Java并发的ABA问题
FserSuN 人气:01.简介
我们将了解在并发编程中的ABA问题。同时学习引起该问题的根因及问题解决办法。
2.Compare and swap
为了理解根本原因,首先回顾一下Compare and swap的概念。Compare and Swap (CAS)在无锁算法中是一种常见的技术。能够保证并发修改共享数据时,一个线程将共享内存修改后,另一线程尝试对共享内存的修改会失败。
我们每次更新时,通过两种信息来实现:要更新的值及原始值。首先Compare and swap 会比较原始值和当前获取到的值。如果相等,那么将值更新为要设置的值。
3. ABA问题
当执行campare and swap会出现失败的情况。例如,一个线程先读取共享内存数据值A,随后因某种原因,线程暂时挂起,同时另一个线程临时将共享内存数据值先改为B,随后又改回为A。随后挂起线程恢复,并通过CAS比较,最终比较结果将会无变化。这样会通过检查,这就是ABA问题。 在CAS比较前会读取原始数据,随后进行原子CAS操作。这个间隙之间由于并发操作,最终可能会带来问题。
3.1 ABA问题的实际场景:账户余额修改
为了通过实例演示ABA问题。我们创建一个银行账户类,该类维护一个整型变量记录账户余额。该类有两个函数:一个用于存钱,一个用于取钱。这些操作使用CAS来修改账户余额。
3.2 账户余额修改时产生的问题
我们来考虑两个线程操作同一个账户时的场景。当线程1取钱时,先读取余额,随后通过CAS操作进行比较。然后,可能由于某些原因,线程1可能发生阻塞。与此同时,线程2同样通过CAS机制,在线程1挂起时,在同一个账户上执行两个操作。首先,改变原始值,这个值已经被线程1在刚才读取。随后线程2又将这个值改为原始值。
一旦线程1恢复后,在线程1看来,没有发生任何变化。cas将会执行成功。
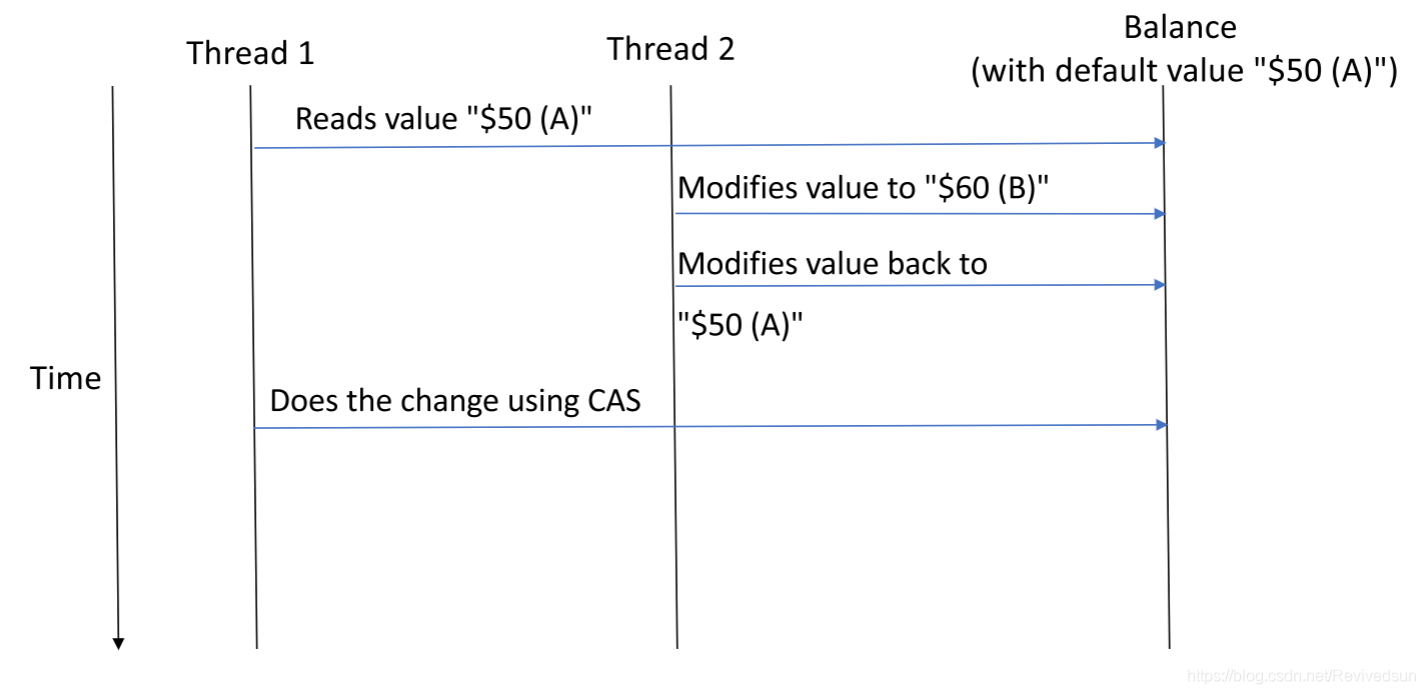
4.银行取款问题代码演示
创建一个Account类,balance记录账户余额。transactionCount记录成功执行的事务数。currentThreadCASFailureCount来记录CAS操作失败的次数。
接着我们实现一个存款的方法deposit,与取款方法withdraw。为了演示ABA问题,同时实现一个maybeWait方法进行延迟等待。
最终的代码如下:
public class Account {
private AtomicInteger balance;
private AtomicInteger transactionCount;
private ThreadLocal<Integer> currentThreadCASFailureCount;
public Account() {
this.balance = new AtomicInteger(0);
this.transactionCount = new AtomicInteger(0);
this.currentThreadCASFailureCount = new ThreadLocal<>();
this.currentThreadCASFailureCount.set(0);
}
public int getBalance() {
return balance.get();
}
public int getTransactionCount() {
return transactionCount.get();
}
public int getCurrentThreadCASFailureCount() {
return Optional.ofNullable(currentThreadCASFailureCount.get()).orElse(0);
}
public boolean withdraw(int amount) {
int current = getBalance();
maybeWait();
boolean result = balance.compareAndSet(current, current - amount);
if (result) {
transactionCount.incrementAndGet();
} else {
int currentCASFailureCount = currentThreadCASFailureCount.get();
currentThreadCASFailureCount.set(currentCASFailureCount + 1);
}
return result;
}
private void maybeWait() {
if ("thread1".equals(Thread.currentThread().getName())) {
try {
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(2);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
Thread.currentThread().interrupt();
}
}
}
public boolean deposit(int amount) {
int current = balance.get();
boolean result = balance.compareAndSet(current, current + amount);
if (result) {
transactionCount.incrementAndGet();
} else {
int currentCASFailureCount = currentThreadCASFailureCount.get();
currentThreadCASFailureCount.set(currentCASFailureCount + 1);
}
return result;
}
}
接着我们对上述代码进行测试。通过maybeWait方法,模拟出现ABA问题。
@Test
public void abaProblemTest() throws InterruptedException {
final int defaultBalance = 50;
final int amountToWithdrawByThread1 = 20;
final int amountToWithdrawByThread2 = 10;
final int amountToDepositByThread2 = 10;
Assert.assertEquals(0, account.getTransactionCount());
Assert.assertEquals(0, account.getCurrentThreadCASFailureCount());
account.deposit(defaultBalance);
Assert.assertEquals(1, account.getTransactionCount());
Thread thread1 = new Thread(() -> {
// this will take longer due to the name of the thread
Assert.assertTrue(account.withdraw(amountToWithdrawByThread1));
// thread 1 fails to capture ABA problem
Assert.assertNotEquals(1, account.getCurrentThreadCASFailureCount());
}, "thread1");
Thread thread2 = new Thread(() -> {
Assert.assertTrue(account.deposit(amountToDepositByThread2));
Assert.assertEquals(defaultBalance + amountToDepositByThread2, account.getBalance());
// this will be fast due to the name of the thread
Assert.assertTrue(account.withdraw(amountToWithdrawByThread2));
// thread 1 didn't finish yet, so the original value will be in place for it
Assert.assertEquals(defaultBalance, account.getBalance());
Assert.assertEquals(0, account.getCurrentThreadCASFailureCount());
}, "thread2");
thread1.start();
thread2.start();
thread1.join();
thread2.join();
// compareAndSet operation succeeds for thread 1
Assert.assertEquals(defaultBalance - amountToWithdrawByThread1, account.getBalance());
//but there are other transactions
Assert.assertNotEquals(2, account.getTransactionCount());
// thread 2 did two modifications as well
Assert.assertEquals(4, account.getTransactionCount());
}
5.值类型与引用类型的场景
上面的例子中使用了getBalance()方法获取了一个值类型数据。由于使用的是值类型,虽然出现ABA问题,但未对结果造成影响。如果我们操作的是引用类型,那么最终会保存不同的引用对象,会带来意外的结果。
对于引用类型,下面以链栈为例说明。
- 线程A希望将A结点出栈,此时读取栈顶元素A,准备执行CAS操作,此时由于某种原因阻塞。
- 线程B开始执行,执行出栈A、B。随后将D、C、A结点压入栈中。
- 线程A恢复执行。接着执行CAS,比较发现栈顶结点A没有被修改。随后将栈顶结点改为B。由于B线程在第二步时,已经将B结点移除,A线程修改后发生错误。栈的结构发生破坏。
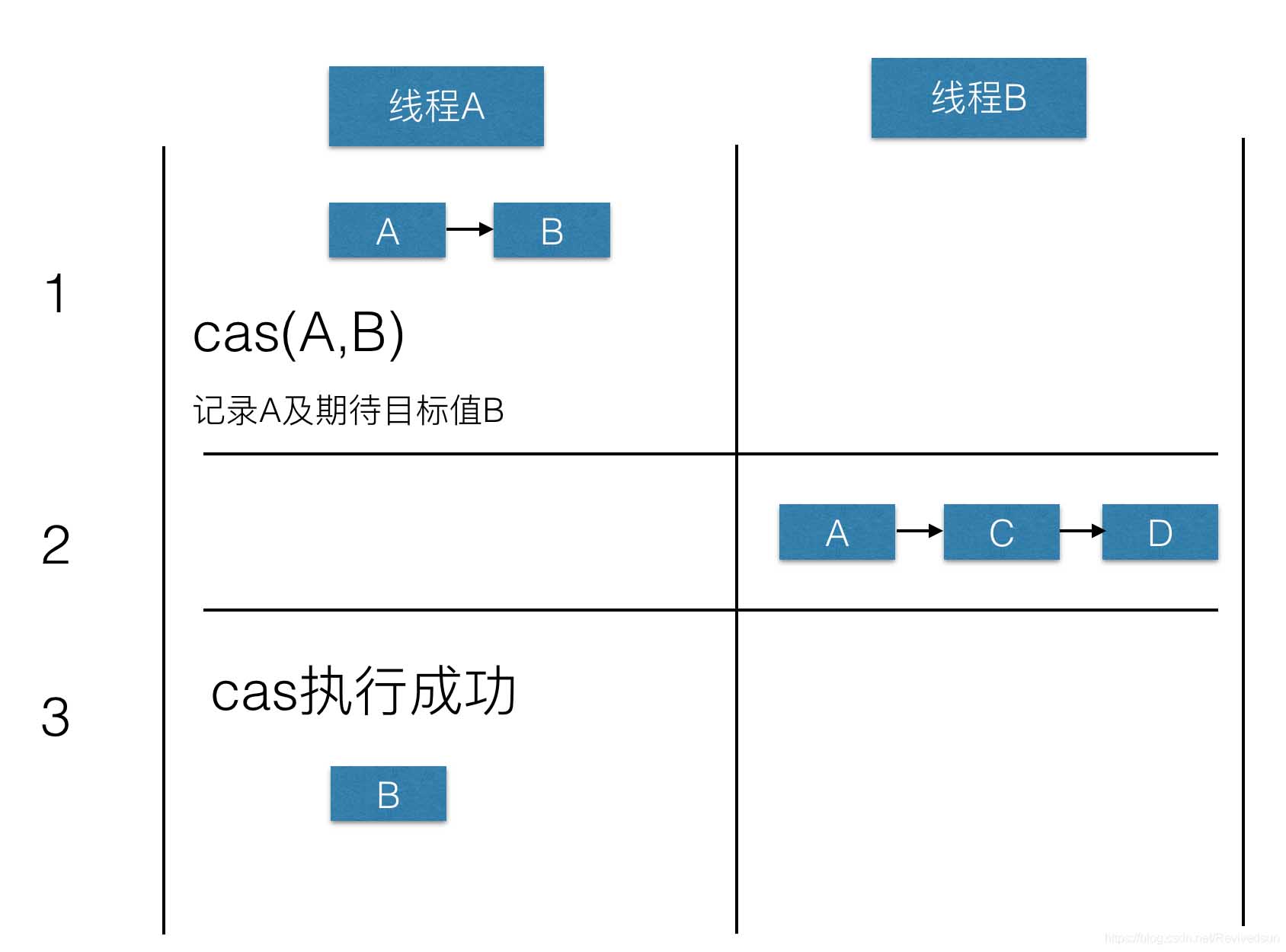
接着我们通过下面的代码进行演示:
static class Stack {
private AtomicReference<Node> top = new AtomicReference<>();
static class Node {
String value;
Node next;
public Node (String value) {
this.value = value;
}
}
//出栈
public Node pop(int time) {
Node newTop;
Node oldTop;
do {
oldTop = top.get();
if (oldTop == null) {
return null;
}
newTop = oldTop.next;
try {
//休眠一段时间,模拟ABA问题
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(time);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
} while (!top.compareAndSet(oldTop, newTop));
return oldTop;
}
public void push (Node node) {
Node oldTop;
do {
oldTop = top.get();
node.next = oldTop;
} while (!top.compareAndSet(oldTop, node));
}
public AtomicReference<Node> getTop() {
return top;
}
}
@Test
public void testStack() throws Exception{
Stack stack = new Stack();
Stack.Node a = new Stack.Node("A");
Stack.Node b = new Stack.Node("B");
// 初始化栈结构
stack.push(b);
stack.push(a);
// ABA 测试
Thread t1 = new Thread(() -> {
stack.pop(2);
});
Stack.Node c = new Stack.Node("C");
Stack.Node d = new Stack.Node("D");
Thread t2 = new Thread(() -> {
stack.pop(0);
stack.pop(0);
stack.push(d);
stack.push(c);
stack.push(a);
});
//
t1.start();
t2.start();
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(5);
Stack.Node top = stack.getTop().get();
do {
System.out.println(top.value);
top = top.next;
} while (top != null);
}
6. 解决方法
- hazard pointer:首先出现问题是因为,多个线程操作共享数据,并未感知到别的线程正在对共享数据进行操作。通过hazard pointer介绍[1],其基本思想就是每个线程维护一个操作列表,在操作一个结点时将其记录。如果一个线程要做结点变更,先搜索线程操作列表,看是否有其它线程操作。如果有则此次操作执行失败。
- 不变性:从上述栈的例子中可以看到,在对结点A进行比较时,由于A依然是多个线程共享并复用,因此CAS会成功。如果每次操作时,新创建对象而不是复用。这样CAS就会正常提示失败。但这样可能会创建大量对象。
7. Java中的解决方法
Java中提供了两个类来解决这个问题。
AtomicStampedReferenceAtomicMarkableReference
在原有类的基础上,除了比较与修改期待的值外,增加了一个时间戳。对时间戳也进行CAS操作。这也称为双重CAS。从上例中看到。每次修改一个结点,其时间戳都发生变化。这样即使共享一个复用结点,最终CAS也能返回正常的结果。
8. 总结
本文介绍了CAS产生ABA问题的背景,通用解决办法及Java中的解决办法。对于值类型有时发生ABA问题可能并不会造成问题。但对于引用类型,就可能造成歧义,同时破坏数据结构。通过链栈的演示,我们可以有所了解ABA产生的问题。
以上为个人经验,希望能给大家一个参考,也希望大家多多支持。
加载全部内容