python多进程,多线程 手把手带你了解python多进程,多线程
Mr DaYang 人气:0想了解手把手带你了解python多进程,多线程的相关内容吗,Mr DaYang在本文为您仔细讲解python多进程,多线程的相关知识和一些Code实例,欢迎阅读和指正,我们先划重点:python多进程,python多线程,下面大家一起来学习吧。
说明
相应的学习视频见链接,本文只对重点进行总结。

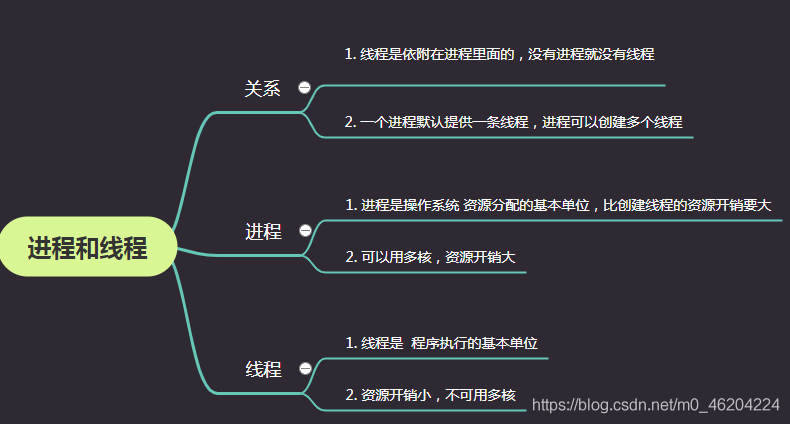
多进程
重点(只要看下面代码的main函数即可)
1.创建
2.如何开守护进程
3.多进程,开销大,用for循环调用多个进程时,后台cpu一下就上去了
import time
import multiprocessing
import os
def dance(who,num):
print("dance父进程:{}".format(os.getppid()))
for i in range(1,num+1):
print("进行编号:{}————{}跳舞。。。{}".format(os.getpid(),who,i))
time.sleep(0.5)
def sing(num):
print("sing父进程:{}".format(os.getppid()))
for i in range(1,num+1):
print("进行编号:{}----唱歌。。。{}".format(os.getpid(),i))
time.sleep(0.5)
def work():
for i in range(10):
print("工作中。。。")
time.sleep(0.2)
if __name__ == '__main__':
# print("main主进程{}".format(os.getpid()))
start= time.time()
#1 进程的创建与启动
# # 1.1创建进程对象,注意dance不能加括号
# # dance_process = multiprocessing.Process(target=dance)#1.无参数
# dance_process=multiprocessing.Process(target=dance,args=("lin",3))#2.以args=元祖方式
# sing_process = multiprocessing.Process(target=sing,kwargs={"num":3})#3.以kwargs={}字典方式
# # 1.2启动进程
# dance_process.start()
# sing_process.start()
#2.默认-主进程和子进程是分开的,主进程只要1s就可以完成,子进程要2s,主进程会等所有子进程执行完,再退出
# 2.1子守护主进程,当主一但完成,子就断开(如qq一关闭,所有聊天窗口就没了).daemon=True
work_process = multiprocessing.Process(target=work,daemon=True)
work_process.start()
time.sleep(1)
print("主进程完成了!")#主进程和子进程是分开的,主进程只要1s就可以完成,子进程要2s,主进程会等所有子进程执行完,再退出
print("main主进程花费时长:",time.time()-start)
#
多线程

重点
1.创建
2.守护线程
3.线程安全问题(多人抢票,会抢到同一张)
import time
import os
import threading
def dance(num):
for i in range(num):
print("进程编号:{},线程编号:{}————跳舞。。。".format(os.getpid(),threading.current_thread()))
time.sleep(1)
def sing(count):
for i in range(count):
print("进程编号:{},线程编号:{}----唱歌。。。".format(os.getpid(),threading.current_thread()))
time.sleep(1)
def task():
time.sleep(1)
thread=threading.current_thread()
print(thread)
if __name__ == '__main__':
# start=time.time()
# # sing_thread =threading.Thread(target=dance,args=(3,),daemon=True)#设置成守护主线程
# sing_thread = threading.Thread(target=dance, args=(3,))
# dance_thread = threading.Thread(target=sing,kwargs={"count":3})
#
# sing_thread.start()
# dance_thread.start()
#
# time.sleep(1)
# print("进程编号:{}主线程结束...用时{}".format(os.getpid(),(time.time()-start)))
for i in range(10):#多线程之间执行是无序的,由cpu调度
sub_thread = threading.Thread(target=task)
sub_thread.start()
线程安全
由于线程直接是无序进行的,且他们共享同一个进程的全部资源,所以会产生线程安全问题(比如多人在线抢票,买到同一张)


#下面代码在没有lock锁时,会卖出0票,加上lock就正常
import threading
import time
lock =threading.Lock()
class Sum_tickets:
def __init__(self,tickets):
self.tickets=tickets
def window(sum_tickets):
while True:
with lock:
if sum_tickets.tickets>0:
time.sleep(0.2)
print(threading.current_thread().name,"取票{}".format(sum_tickets.tickets))
sum_tickets.tickets-=1
else:
break
if __name__ == '__main__':
sum_tickets=Sum_tickets(10)
sub_thread1 = threading.Thread(name="窗口1",target=window,args=(sum_tickets,))
sub_thread2 = threading.Thread(name="窗口2",target=window,args=(sum_tickets,))
sub_thread1.start()
sub_thread2.start()
高并发拷贝(多进程,多线程)
import os
import multiprocessing
import threading
import time
def copy_file(file_name,source_dir,dest_dir):
source_path = source_dir+"/"+file_name
dest_path =dest_dir+"/"+file_name
print("当前进程为:{}".format(os.getpid()))
with open(source_path,"rb") as source_file:
with open(dest_path,"wb") as dest_file:
while True:
data=source_file.read(1024)
if data:
dest_file.write(data)
else:
break
pass
if __name__ == '__main__':
source_dir=r'C:\Users\Administrator\Desktop\注意力'
dest_dir=r'C:\Users\Administrator\Desktop\test'
start = time.time()
try:
os.mkdir(dest_dir)
except:
print("目标文件已存在")
file_list =os.listdir(source_dir)
count=0
#1多进程
for file_name in file_list:
count+=1
print(count)
sub_processor=multiprocessing.Process(target=copy_file,
args=(file_name,source_dir,dest_dir))
sub_processor.start()
# time.sleep(20)
print(time.time()-start)
#这里有主进程和子进程,通过打印可以看出,主进程在创建1,2,3,4,,,21过程中,子进程已有的开始执行,也就是说,每个进程是互不影响的
# 9
# 10
# 11
# 12
# 13
# 当前进程为:2936(当主进程创建第13个时,此时,第一个子进程开始工作)
# 14
# 当前进程为:10120
# 当前进程为:10440
# 15
# 当前进程为:9508
# 2多线程
# for file_name in file_list:
# count += 1
# print(count)
# sub_thread = threading.Thread(target=copy_file,
# args=(file_name, source_dir, dest_dir))
# sub_thread.start()
# # time.sleep(20)
# print(time.time() - start)
总结
本篇文章就到这里了,希望能给你带来帮助,也希望您能够多多关注的更多内容!
加载全部内容