pandas数据合并与拼接 pandas数据的合并与拼接的实现
石头 人气:0Pandas包的merge、join、concat方法可以完成数据的合并和拼接,merge方法主要基于两个dataframe的共同列进行合并,join方法主要基于两个dataframe的索引进行合并,concat方法是对series或dataframe进行行拼接或列拼接。
1. Merge方法
pandas的merge方法是基于共同列,将两个dataframe连接起来。merge方法的主要参数:
- left/right:左/右位置的dataframe。
- how:数据合并的方式。left:基于左dataframe列的数据合并;right:基于右dataframe列的数据合并;outer:基于列的数据外合并(取并集);inner:基于列的数据内合并(取交集);默认为'inner'。
- on:用来合并的列名,这个参数需要保证两个dataframe有相同的列名。
- left_on/right_on:左/右dataframe合并的列名,也可为索引,数组和列表。
- left_index/right_index:是否以index作为数据合并的列名,True表示是。
- sort:根据dataframe合并的keys排序,默认是。
- suffixes:若有相同列且该列没有作为合并的列,可通过suffixes设置该列的后缀名,一般为元组和列表类型。
merges通过设置how参数选择两个dataframe的连接方式,有内连接,外连接,左连接,右连接,下面通过例子介绍连接的含义。
1.1 内连接
how='inner',dataframe的链接方式为内连接,我们可以理解基于共同列的交集进行连接,参数on设置连接的共有列名。
# 单列的内连接
# 定义df1
import pandas as pd
import numpy as np
df1 = pd.DataFrame({'alpha':['A','B','B','C','D','E'],'feature1':[1,1,2,3,3,1],
'feature2':['low','medium','medium','high','low','high']})
# 定义df2
df2 = pd.DataFrame({'alpha':['A','A','B','F'],'pazham':['apple','orange','pine','pear'],
'kilo':['high','low','high','medium'],'price':np.array([5,6,5,7])})
# print(df1)
# print(df2)
# 基于共同列alpha的内连接
df3 = pd.merge(df1,df2,how='inner',on='alpha')
df3

取共同列alpha值的交集进行连接。
1.2 外连接
how='outer',dataframe的链接方式为外连接,我们可以理解基于共同列的并集进行连接,参数on设置连接的共有列名。
# 单列的外连接
# 定义df1
df1 = pd.DataFrame({'alpha':['A','B','B','C','D','E'],'feature1':[1,1,2,3,3,1],
'feature2':['low','medium','medium','high','low','high']})
# 定义df2
df2 = pd.DataFrame({'alpha':['A','A','B','F'],'pazham':['apple','orange','pine','pear'],
'kilo':['high','low','high','medium'],'price':np.array([5,6,5,7])})
# 基于共同列alpha的内连接
df4 = pd.merge(df1,df2,how='outer',on='alpha')
df4

若两个dataframe间除了on设置的连接列外并无相同列,则该列的值置为NaN。
1.3 左连接
how='left',dataframe的链接方式为左连接,我们可以理解基于左边位置dataframe的列进行连接,参数on设置连接的共有列名。
# 单列的左连接
# 定义df1
df1 = pd.DataFrame({'alpha':['A','B','B','C','D','E'],'feature1':[1,1,2,3,3,1],
'feature2':['low','medium','medium','high','low','high']})
# 定义df2
df2 = pd.DataFrame({'alpha':['A','A','B','F'],'pazham':['apple','orange','pine','pear'],
'kilo':['high','low','high','medium'],'price':np.array([5,6,5,7])})
# 基于共同列alpha的左连接
df5 = pd.merge(df1,df2,how='left',on='alpha')
df5
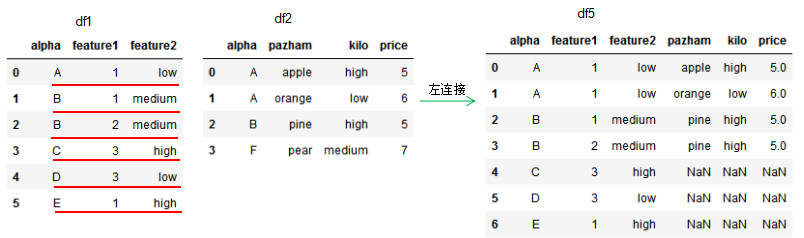
因为df2的连接列alpha有两个'A'值,所以左连接的df5有两个'A'值,若两个dataframe间除了on设置的连接列外并无相同列,则该列的值置为NaN。
1.4 右连接
how='right',dataframe的链接方式为左连接,我们可以理解基于右边位置dataframe的列进行连接,参数on设置连接的共有列名。
# 单列的右连接
# 定义df1
df1 = pd.DataFrame({'alpha':['A','B','B','C','D','E'],'feature1':[1,1,2,3,3,1],
'feature2':['low','medium','medium','high','low','high']})
# 定义df2
df2 = pd.DataFrame({'alpha':['A','A','B','F'],'pazham':['apple','orange','pine','pear'],
'kilo':['high','low','high','medium'],'price':np.array([5,6,5,7])})
# 基于共同列alpha的右连接
df6 = pd.merge(df1,df2,how='right',on='alpha')
df6
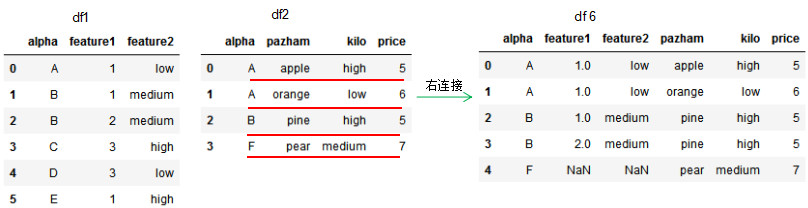
因为df1的连接列alpha有两个'B'值,所以右连接的df6有两个'B'值。若两个dataframe间除了on设置的连接列外并无相同列,则该列的值置为NaN。
1.5 基于多列的连接算法
多列连接的算法与单列连接一致,本节只介绍基于多列的内连接和右连接,读者可自己编码并按照本文给出的图解方式去理解外连接和左连接。
多列的内连接:
# 多列的内连接
# 定义df1
df1 = pd.DataFrame({'alpha':['A','B','B','C','D','E'],'beta':['a','a','b','c','c','e'],
'feature1':[1,1,2,3,3,1],'feature2':['low','medium','medium','high','low','high']})
# 定义df2
df2 = pd.DataFrame({'alpha':['A','A','B','F'],'beta':['d','d','b','f'],'pazham':['apple','orange','pine','pear'],
'kilo':['high','low','high','medium'],'price':np.array([5,6,5,7])})
# 基于共同列alpha和beta的内连接
df7 = pd.merge(df1,df2,on=['alpha','beta'],how='inner')
df7
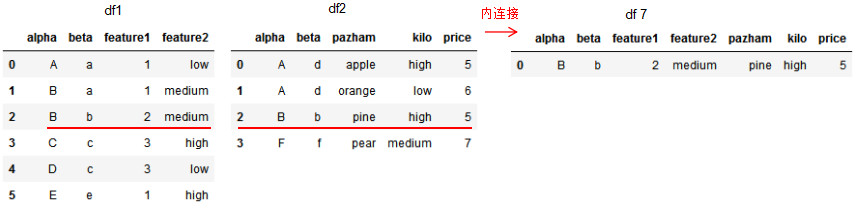
多列的右连接:
# 多列的右连接
# 定义df1
df1 = pd.DataFrame({'alpha':['A','B','B','C','D','E'],'beta':['a','a','b','c','c','e'],
'feature1':[1,1,2,3,3,1],'feature2':['low','medium','medium','high','low','high']})
# 定义df2
df2 = pd.DataFrame({'alpha':['A','A','B','F'],'beta':['d','d','b','f'],'pazham':['apple','orange','pine','pear'],
'kilo':['high','low','high','medium'],'price':np.array([5,6,5,7])})
print(df1)
print(df2)
# 基于共同列alpha和beta的右连接
df8 = pd.merge(df1,df2,on=['alpha','beta'],how='right')
df8
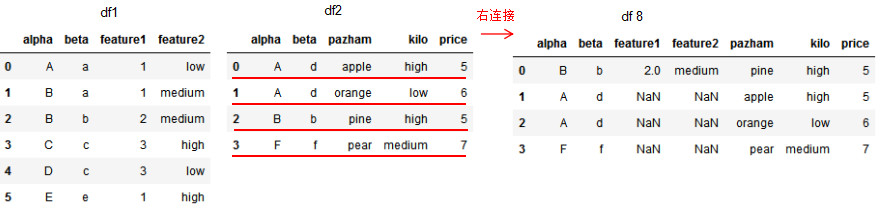
1.6 基于index的连接方法
前面介绍了基于column的连接方法,merge方法亦可基于index连接dataframe。
# 基于column和index的右连接
# 定义df1
df1 = pd.DataFrame({'alpha':['A','B','B','C','D','E'],'beta':['a','a','b','c','c','e'],
'feature1':[1,1,2,3,3,1],'feature2':['low','medium','medium','high','low','high']})
# 定义df2
df2 = pd.DataFrame({'alpha':['A','A','B','F'],'pazham':['apple','orange','pine','pear'],
'kilo':['high','low','high','medium'],'price':np.array([5,6,5,7])},index=['d','d','b','f'])
print(df1)
print(df2)
# 基于df1的beta列和df2的index连接
df9 = pd.merge(df1,df2,how='inner',left_on='beta',right_index=True)
df9
图解index和column的内连接方法:

设置参数suffixes以修改除连接列外相同列的后缀名。
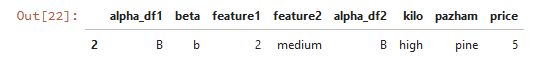
# 基于df1的alpha列和df2的index内连接
df9 = pd.merge(df1,df2,how='inner',left_on='beta',right_index=True,suffixes=('_df1','_df2'))
df9
2. join方法
join方法是基于index连接dataframe,merge方法是基于column连接,连接方法有内连接,外连接,左连接和右连接,与merge一致。
index与index的连接:
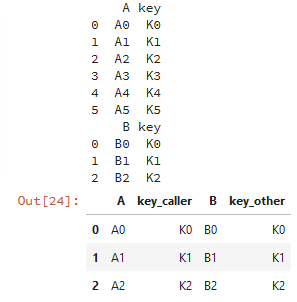
caller = pd.DataFrame({'key': ['K0', 'K1', 'K2', 'K3', 'K4', 'K5'], 'A': ['A0', 'A1', 'A2', 'A3', 'A4', 'A5']})
other = pd.DataFrame({'key': ['K0', 'K1', 'K2'],'B': ['B0', 'B1', 'B2']})
print(caller)print(other)# lsuffix和rsuffix设置连接的后缀名
caller.join(other,lsuffix='_caller', rsuffix='_other',how='inner')
join也可以基于列进行连接:
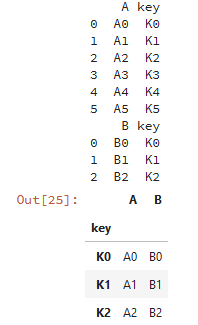
caller = pd.DataFrame({'key': ['K0', 'K1', 'K2', 'K3', 'K4', 'K5'], 'A': ['A0', 'A1', 'A2', 'A3', 'A4', 'A5']})
other = pd.DataFrame({'key': ['K0', 'K1', 'K2'],'B': ['B0', 'B1', 'B2']})
print(caller)
print(other)
# 基于key列进行连接
caller.set_index('key').join(other.set_index('key'),how='inner')
因此,join和merge的连接方法类似,这里就不展开join方法了,建议用merge方法。
3. concat方法
concat方法是拼接函数,有行拼接和列拼接,默认是行拼接,拼接方法默认是外拼接(并集),拼接的对象是pandas数据类型。
3.1 series类型的拼接方法
行拼接:
df1 = pd.Series([1.1,2.2,3.3],index=['i1','i2','i3']) df2 = pd.Series([4.4,5.5,6.6],index=['i2','i3','i4']) print(df1) print(df2) # 行拼接 pd.concat([df1,df2])

行拼接若有相同的索引,为了区分索引,我们在最外层定义了索引的分组情况。
# 对行拼接分组 pd.concat([df1,df2],keys=['fea1','fea2'])

列拼接:
默认以并集的方式拼接:
# 列拼接,默认是并集 pd.concat([df1,df2],axis=1)

以交集的方式拼接:
# 列拼接的内连接(交) pd.concat([df1,df2],axis=1,join='inner')

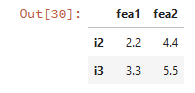
设置列拼接的列名:
# 列拼接的内连接(交) pd.concat([df1,df2],axis=1,join='inner',keys=['fea1','fea2'])
对指定的索引拼接:
# 指定索引[i1,i2,i3]的列拼接 pd.concat([df1,df2],axis=1,join_axes=[['i1','i2','i3']])

3.2 dataframe类型的拼接方法
行拼接:
df1 = pd.DataFrame({'key': ['K0', 'K1', 'K2', 'K3', 'K4', 'K5'], 'A': ['A0', 'A1', 'A2', 'A3', 'A4', 'A5']})
df2 = pd.DataFrame({'key': ['K0', 'K1', 'K2'],'B': ['B0', 'B1', 'B2']})
print(df1)
print(df2)
# 行拼接
pd.concat([df1,df2])

列拼接:
# 列拼接 pd.concat([df1,df2],axis=1)
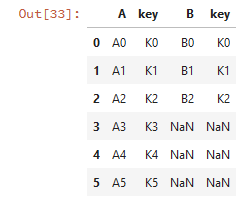
若列拼接或行拼接有重复的列名和行名,则报错:
# 判断是否有重复的列名,若有则报错 pd.concat([df1,df2],axis=1,verify_integrity = True)
ValueError: Indexes have overlapping values: ['key']
4. 小结
merge和join方法基本上能实现相同的功能,建议用merge。
加载全部内容