Java 多线程 Java多线程学习笔记
四季人06 人气:0想了解Java多线程学习笔记的相关内容吗,四季人06在本文为您仔细讲解Java 多线程的相关知识和一些Code实例,欢迎阅读和指正,我们先划重点:Java,多线程,Java,Thread,Java,Runable,下面大家一起来学习吧。
多任务、多线程
在多任务场景下,两件事看上去同时在做,但实际上,你的大脑在同一时间只做一件事,间隔时间可能很少,但这似乎让你感觉这两件事是同时在做
考虑阻塞问题,引入多线程的场景,多线程并发场景

程序、进程、线程
程序=指令+数据(静态的)
在操作系统中运行的程序就是进程,一个进程可以有多个线程
比如,看视频时听声音,看图像,看弹幕等
学着看jdk文档
比如你要看Thread
你可以搜索,然后阅读
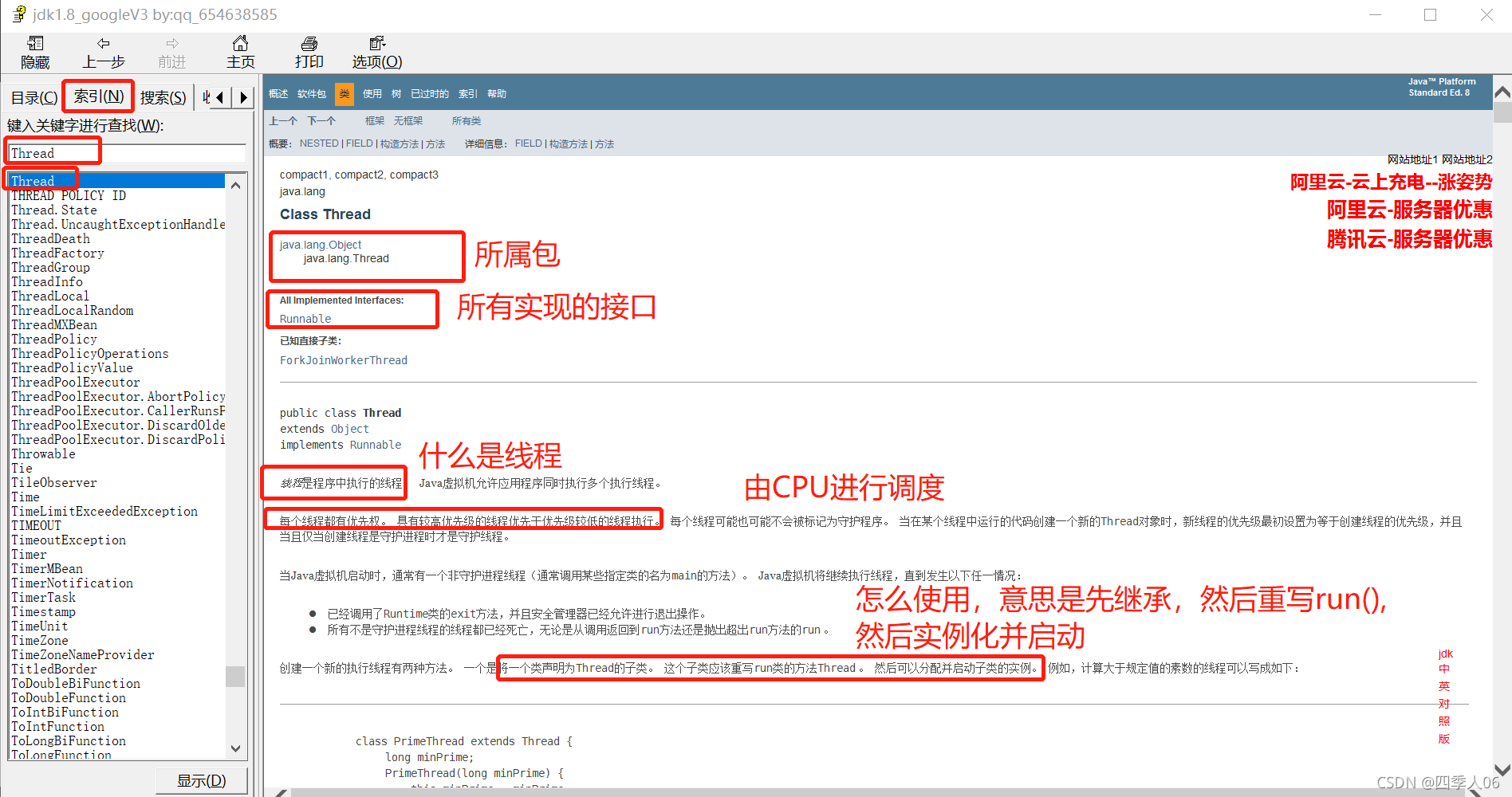
往下翻你会看到:
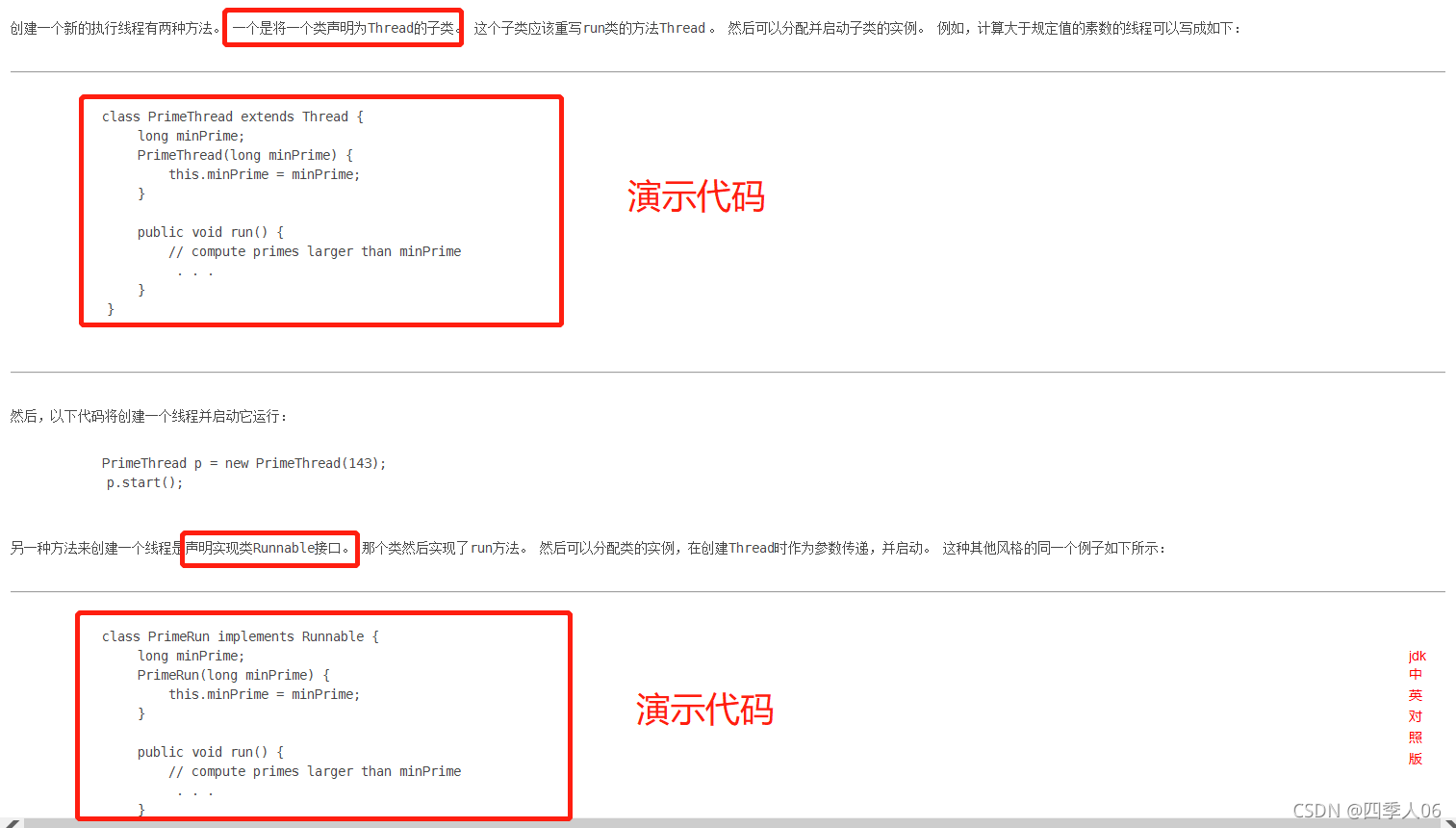

线程的创建
1.继承Thread类
//创建线程方式一:继承Thread类,重写run方法,调用start()方法开启线程
public class TestThread1 extends Thread{
@Override
public void run() {
//run()方法线程体
IntStream.range(0,20).forEach(i->{
System.out.println("我在看代码"+i);
});
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
//创建一个线程对象
TestThread1 testThread1=new TestThread1();
//调用start()方法,启动线程,不一定立即执行,由cpu调度执行
testThread1.start();
//主方法 main方法
IntStream.range(0,20).forEach(i->{
System.out.println("我在学习多线程"+i);
});
}
}
一个小练习:
//练习thread实现对线程同步下载图片
public class TestThread2 extends Thread{
private String url;
private String name;
public TestThread2(String url, String name) {
this.url = url;
this.name = name;
}
@Override
public void run() {
WebDownload webDownload=new WebDownload();
webDownload.downloader(url,name);
System.out.println("下载了文件名:"+name);
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
TestThread2 t1=new TestThread2("http://profile.csdnimg.cn/B/D/2/3_sxh06","1.jpg");
TestThread2 t2=new TestThread2("http://profile.csdnimg.cn/B/D/2/3_sxh06","2.jpg");
TestThread2 t3=new TestThread2("http://profile.csdnimg.cn/B/D/2/3_sxh06","3.jpg");
t1.start();
t2.start();
t3.start();
}
}
//下载器
class WebDownload{
//下载方法
public void downloader(String url,String name) {
try {
FileUtils.copyURLToFile(new URL(url),new File(name));
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
System.out.println("IO异常,downloader方法出错");
}
}
}
2.实现Runable接口
//创建线程的方法2:实现Runable接口
public class TestThread3 implements Runnable{
@Override
public void run() {
//run()方法线程体
IntStream.range(0,20).forEach(i->{
System.out.println("我在看代码"+i);
});
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
//创建一个线程对象
TestThread3 testThread3=new TestThread3();
//调用start()方法,启动线程,不一定立即执行,由cpu调度执行
// Thread thread=new Thread(testThread3);
// thread.start();
//或者这样简写
new Thread(testThread3).start();
//主方法 main方法
IntStream.range(0,100).forEach(i->{
System.out.println("我在学习多线程"+i);
});
}
}
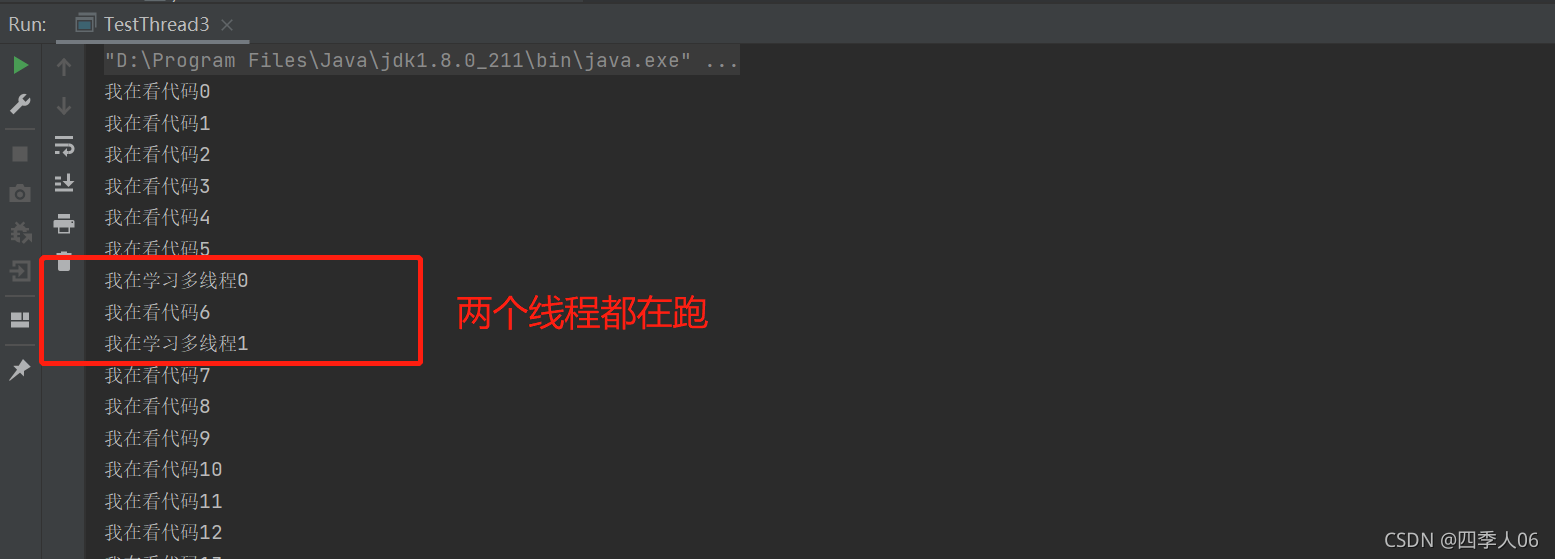
理解并发的场景
当多个线程使用同一个资源时,会出现问题,看看下面这个买火车票的例子:
public class TestThread4 implements Runnable{
//票数
private int ticketNums=10;
@Override
public void run() {
while(true){
if (ticketNums<=0){
break;
}
//模拟延迟
try {
Thread.sleep(200);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"-->拿到了第"+ticketNums--+"张票");
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
TestThread4 ticket=new TestThread4();
new Thread(ticket,"小明").start();
new Thread(ticket,"张三").start();
new Thread(ticket,"李四").start();
}
}
看看运行的结果:
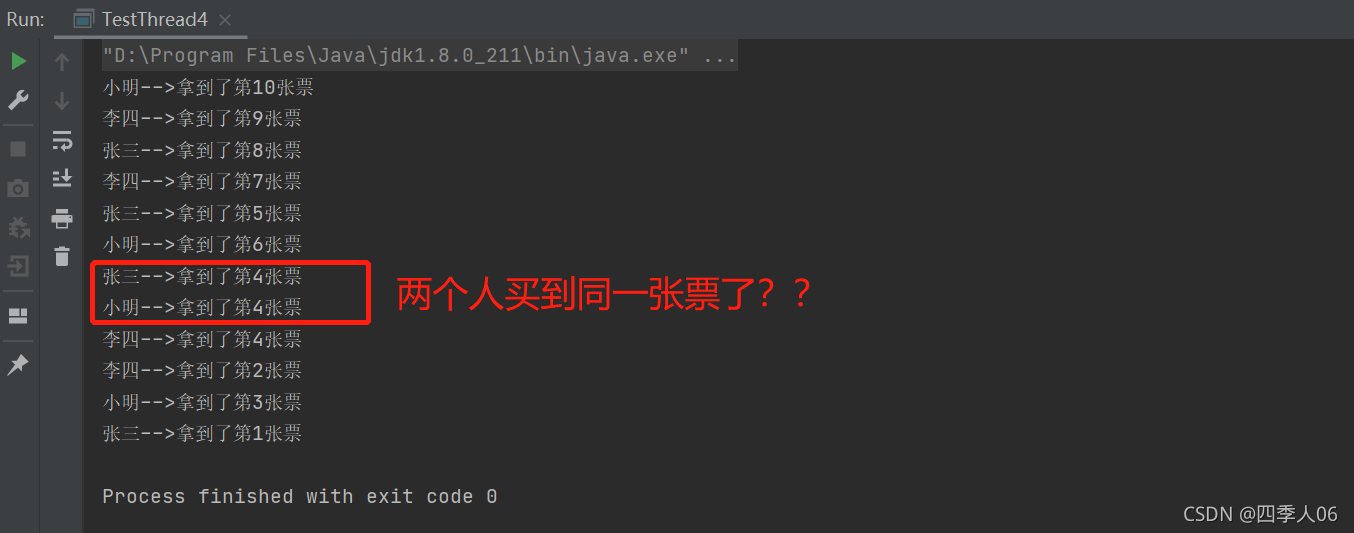
可以看到案例中的线程不安全问题,同时数据也是不正确的
龟兔赛跑场景
/**
* 模拟龟兔赛跑
*/
public class Race implements Runnable{
//胜利者
private static String winner;
@Override
public void run() {
for (int i=0;i<=100;i++){
//模拟兔子休息
if (Thread.currentThread().getName().equals("兔子")&&i%10==0){
try {
Thread.sleep(1);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
boolean flag=gameOver(i);
if (flag){ //判断比赛是否结束
break;
}
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"-->跑了"+i+"步");
}
}
/**
* 判断比赛是否结束
*/
private boolean gameOver(int steps){
//判断是否有胜利者
if (winner !=null){
//已经存在胜利者
return true;
}else if (steps >= 100){
winner=Thread.currentThread().getName();
System.out.println("胜利者是:"+winner);
return true;
}else{
return false;
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Race race=new Race();
new Thread(race,"兔子").start();
new Thread(race,"乌龟").start();
}
}
实现callable接口
//线程创建方式3
public class TestCallable implements Callable<Boolean> {
private String url;
private String name;
public TestCallable(String url, String name) {
this.url = url;
this.name = name;
}
@Override
public Boolean call() {
com.sxh.thread.WebDownload webDownload=new com.sxh.thread.WebDownload();
webDownload.downloader(url,name);
System.out.println("下载了文件名:"+name);
return true;
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws ExecutionException, InterruptedException {
TestCallable t1=new TestCallable("http://profile.csdnimg.cn/B/D/2/3_sxh06","1.jpg");
TestCallable t2=new TestCallable("http://profile.csdnimg.cn/B/D/2/3_sxh06","2.jpg");
TestCallable t3=new TestCallable("http://profile.csdnimg.cn/B/D/2/3_sxh06","3.jpg");
//创建执行服务
ExecutorService ser= Executors.newFixedThreadPool(3);
//提交执行
Future<Boolean> r1=ser.submit(t1);
Future<Boolean> r2=ser.submit(t2);
Future<Boolean> r3=ser.submit(t3);
//获取结果
boolean rs1=r1.get();
boolean rs2=r2.get();
boolean rs3=r3.get();
//关闭服务
ser.shutdownNow();
}
}
理解函数式接口
任何接口,只包含唯一一个抽象方法,就是函数式接口
/**
* lambdab表达式的发展
*/
public class TestLambda1 {
//3.静态内部类
static class Like2 implements ILike{
@Override
public void lambda() {
System.out.println("i like lambda2");
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
ILike like=new Like();
like.lambda();
like=new Like2();
like.lambda();
//4.局部内部类
class Like3 implements ILike{
@Override
public void lambda() {
System.out.println("i like lambda3");
}
}
like=new Like3();
like.lambda();
//5.匿名内部类
like=new ILike() {
@Override
public void lambda() {
System.out.println("i like lambda4");
}
};
like.lambda();
//6.用lambda简化
like=()->{
System.out.println("i like lambda5");
};
like.lambda();
}
}
//1.定义一个函数式接口
interface ILike{
void lambda();
}
//2.实现类
class Like implements ILike{
@Override
public void lambda() {
System.out.println("i like lambda");
}
}
理解线程的状态
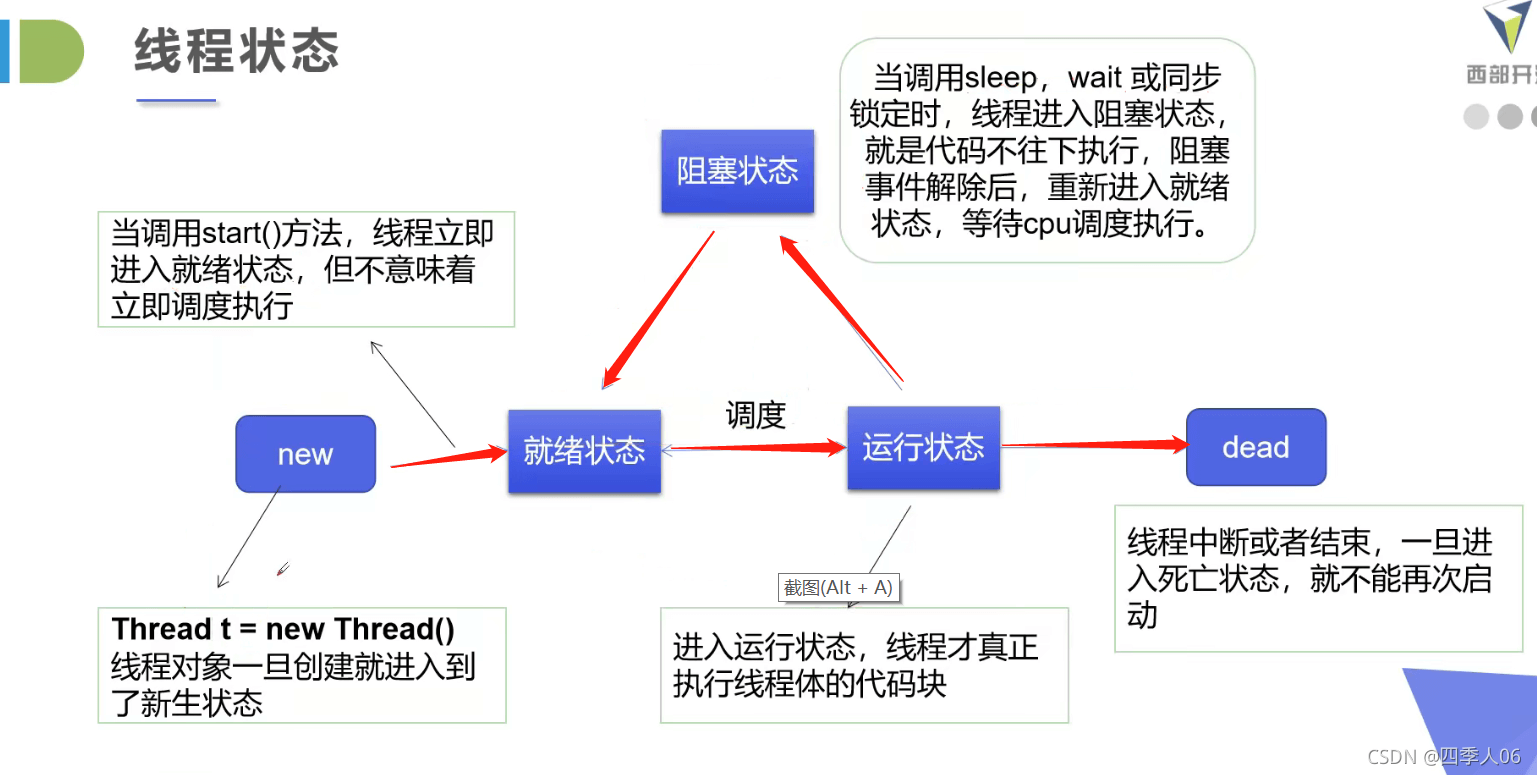
线程停止
public class TestStop implements Runnable{
//1.设置一个标志位
private boolean flag=true;
@Override
public void run() {
int i=0;
while (flag){
System.out.println("run...thread.."+i++);
}
}
//2.设置一个公开的方法停止线程,转换标志位
public void stop(){
this.flag=false;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
TestStop stop=new TestStop();
new Thread(stop).start();
for (int i = 0; i < 1000; i++) {
System.out.println("main"+i);
if (i==900){
//调用stop方法,让线程停止
stop.stop();
System.out.println("线程该停止了");
}
}
// IntStream.range(0,1000).forEach(i->{
//
// });
}
}
线程休眠sleep
每个对象都有一把锁,sleep不会释放锁
1.网路延迟
//模拟延迟
try {
Thread.sleep(200); //ms
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
2.倒计时等
public static void main(String[] args) {
try {
tendown();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
public static void tendown() throws InterruptedException {
int num=10;
while (true){
Thread.sleep(1000);
System.out.println(num--);
if(num<=0)
{
break;
}
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
//打印系统当前时间
Date startTime=new Date(System.currentTimeMillis());
while (true){
try {
Thread.sleep(1000);
System.out.println(new SimpleDateFormat("HH:mm:ss").format(startTime));
startTime=new Date(System.currentTimeMillis());//更新时间
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
线程礼让yield
//线程礼让 礼让不一定成功,由cpu重新调度
public class TestYield {
public static void main(String[] args) {
MyYield myYield=new MyYield();
new Thread(myYield,"a").start();
new Thread(myYield,"b").start();
}
}
class MyYield implements Runnable{
@Override
public void run() {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"线程开始执行");
Thread.yield();
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"线程停止执行");
}
}
线程强制执行
//测试join方法 想象为插队
public class TestJoin implements Runnable{
@Override
public void run() {
for (int i = 0; i < 100; i++) {
System.out.println("线程vip来了"+i);
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
//启动线程
TestJoin testJoin=new TestJoin();
Thread thread=new Thread(testJoin);
thread.start();
//主线程
for (int i = 0; i < 1000; i++) {
if (i==200){
thread.join(); //插队
}
System.out.println("main"+i);
}
}
}
观察线程状态
public class TestState {
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
Thread thread=new Thread(()->{
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) {
try {
Thread.sleep(1000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
System.out.println("//");
});
//观察状态
Thread.State state=thread.getState();
System.out.println(state); //NEW
//启动后
thread.start();
state=thread.getState();
System.out.println(state); //Run
while (state != Thread.State.TERMINATED)
{
Thread.sleep(100);
state=thread.getState();//更新线程状态
System.out.println(state); //Run
}
}
}
线程的优先级
//测试线程的优先级
public class TestPriority {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//主线程默认优先级
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"--->"+Thread.currentThread().getPriority());
MyPriority myPriority=new MyPriority();
Thread t1=new Thread(myPriority);
Thread t2=new Thread(myPriority);
Thread t3=new Thread(myPriority);
Thread t4=new Thread(myPriority);
Thread t5=new Thread(myPriority);
Thread t6=new Thread(myPriority);
//先设置优先级,在启动
t1.start();
t2.setPriority(1);
t2.start();
t3.setPriority(4);
t3.start();
t4.setPriority(Thread.MAX_PRIORITY);
t4.start();
t5.setPriority(-1);
t5.start();
t6.setPriority(11);
t6.start();
}
}
class MyPriority implements Runnable{
@Override
public void run() {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"--->"+Thread.currentThread().getPriority());
}
}
守护线程
线程分为用户线程和守护线程
//测试守护线程
public class TestDaemon {
public static void main(String[] args) {
God god=new God();
You you=new You();
Thread thread=new Thread(god);
thread.setDaemon(true); //默认是false表示用户线程
thread.start();
new Thread(you).start();
}
}
class God implements Runnable{
@Override
public void run() {
while (true){
System.out.println("上帝保佑着你");
}
}
}
class You implements Runnable{
@Override
public void run() {
for (int i = 0; i < 36000; i++) {
System.out.println("你活着"+i);
}
System.out.println("goodbye!!");
}
}
线程同步机制
解决安全性问题:队列+锁
1.synchronized 同步方法
默认锁的是this,如需锁其他的,使用下面的同步块
//synchronized 同步方法
private synchronized void buy(){
if (ticketNums<=0){
flag=false;
return;
}
//模拟延迟
try {
Thread.sleep(100);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
//买票
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"-->拿到了第"+ticketNums--+"张票");
}
2.同步块synchronized(Obj){}
锁的对象是变化的量,需要增删改的对象
obj称之为同步监视器,即监视对象
public class UnsafeList {
public static void main(String[] args) {
List<String> list=new ArrayList<String>();
for (int i = 0; i < 10000; i++) {
new Thread(()->{
synchronized (list){
list.add(Thread.currentThread().getName());
}
}).start();
}
try {
Thread.sleep(3000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println(list.size());
}
}
lock
class A{
//ReentrantLock 可重入锁
private final ReentrantLock lock=new ReentrantLock();
public void f(){
lock.lock();//加锁
try{
//.....
}
finally{
lock.unlock();//释放锁
}
}
}
synchronized与lock
- lock是显示锁需要手动开关,synchronized是隐式锁,出了作用域自动释放
- lock只有代码块锁,synchronized有代码块锁和方法锁
- JVM将花费更少的时间来调度线程,性能更好,更有扩展性
- 优先使用:Lock>同步代码块>同步方法
加载全部内容