Python获取天气信息
Huterox 人气:0前言
本来是想要更新scrapy的,但是怎么说呢,这玩意不难,看着官方文档,基本上就能做,主要是前面的如果你的爬虫基础不好的话,这个scrapy你也玩不好,而且对于大部分的人来说安装scrapy可能都是个问题,因为有一些历史遗留的问题,毕竟是从python2过来的老框架。当然还有个原因,我要做的东西,用不上scrapy,能够用上scrapy如果只是做爬虫,那必然是分布式爬虫,但是我这里要做的可能只是一个客户端,也就是一个spider采集软件,所以这个scrapy没法上。
目标
今天我们要搞的是获取天气,用的API是中国天气网。
BaseUrl = "http://wthrcdn.etouch.cn/weather_mini?city={}"网上呢也有很多,那个直接爬取中国天气网的爬虫,但是我就是搞不懂,为啥非要去网页里面然后去xpath或者正则去搞,明明用的都是同一个api出来的数据,我为啥要去页面把人家渲染后的结果去反向解析出数据?我直接拿数据不好嘛?
请求格式
回到这里,咱们的这个接口呢,是一个get请求,然后的话,那啥只需要把城市或者编号放在city那个字段就行了,返回结果是个json,我们把这玩意变成字典后是这样的
{'data':
{'yesterday':
{'date': '5日星期六', 'high': '高温 16℃', 'fx': '东北风', 'low': '低温 9℃', 'fl': '<![CDATA[3级]]>', 'type': '多云'},
'city': '九江',
'forecast': [{'date': '6日星期天', 'high': '高温 12℃', 'fengli': '<![CDATA[3级]]>', 'low': '低温 7℃', 'fengxiang': '东北风', 'type': '中雨'},
{'date': '7日星期一', 'high': '高温 14℃', 'fengli': '<![CDATA[2级]]>', 'low': '低温 7℃', 'fengxiang': '北风', 'type': '多云'},
{'date': '8日星期二', 'high': '高温 19℃', 'fengli': '<![CDATA[2级]]>', 'low': '低温 8℃', 'fengxiang': '东南风', 'type': '晴'},
{'date': '9日星期三', 'high': '高温 21℃', 'fengli': '<![CDATA[2级]]>', 'low': '低温 11℃', 'fengxiang': '东南风', 'type': '晴'},
{'date': '10日星期四', 'high': '高温 23℃', 'fengli': '<![CDATA[1级]]>', 'low': '低温 11℃', 'fengxiang': '南风', 'type': '多云'}
],
'ganmao': '感冒多发期,适当减少外出频率,适量补充水分,适当增减衣物。', 'wendu': '8'}, 'status': 1000, 'desc': 'OK'}请求限制
这里不得不说一下,中国天气网 yyds 这个接口完全没有限制。为啥,我要做的是获取全国的天气信息,包括县城,中国大大小小几千个县城,而且还要分时段去分析,所以每天的请求访问至少2w起步。如果有限制的话,咱们就得那啥反反爬了,但是通过我的测试,没问题。
requests非异步获取
来,我们来先做一个对比,没有对比就没有伤害是吧,由于非常简单我就直接上代码了。
import requests
from datetime import datetime
class GetWeather(object):
urlWheather = "http://wthrcdn.etouch.cn/weather_mini?city={}"
requests = requests
error = {}
today = datetime.today().day
weekday = datetime.today().weekday()
week = {0:"星期一",1:"星期二",2:"星期三",3:"星期四",4:"星期五",5:"星期六",6:"星期天"}
def __getday(self)->str:
day = str(self.today)+"日"+self.week.get(self.weekday)
return day
def get_today_wheather(self,city:str)->dict:
data = self.getweather(city)
data = data.get("data").get("forecast")
today = self.__getday()
for today_w in data:
if(today_w.get("date")==today):
return today_w
def getweather(self,city:str,timeout:int=3)->dict:
url = self.urlWheather.format(city)
try:
resp = self.requests.get(url,timeout=timeout)
jsondata = resp.json()
return jsondata
except Exception as e:
self.error['error'] = "天气获取异常"
return self.error
def getweathers(self,citys:list,timeout:int=3):
wheathers_data = {}
for city in citys:
url = self.urlWheather.format(city)
try:
resp = self.requests.get(url=url,timeout=timeout)
wheather_data = resp.json()
wheathers_data[city]=wheather_data
except Exception as e:
self.error['error'] = "天气获取异常"
return self.error
return wheathers_data
if __name__ == '__main__':
getwheather = GetWeather()
start = time.time()
times = 1
for i in range(5000):
data = getwheather.get_today_wheather("九江")
if((times%100==0)):
print(data,"第",times,"次访问")
times+=1
print("访问",times,"次耗时",time.time()-start,"秒")这段代码呢,我做了一个简单的封装。 我们来看看结果,5000次访问花了多久

这里我5000次重复访问的是同一个城市 九江
异步获取
这个代码的话我是没有封装的,所以看起来比较乱。 这里有几个注意点先说一下
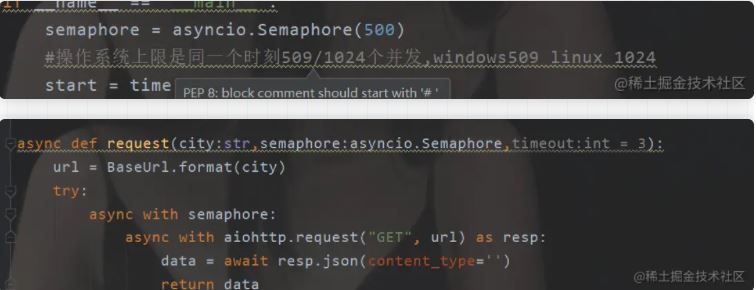
系统上限
由于这个,异步的话还是使用的操作系统的一个底层嘛,所以这个并发是有上限的,因为这个协程异步是要不断切换的是吧。看起来有点像python自己的多线程,只是这个“多线程”完全是当IO的时候才会切换,不然不会切换。 所以哟啊限制一下
编码
import time
import aiohttp
from datetime import datetime
import asyncio
BaseUrl = "http://wthrcdn.etouch.cn/weather_mini?city={}"
WeekIndex = {0:"星期一",1:"星期二",2:"星期三",3:"星期四",4:"星期五",5:"星期六",6:"星期天"}
today = datetime.today().day
day = str(today)+"日"+WeekIndex.get(datetime.today().weekday())
TIMES = 0
async def request(city:str,semaphore:asyncio.Semaphore,timeout:int = 3):
url = BaseUrl.format(city)
try:
async with semaphore:
async with aiohttp.request("GET", url) as resp:
data = await resp.json(content_type='')
return data
except Exception as e:
raise e
def getwheater(task):
data = task.result()
return data
def get_today_weather(task):
global TIMES
data = task.result() #得到返回结果
data = data.get("data").get("forecast")
for today_w in data:
if (today_w.get("date") == day):
TIMES+=1#只有IO操作的时候才会切换,所以这个++操作还是一个原子性操作
if(TIMES%100==0):
print(today_w,"第",TIMES,"次访问")
return today_w
if __name__ == '__main__':
semaphore = asyncio.Semaphore(500)
#操作系统上限是同一个时刻509/1024个并发,windows509 linux 1024
start = time.time()
tasks = []
for i in range(5000):
c = request("九江",semaphore,3)
task = asyncio.ensure_future(c)
task.add_done_callback(get_today_weather)
tasks.append(task)
loop = asyncio.get_event_loop()
loop.run_until_complete(asyncio.wait(tasks))
print("耗时",time.time() - start,"秒")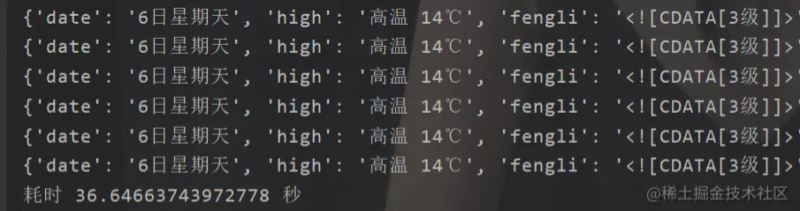
加载全部内容