C语言 数据结构 C语言数据结构之复杂链表的拷贝
i_Crave 人气:0想了解C语言数据结构之复杂链表的拷贝的相关内容吗,i_Crave在本文为您仔细讲解C语言 数据结构的相关知识和一些Code实例,欢迎阅读和指正,我们先划重点:C语言,数据结构,C语言,复杂链表,下面大家一起来学习吧。
题目:
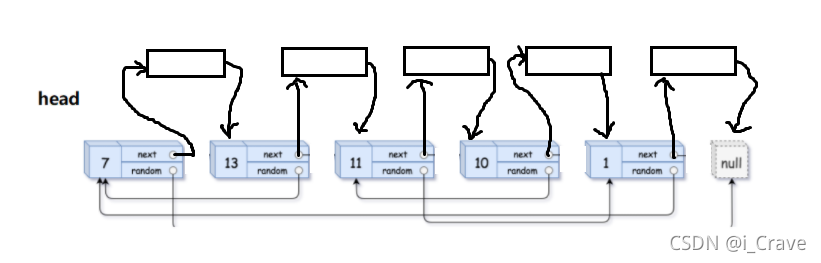
给你一个长度为 n 的链表,每个节点包含一个额外增加的随机指针 random ,该指针可以指向链表中的任何节点或空节点。
构造这个链表的 深拷贝。 深拷贝应该正好由 n 个 全新 节点组成,其中每个新节点的值都设为其对应的原节点的值。新节点的 next 指针和 random 指针也都应指向复制链表中的新节点,并使原链表和复制链表中的这些指针能够表示相同的链表状态。复制链表中的指针都不应指向原链表中的节点 。
例如,如果原链表中有 X 和 Y 两个节点,其中 X.random --> Y 。那么在复制链表中对应的两个节点 x 和 y ,同样有 x.random --> y 。
返回复制链表的头节点。
struct Node {
int val;
struct Node *next;
struct Node *random;
};

思路:
因为每个节点还有一个随机指针,向拷贝标准单向链表的方式才处理,是有困难的;
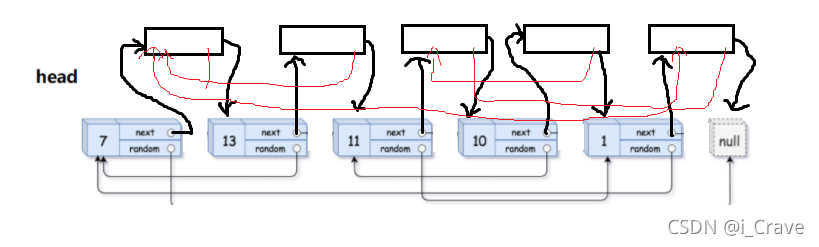
第一步,先将拷贝的节点链在原节点后面
struct Node* cur = head;
while (cur)
{
struct Node* new = (struct Node*)malloc(sizeof(struct Node));
new->val = cur->val;
new->next = cur->next;
cur->next = new;
cur = new->next;
}
第二步,处理随机指针,因为拷贝的就在原节点后面,拷贝的随机指针就指向原节点随机指针的后一个;
struct Node* cur = head;
while (cur)
{
struct Node* copy = cur->next;
if (cur->random == NULL)
{
copy->random = NULL;
}
else
{
copy->random = cur->random->next;
}
cur = copy->next;
}
第三步,将链表分开,并返回拷贝链表的头;
程序:
struct Node* copyRandomList(struct Node* head)
{
if (head == NULL)
{
return NULL;
}
struct Node* cur = head;
while (cur)
{
struct Node* new = (struct Node*)malloc(sizeof(struct Node));
new->val = cur->val;
new->next = cur->next;
cur->next = new;
cur = new->next;
}
cur = head;
while (cur)
{
struct Node* copy = cur->next;
if (cur->random == NULL)
{
copy->random = NULL;
}
else
{
copy->random = cur->random->next;
}
cur = copy->next;
}
cur = head;
struct Node* copyHead = head->next ,*copy_n=copyHead->next,*copy=copyHead;
while (cur)
{
if (copy_n == NULL)
{
copy->next = NULL;
cur->next = NULL;
return copyHead;
}
else
{
cur->next = copy_n;
copy->next = copy_n->next;
}
cur = copy_n;
copy = copy_n->next;
copy_n = copy->next;
}
return copyHead;
}
加载全部内容