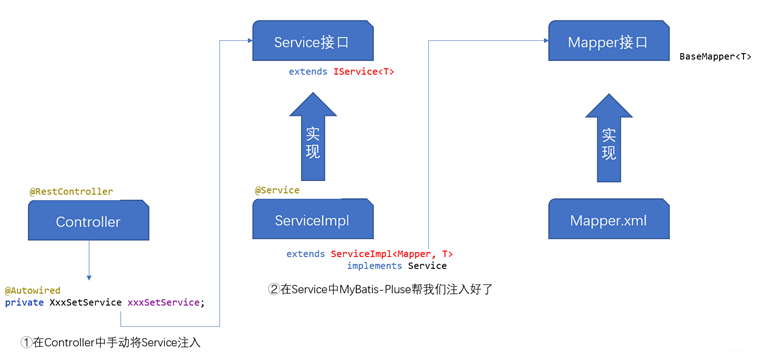
Controller层
通过url:/admin/cmn/dict/findChildData/{id} 访问资源到达控制层后,控制层调用服务层的findChildData(Long id)方法。
@Api(tags = "数据字典接口")
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/admin/cmn/dict")
@CrossOrigin
public class DictController {
@Autowired
private DictService dictService;
@ApiOperation(value = "根据id查询子数据列表")
@GetMapping("findChildData/{id}")
public Result findChildData(@PathVariable Long id) {
List<Dict> list = dictService.findChildData(id);
return Result.ok(list);
}
}
Service层
在服务层根据id查询子数据列表,调用数据层的查询方法查到子数据集合后,将集合遍历,遍历过程中为每条记录的hasChildren属性赋值。具体业务逻辑详见下面的代码:
Service接口继承IService<T>接口:
public interface DictService extends IService<Dict> {
/**
* 根据id查询子数据列表
* @param id
* @return list
*/
List<Dict> findChildData(Long id);
}
Service实现类继承ServiceImpl<TMapper, T>类:
@Service
public class DictServiceImpl extends ServiceImpl<DictMapper, Dict> implements DictService {
/**
* 根据id查询子数据列表
* @param id
* @return list
*/
@Override
public List<Dict> findChildData(Long id) {
QueryWrapper<Dict> queryWrapper = new QueryWrapper<>();
queryWrapper.eq("parent_id", id);
List<Dict> dictList = baseMapper.selectList(queryWrapper);
for (Dict dict : dictList) {
// 得到每一条记录的id值
Long dictId = dict.getId();
// 调用hasChildren方法判断是否包含子节点
boolean flag = this.hasChildren(dictId);
// 为每条记录设置hasChildren属性
dict.setHasChildren(flag);
}
return dictList;
}
/**
* 判断id下面是否有子结点
* @param id
* @return true:有子结点,false:无子结点
*/
private boolean hasChildren(Long id) {
QueryWrapper<Dict> queryWrapper = new QueryWrapper<>();
queryWrapper.eq("parent_id", id);
Integer count = baseMapper.selectCount(queryWrapper);
return count > 0;
}
}
Mapper层
Mapper接口继承了BaseMapper<T>接口。由于服务层调用的方法是BaseMapper自带的方法,所以在数据层,我们并没有给出具体的方法。
public interface DictMapper extends BaseMapper<Dict> {
}
由于在数据字典模块中配置类、配置文件不是我们主要研究的内容,所以这里不再给出,具体可参考github仓库代码。至此,数据字典模块的后端接口已经完成:

二、前端页面
1.添加路由
由于数据管理中的数据字典是一个全新的页面,我们可以将数据字典的路由设置为/cmn/list,路由到/cmn/list后,会跳转到/views/dict/list.js资源。
// 数据字典路由
{
path: '/cmn',
component: Layout,
redirect: '/cmn/list',
name: '数据管理',
meta: { title: '数据管理', icon: 'example' },
// 如果只有一级会仅显示子按钮,添加alwaysShow=true 可以使父按钮也显示
alwaysShow:true,
children: [
{
path: 'list',
name: '数据字典',
component: () => import('@/views/dict/list'),
meta: { title: '数据字典', icon: 'table' }
}
]
},
2.添加跳转页面
路由后,跳转到/views/dict/list.js页面,下面给出此页面的逻辑片段代码和其调用的api接口代码:
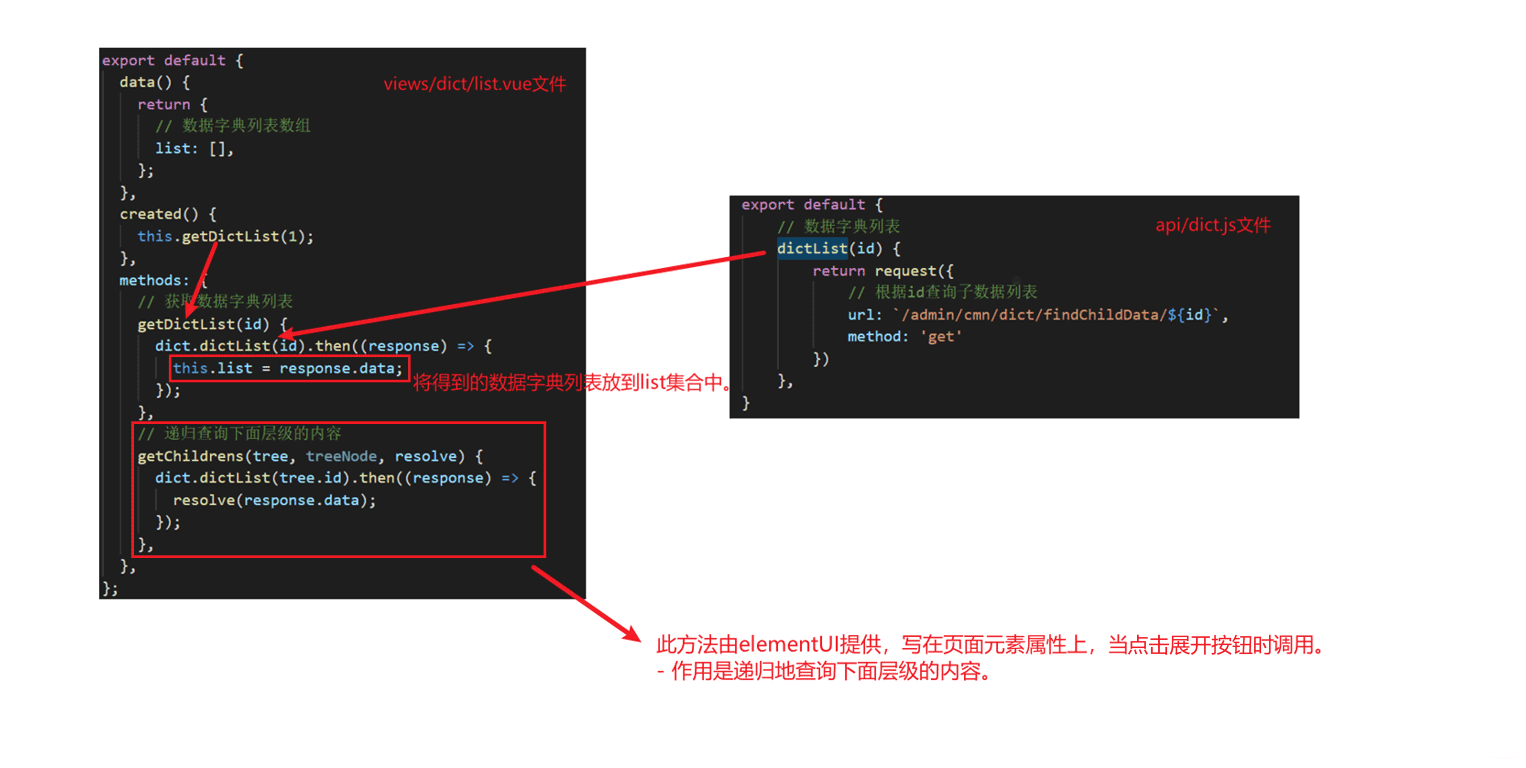
3.页面表格渲染
表格渲染我们使用elementUI提供开发文档:树形数据与懒加载表格组件。
修改后的代码如下:
:data=“list”
查出来的数据。
:load=“getChildrens”
加载getChildrens方法。
:tree-props="{ children: ‘children’, hasChildren: ‘hasChildren’ }"
树的属性值,通过属性值来判断hasChildren中的值是true还是false。
<template>
<div class="app-container">
<el-table
:data="list"
:load="getChildrens"
:tree-props="{ children: 'children', hasChildren: 'hasChildren' }"
style="width: 100%"
row-key="id"
border
lazy>
<el-table-column label="名称" width="230" align="left">
<template slot-scope="scope">
<span>{{ scope.row.name }}</span>
</template>
</el-table-column>
<el-table-column label="编码" width="220">
<template slot-scope="{ row }">
{{ row.dictCode }}
</template>
</el-table-column>
<el-table-column label="值" width="230" align="left">
<template slot-scope="scope">
<span>{{ scope.row.value }}</span>
</template>
</el-table-column>
<el-table-column label="创建时间" align="center">
<template slot-scope="scope">
<span>{{ scope.row.createTime }}</span>
</template>
</el-table-column>
</el-table>
</div>
</template>
三、标准Debug流程
目前数据字典模块的前后端已经开发完成了,但是此刻如果允许程序,页面并不会加载到后端传过来的数据。因为不同的访问请求访问到不同的服务器中,我们为数据字典模块设置端口是8202,而前端config/dev.env.js中,配置的是之前医院设置模块中的8201端口。
我们可以加入Nginx暂时解决,后期也会加入路由来替换掉Nginx,不过仅为了展示效果,这里简单的将前端 config/dev.env.js 中的端口改为和数据字典模块8202统一的端口。关于Nginx和添加统一路由会在后续的文章中进行介绍。
至此,数据字典模块的初步功能就已经实现完成了。
加载全部内容