sharding-jdbc 水平分表 使用sharding-jdbc实现水平分表的代码实例
穿条秋裤到处跑 人气:0想了解使用sharding-jdbc实现水平分表的代码实例的相关内容吗,穿条秋裤到处跑在本文为您仔细讲解sharding-jdbc 水平分表的相关知识和一些Code实例,欢迎阅读和指正,我们先划重点:sharding-jdbc,水平分表,sharding-jdbc,分表,下面大家一起来学习吧。
在mysql中新建数据库sharding_db,新增两张结构一样的表student_1和student_2。
CREATE TABLE `student_1` ( `ID` bigint(20) NOT NULL , `NAME` varchar(50) CHARACTER SET utf8mb4 COLLATE utf8mb4_bin NOT NULL , `AGE` int(11) NOT NULL , `GENDER` varchar(1) CHARACTER SET utf8mb4 COLLATE utf8mb4_bin NOT NULL , PRIMARY KEY (`ID`) );
此处未指定主键自增,因为两张表的id不能重复,所以只能从后端传入id。
添加依赖
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-jdbc</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId>
</dependency>
<!-- Druid连接池 -->
<dependency>
<groupId>com.alibaba</groupId>
<artifactId>druid</artifactId>
<version>1.1.20</version>
</dependency>
<!-- Mysql驱动依赖 -->
<dependency>
<groupId>mysql</groupId>
<artifactId>mysql-connector-java</artifactId>
</dependency>
<!-- MybatisPlus -->
<dependency>
<groupId>com.baomidou</groupId>
<artifactId>mybatis-plus-boot-starter</artifactId>
<version>3.0.5</version>
</dependency>
<!-- Sharding-JDBC -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.shardingsphere</groupId>
<artifactId>sharding-jdbc-spring-boot-starter</artifactId>
<version>4.0.0-RC1</version>
</dependency>
<!-- lombok -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.projectlombok</groupId>
<artifactId>lombok</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-test</artifactId>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>junit</groupId>
<artifactId>junit</artifactId>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-test</artifactId>
<scope>test</scope>
<exclusions>
<exclusion>
<groupId>org.junit.vintage</groupId>
<artifactId>junit-vintage-engine</artifactId>
</exclusion>
</exclusions>
</dependency>
编写配置文件
spring.main.allow-bean-definition-overriding=true
# 配置Sharding-JDBC的分片策略
# 配置数据源,给数据源起名g1,g2...此处可配置多数据源
spring.shardingsphere.datasource.names=g1
# 配置数据源具体内容:连接池,驱动,地址,用户名,密码
# 由于上面配置数据源只有g1因此下面只配置g1.type,g1.driver-class-name,g1.url,g1.username,g1.password
spring.shardingsphere.datasource.g1.type=com.alibaba.druid.pool.DruidDataSource
spring.shardingsphere.datasource.g1.driver-class-name=com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver
spring.shardingsphere.datasource.g1.url=jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/sharding_db?characterEncoding=utf-8&useUnicode=true&useSSL=false&serverTimezone=UTC
spring.shardingsphere.datasource.g1.username=root
spring.shardingsphere.datasource.g1.password=123456
# 配置表的分布,表的策略
spring.shardingsphere.sharding.tables.student.actual-data-nodes=g1.student_$->{1..2}
# 指定student表 主键gid 生成策略为 SNOWFLAKE
spring.shardingsphere.sharding.tables.student.key-generator.column=id
spring.shardingsphere.sharding.tables.student.key-generator.type=SNOWFLAKE
# 指定分片策略 约定id值是偶数添加到student_1表,如果id是奇数添加到student_2表
spring.shardingsphere.sharding.tables.student.table-strategy.inline.sharding-column=id
spring.shardingsphere.sharding.tables.student.table-strategy.inline.algorithm-expression=student_$->{id % 2 + 1}
# 打开sql输出日志
spring.shardingsphere.props.sql.show=true
或者是yml格式
spring:
main:
allow-bean-definition-overriding: true
shardingsphere:
datasource:
g1:
driver-class-name: com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver
password: 123456
type: com.alibaba.druid.pool.DruidDataSource
url: jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/sharding_db?characterEncoding=utf-8&useUnicode=true&useSSL=false&serverTimezone=UTC
username: root
names: g1
props:
sql:
show: true
sharding:
tables:
student:
actual-data-nodes: g1.student_$->{1..2}
key-generator:
column: id
type: SNOWFLAKE
table-strategy:
inline:
algorithm-expression: student_$->{id % 2 + 1}
sharding-column: id
编写实体类
@Data
public class Student {
private Long id;
private String name;
private int age;
private String gender;
}
编写mapper接口
@Repository
public interface StudentMapper extends BaseMapper<Student> {
}
编写测试类
@SpringBootTest
class ShardingJdbcDemoApplicationTests {
@Autowired
private StudentMapper studentMapper;
@Test
public void test01() {
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
Student student = new Student();
student.setName("wuwl");
student.setAge(27);
student.setGender("男");
studentMapper.insert(student);
}
}
}
执行测试

执行成功,主键通过雪花算法在后端生成,传入到数据库中,根据奇偶性进行分表。
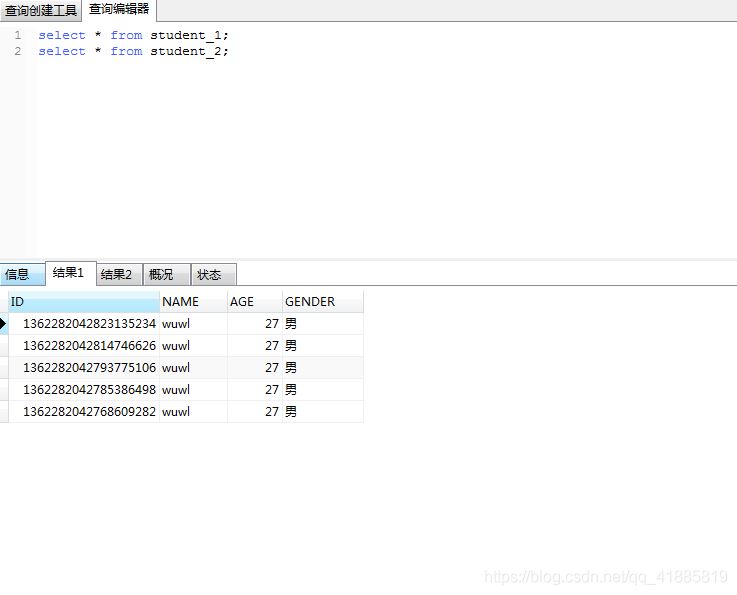
student_1表数据:
student_2表数据:
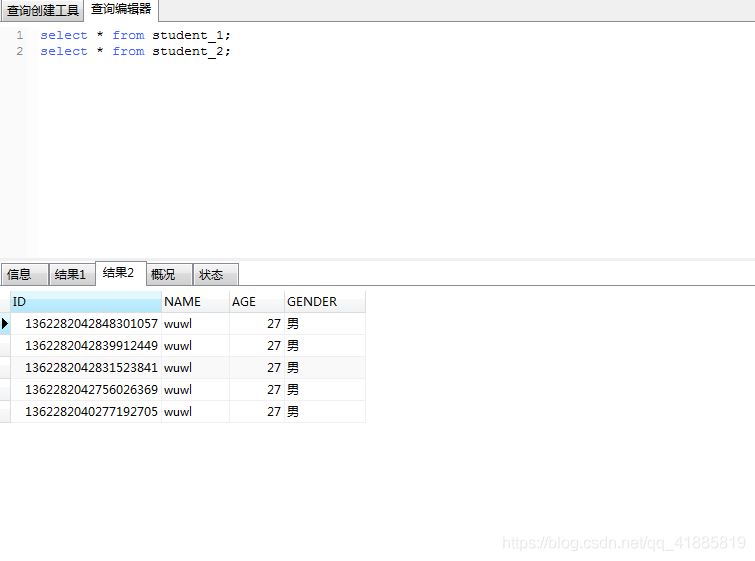
两张表的数据分别有5条,但这只是因为雪花算法生成的id奇数偶数各5个,不是1:1的关系,需要注意。
主键生成后,根据策略插入到对应的表中,从打印出来的sql可以证明这一点。
通过mapper接口的selectById方法进行查询时,会先根据主键策略判断在哪个库,再直接去那个库根据主键查询。而如果是通过其它条件查询,或者是多个id的selectById方法查询,又是如何的呢?
@Test
public void test03() {
List<Long> list = new ArrayList<>();
list.add(1362282042768609282l);
list.add(1362282040277192705l);
List<Student> studentList = studentMapper.selectBatchIds(list);
System.out.println(studentList);
}
取了两张表的id进行查询。
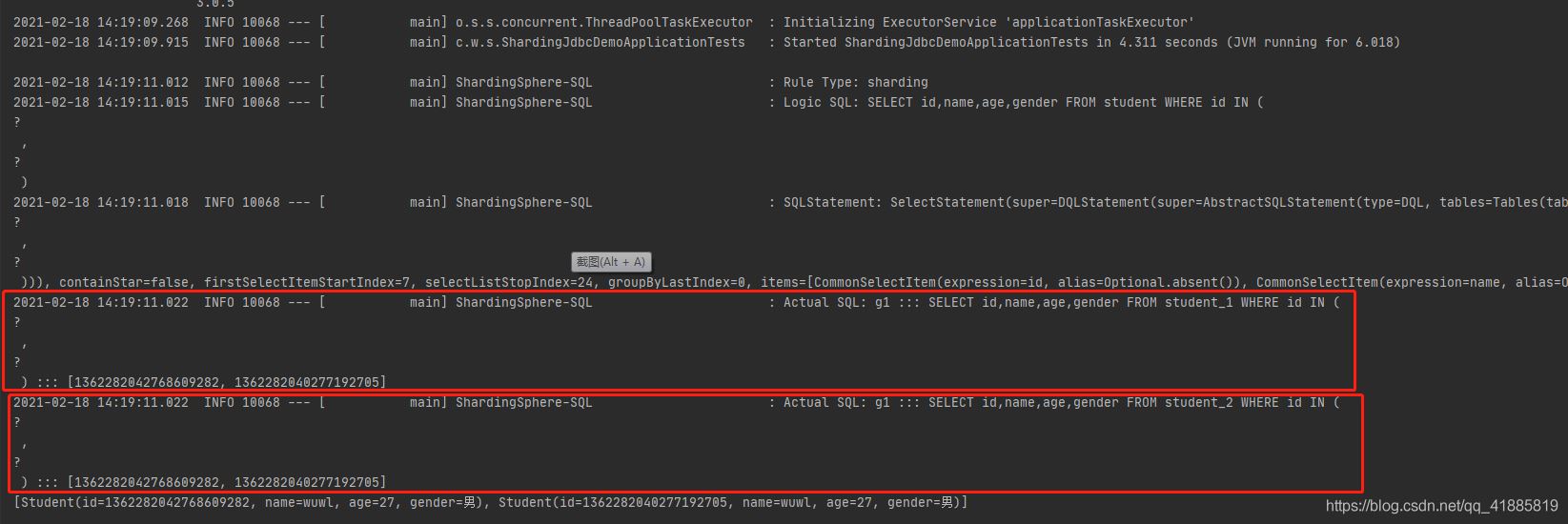
执行同样的sql,在两张表中都查询一遍,再组合结果。
如果所有的id,都来自同一张表,那是否会去多个表中重复查询呢?
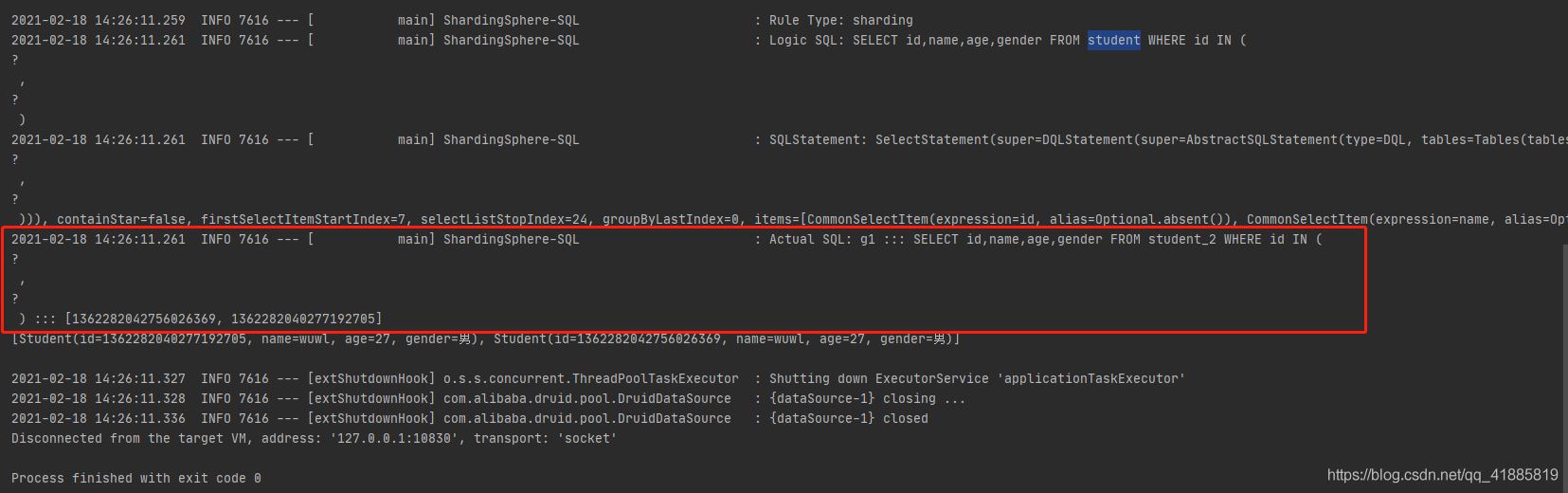
只执行了一遍。所以,在执行查询时,sharding会先判断是否可以确定需要的数据来自那张表,如果能,则直接去那一张表中查询数据即可,而如果不能确定,则会多个表重复查询,以确定查询结果的完整性。
加载全部内容