pytorch准确率召回率F1值 在pytorch中计算准确率,召回率和F1值的操作
coding_zhang 人气:0想了解在pytorch中计算准确率,召回率和F1值的操作的相关内容吗,coding_zhang在本文为您仔细讲解pytorch准确率召回率F1值的相关知识和一些Code实例,欢迎阅读和指正,我们先划重点:pytorch,计算准确率,召回率,F1值,下面大家一起来学习吧。
看代码吧~
predict = output.argmax(dim = 1)
confusion_matrix =torch.zeros(2,2)
for t, p in zip(predict.view(-1), target.view(-1)):
confusion_matrix[t.long(), p.long()] += 1
a_p =(confusion_matrix.diag() / confusion_matrix.sum(1))[0]
b_p = (confusion_matrix.diag() / confusion_matrix.sum(1))[1]
a_r =(confusion_matrix.diag() / confusion_matrix.sum(0))[0]
b_r = (confusion_matrix.diag() / confusion_matrix.sum(0))[1]
补充:pytorch 查全率 recall 查准率 precision F1调和平均 准确率 accuracy
看代码吧~
def eval():
net.eval()
test_loss = 0
correct = 0
total = 0
classnum = 9
target_num = torch.zeros((1,classnum))
predict_num = torch.zeros((1,classnum))
acc_num = torch.zeros((1,classnum))
for batch_idx, (inputs, targets) in enumerate(testloader):
if use_cuda:
inputs, targets = inputs.cuda(), targets.cuda()
inputs, targets = Variable(inputs, volatile=True), Variable(targets)
outputs = net(inputs)
loss = criterion(outputs, targets)
# loss is variable , if add it(+=loss) directly, there will be a bigger ang bigger graph.
test_loss += loss.data[0]
_, predicted = torch.max(outputs.data, 1)
total += targets.size(0)
correct += predicted.eq(targets.data).cpu().sum()
pre_mask = torch.zeros(outputs.size()).scatter_(1, predicted.cpu().view(-1, 1), 1.)
predict_num += pre_mask.sum(0)
tar_mask = torch.zeros(outputs.size()).scatter_(1, targets.data.cpu().view(-1, 1), 1.)
target_num += tar_mask.sum(0)
acc_mask = pre_mask*tar_mask
acc_num += acc_mask.sum(0)
recall = acc_num/target_num
precision = acc_num/predict_num
F1 = 2*recall*precision/(recall+precision)
accuracy = acc_num.sum(1)/target_num.sum(1)
#精度调整
recall = (recall.numpy()[0]*100).round(3)
precision = (precision.numpy()[0]*100).round(3)
F1 = (F1.numpy()[0]*100).round(3)
accuracy = (accuracy.numpy()[0]*100).round(3)
# 打印格式方便复制
print('recall'," ".join('%s' % id for id in recall))
print('precision'," ".join('%s' % id for id in precision))
print('F1'," ".join('%s' % id for id in F1))
print('accuracy',accuracy)
补充:Python scikit-learn,分类模型的评估,精确率和召回率,classification_report
分类模型的评估标准一般最常见使用的是准确率(estimator.score()),即预测结果正确的百分比。
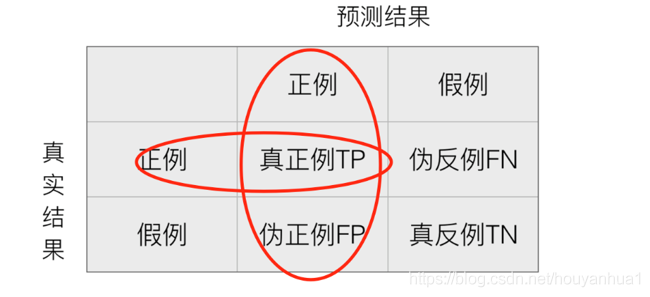
混淆矩阵:

准确率是相对所有分类结果;精确率、召回率、F1-score是相对于某一个分类的预测评估标准。
精确率(Precision):预测结果为正例样本中真实为正例的比例(查的准)()
召回率(Recall):真实为正例的样本中预测结果为正例的比例(查的全)()
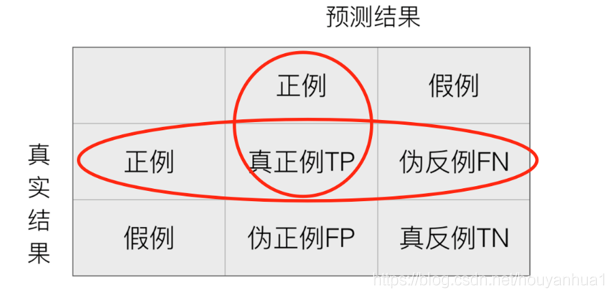
分类的其他评估标准:F1-score,反映了模型的稳健型
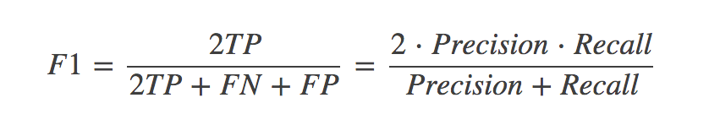

demo.py(分类评估,精确率、召回率、F1-score,classification_report):
from sklearn.datasets import fetch_20newsgroups
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
from sklearn.feature_extraction.text import TfidfVectorizer
from sklearn.naive_bayes import MultinomialNB
from sklearn.metrics import classification_report
# 加载数据集 从scikit-learn官网下载新闻数据集(共20个类别)
news = fetch_20newsgroups(subset='all') # all表示下载训练集和测试集
# 进行数据分割 (划分训练集和测试集)
x_train, x_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(news.data, news.target, test_size=0.25)
# 对数据集进行特征抽取 (进行特征提取,将新闻文档转化成特征词重要性的数字矩阵)
tf = TfidfVectorizer() # tf-idf表示特征词的重要性
# 以训练集数据统计特征词的重要性 (从训练集数据中提取特征词)
x_train = tf.fit_transform(x_train)
print(tf.get_feature_names()) # ["condensed", "condescend", ...]
x_test = tf.transform(x_test) # 不需要重新fit()数据,直接按照训练集提取的特征词进行重要性统计。
# 进行朴素贝叶斯算法的预测
mlt = MultinomialNB(alpha=1.0) # alpha表示拉普拉斯平滑系数,默认1
print(x_train.toarray()) # toarray() 将稀疏矩阵以稠密矩阵的形式显示。
'''
[[ 0. 0. 0. ..., 0.04234873 0. 0. ]
[ 0. 0. 0. ..., 0. 0. 0. ]
...,
[ 0. 0.03934786 0. ..., 0. 0. 0. ]
'''
mlt.fit(x_train, y_train) # 填充训练集数据
# 预测类别
y_predict = mlt.predict(x_test)
print("预测的文章类别为:", y_predict) # [4 18 8 ..., 15 15 4]
# 准确率
print("准确率为:", mlt.score(x_test, y_test)) # 0.853565365025
print("每个类别的精确率和召回率:", classification_report(y_test, y_predict, target_names=news.target_names))
'''
precision recall f1-score support
alt.atheism 0.86 0.66 0.75 207
comp.graphics 0.85 0.75 0.80 238
sport.baseball 0.96 0.94 0.95 253
...,
'''
召回率的意义(应用场景):产品的不合格率(不想漏掉任何一个不合格的产品,查全);癌症预测(不想漏掉任何一个癌症患者)
以上为个人经验,希望能给大家一个参考,也希望大家多多支持。
加载全部内容