Redis项目中使用
HongMaJu 人气:0springboot中redis相关配置
1、pom.xml中引入依赖
<dependency> <groupId>redis.clients</groupId> <artifactId>jedis</artifactId> <version>2.9.0</version> </dependency>
2、springboot的习惯优于配置。也在项目中使用了application.yml文件配置mysql的基本配置项。这里也在application.yml里面配置redis的配置项。
spring:
datasource:
# 驱动配置信息
url: jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/spring_boot?useUnicode=true&characterEncoding=utf8
username: root
password: root
type: com.alibaba.druid.pool.DruidDataSource
driver-class-name: com.mysql.jdbc.Driver
# 连接池的配置信息
filters: stat
maxActive: 20
initialSize: 1
maxWait: 60000
minIdle: 1
timeBetweenEvictionRunsMillis: 60000
minEvictableIdleTimeMillis: 300000
validationQuery: select 'x'
testWhileIdle: true
testOnBorrow: false
testOnReturn: false
poolPreparedStatements: true
maxOpenPreparedStatements: 20
redis:
host: 127.0.0.1
port: 6379
password: pass1234
pool:
max-active: 100
max-idle: 10
max-wait: 100000
timeout: 0
springboot中redis相关类
- 项目操作redis是使用的RedisTemplate方式,另外还可以完全使用JedisPool和Jedis来操作redis。整合的内容也是从网上收集整合而来,网上整合的方式和方法非常的多,有使用注解形式的,有使用Jackson2JsonRedisSerializer来序列化和反序列化key value的值等等,很多很多。这里使用的是我认为比较容易理解和掌握的,基于JedisPool配置,使用RedisTemplate来操作redis的方式。
redis单独放在一个包redis里,在包里先创建RedisConfig.java文件。
RedisConfig.java
@Configuration
@EnableAutoConfiguration
public class RedisConfig {
@Bean
@ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "spring.redis.pool")
public JedisPoolConfig getRedisConfig(){
JedisPoolConfig config = new JedisPoolConfig();
return config;
}
@Bean
@ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "spring.redis")
public JedisConnectionFactory getConnectionFactory() {
JedisConnectionFactory factory = new JedisConnectionFactory();
factory.setUsePool(true);
JedisPoolConfig config = getRedisConfig();
factory.setPoolConfig(config);
return factory;
}
@Bean
public RedisTemplate<?, ?> getRedisTemplate() {
JedisConnectionFactory factory = getConnectionFactory();
RedisTemplate<?, ?> template = new StringRedisTemplate(factory);
return template;
}
}
- 在包里创建RedisService接口的实现类RedisServiceImpl,这个类实现了接口的所有方法。
RedisServiceImpl.java
@Service("redisService")
public class RedisServiceImpl implements RedisService {
@Resource
private RedisTemplate<String, ?> redisTemplate;
@Override
public boolean set(final String key, final String value) {
boolean result = redisTemplate.execute(new RedisCallback<Boolean>() {
@Override
public Boolean doInRedis(RedisConnection connection) throws DataAccessException {
RedisSerializer<String> serializer = redisTemplate.getStringSerializer();
connection.set(serializer.serialize(key), serializer.serialize(value));
return true;
}
});
return result;
}
@Override
public String get(final String key) {
String result = redisTemplate.execute(new RedisCallback<String>() {
@Override
public String doInRedis(RedisConnection connection) throws DataAccessException {
RedisSerializer<String> serializer = redisTemplate.getStringSerializer();
byte[] value = connection.get(serializer.serialize(key));
return serializer.deserialize(value);
}
});
return result;
}
@Override
public boolean expire(final String key, long expire) {
return redisTemplate.expire(key, expire, TimeUnit.SECONDS);
}
@Override
public boolean remove(final String key) {
boolean result = redisTemplate.execute(new RedisCallback<Boolean>() {
@Override
public Boolean doInRedis(RedisConnection connection) throws DataAccessException {
RedisSerializer<String> serializer = redisTemplate.getStringSerializer();
connection.del(key.getBytes());
return true;
}
});
return result;
}
}
在这里execute()方法具体的底层没有去研究,只知道这样能实现对于redis数据的操作。
redis保存的数据会在内存和硬盘上存储,所以需要做序列化;这个里面使用的StringRedisSerializer来做序列化,不过这个方式的泛型指定的是String,只能传String进来。所以项目中采用json字符串做redis的交互。
到此,redis在springboot中的整合已经完毕,下面就来测试使用一下。
5. springboot项目中使用redis
在这里就直接使用springboot项目中自带的单元测试类SpringbootApplicationTests进行测试。
@RunWith(SpringRunner.class)
@SpringBootTest
public class SpringbootApplicationTests {
private JSONObject json = new JSONObject();
@Autowired
private RedisService redisService;
@Test
public void contextLoads() throws Exception {
}
/**
* 插入字符串
*/
@Test
public void setString() {
redisService.set("redis_string_test", "springboot redis test");
}
/**
* 获取字符串
*/
@Test
public void getString() {
String result = redisService.get("redis_string_test");
System.out.println(result);
}
/**
* 插入对象
*/
@Test
public void setObject() {
Person person = new Person("person", "male");
redisService.set("redis_obj_test", json.toJSONString(person));
}
/**
* 获取对象
*/
@Test
public void getObject() {
String result = redisService.get("redis_obj_test");
Person person = json.parseObject(result, Person.class);
System.out.println(json.toJSONString(person));
}
/**
* 插入对象List
*/
@Test
public void setList() {
Person person1 = new Person("person1", "male");
Person person2 = new Person("person2", "female");
Person person3 = new Person("person3", "male");
List<Person> list = new ArrayList<>();
list.add(person1);
list.add(person2);
list.add(person3);
redisService.set("redis_list_test", json.toJSONString(list));
}
/**
* 获取list
*/
@Test
public void getList() {
String result = redisService.get("redis_list_test");
List<String> list = json.parseArray(result, String.class);
System.out.println(list);
}
@Test
public void remove() {
redisService.remove("redis_test");
}
}
class Person {
private String name;
private String sex;
public Person() {
}
public Person(String name, String sex) {
this.name = name;
this.sex = sex;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public String getSex() {
return sex;
}
public void setSex(String sex) {
this.sex = sex;
}
}
在这里先是用@Autowired注解把redisService注入进来,然后由于是使用json字符串进行交互,所以引入fastjson的JSONObject类。然后为了方便,直接在这个测试类里面加了一个Person的内部类。
一共测试了:对于string类型的存取,对于object类型的存取,对于list类型的存取,其实本质都是转成了json字符串。还有就是根据key来执行remove操作。
获取字符串:
获取对象:
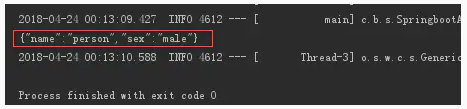
获取list:

redis管理客户端数据:
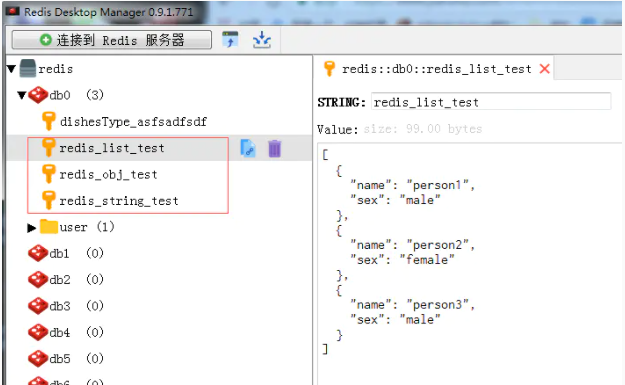
到此,测试完成,对于常用的一些数据类型的转换存取操作也基本调试通过。所以本文对于springboot整合redis到此结束。
加载全部内容