vue传值方式 vue传值方式的十二种方法总结
Frazier_梁超 人气:0一.父传子传递
(1)在父组件的子组件标签上绑定一个属性,挂载要传输的变量
(2)在子组件中通过props来接受数据,props可以是数组也可以是对象,接受的数据可以直接使用 props: [“属性 名”] props:{属性名:数据类型}
代码示例:
//父组件
<template>
<div>
<i>父组件</i>
<!--页面使用-->
<son :data='name'></son>
</div>
</template>
<script>
import son from "./son.vue";//导入父组件
export default {
components: { son },//注册组件
name: "父组件",
data() {
return {
name: "Frazier", //父组件定义变量
};
},
};
</script>
//子组件
<template>
<div>{{data}}</div>
</template>
<script>
export default {
components: { },
name: '子组件',
props:["data"],
};
</script>
二.子传父传递
(1)在父组件的子组件标签上自定义一个事件,然后调用需要的方法
(2)在子组件的方法中通过 this.$emit(“事件”)来触发在父组件中定义的事件,数据是以参数的形式进行传递的
代码示例:
//父组件
<template>
<div>
<i>父组件</i>
<!--页面使用-->
<son @lcclick="lcclick"></son>//自定义一个事件
</div>
</template>
<script>
import son from "./son.vue"; //导入父组件
export default {
components: { son }, //注册组件
name: "父组件",
data() {
return {};
},
methods: {
lcclick(){
alert('子传父')
}
},
};
</script>
//子组件
<template>
<div>
<button @click="lcalter">点我</button>
</div>
</template>
<script>
export default {
components: { },
name: '子组件',
methods: {
lcalter(){
this.$emit('lcclick')//通过emit来触发事件
}
},
};
</script>
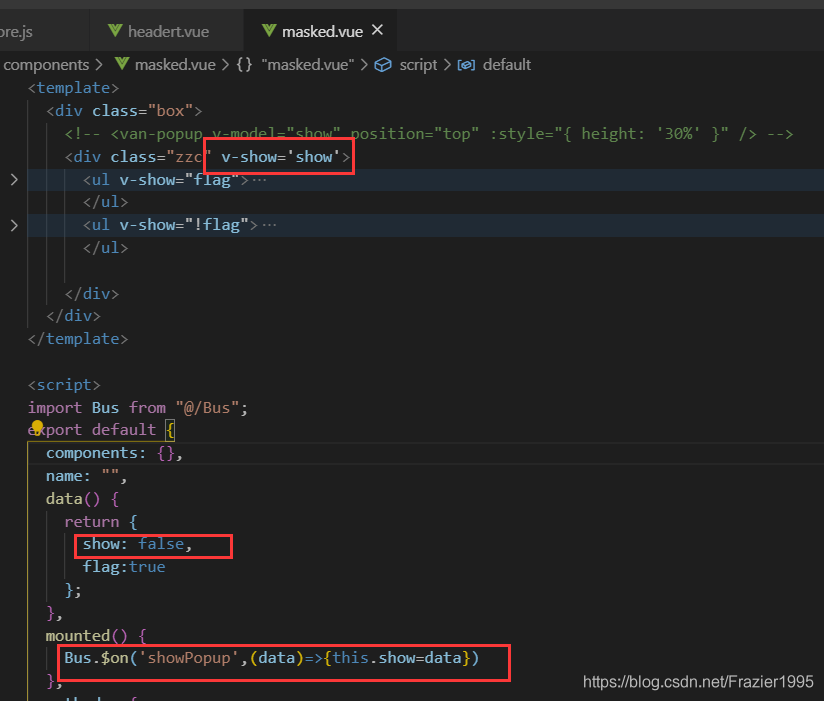
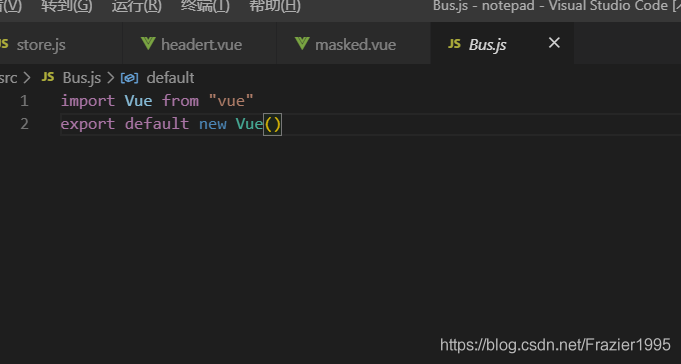
三.兄弟组件通信(bus总线)
(1)在src中新建一个Bus.js的文件,然后导出一个空的vue实例
(2)在传输数据的一方引入Bus.js 然后通过Bus. e m i t ( “ 事 件 名 ” , " 参 数 " ) 来 来 派 发 事 件 , 数 据 是 以 emit(“事件名”,"参数")来来派发事件,数据是以 emit(“事件名”,"参数")来来派发事件,数据是以emit()的参 数形式来传递
(3)在接受的数据的一方 引入 Bus.js 然后通过 Bus.$on(“事件名”,(data)=>{data是接受的数据})
图片示例:

四.ref/refs(父子组件通信)
(1)ref 如果在普通的 DOM 元素上使用,引用指向的就是 DOM 元素;如果用在子组件上,引用就指向组件实例,
(2)可以通过实例直接调用组件的方法或访问数据。也算是子组件向父组件传值的一种
代码示例:
//父组件
<template>
<div>
<button @click="sayHello">sayHello</button>
<child ref="childForRef"></child>
</div>
</template>
<script>
import child from './child.vue'
export default {
components: { child },
data () {
return {
childForRef: null,
}
},
mounted() {
this.childForRef = this.$refs.childForRef;
console.log(this.childForRef.name);
},
methods: {
sayHello() {
this.childForRef.sayHello()
}
}
}
</script>
//子组件
<template>
<div>child 的内容</div>
</template>
<script>
export default {
data () {
return {
name: '我是 child',
}
},
methods: {
sayHello () {
console.log('hello');
alert('hello');
}
}
}
</script>
五.Vuex通信
组件通过 dispatch 到 actions,actions 是异步操作,再 actions中通过 commit 到 mutations,mutations 再通过逻辑操作改变 state,从而同步到组件,更新其数据状态
代码示例:
//父组件
template>
<div id="app">
<ChildA/>
<ChildB/>
</div>
</template>
<script>
import ChildA from './ChildA' // 导入A组件
import ChildB from './ChildB' // 导入B组件
export default {
components: {ChildA, ChildB} // 注册组件
}
</script>
//子组件A
<template>
<div id="childA">
<h1>我是A组件</h1>
<button @click="transform">点我让B组件接收到数据</button>
<p>因为点了B,所以信息发生了变化:{{BMessage}}</p>
</div>
</template>
<script>
export default {
data() {
return {
AMessage: 'Hello,B组件,我是A组件'
}
},
computed: {
BMessage() {
// 这里存储从store里获取的B组件的数据
return this.$store.state.BMsg
}
},
methods: {
transform() {
// 触发receiveAMsg,将A组件的数据存放到store里去
this.$store.commit('receiveAMsg', {
AMsg: this.AMessage
})
}
}
}
</script>
//子组件B
<template>
<div id="childB">
<h1>我是B组件</h1>
<button @click="transform">点我让A组件接收到数据</button>
<p>点了A,我的信息发生了变化:{{AMessage}}</p>
</div>
</template>
<script>
export default {
data() {
return {
BMessage: 'Hello,A组件,我是B组件'
}
},
computed: {
AMessage() {
// 这里存储从store里获取的A组件的数据
return this.$store.state.AMsg
}
},
methods: {
transform() {
// 触发receiveBMsg,将B组件的数据存放到store里去
this.$store.commit('receiveBMsg', {
BMsg: this.BMessage
})
}
}
}
</script>
//vuex
import Vue from 'vue'
import Vuex from 'vuex'
Vue.use(Vuex)
const state = {
AMsg: '',
BMsg: ''
}
const mutations = {
receiveAMsg(state, payload) {
// 将A组件的数据存放于state
state.AMsg = payload.AMsg
},
receiveBMsg(state, payload) {
// 将B组件的数据存放于state
state.BMsg = payload.BMsg
}
}
export default new Vuex.Store({
state,
mutations
})
六.$parent
通过parent可以获父组件实例 ,然 后通过这个实例就可以访问父组件的属 性和方法 ,它还有一个兄弟parent可以获父组件实例,然后通过这个实例就可以访问父组件的属性和方法,它还有一个兄弟parent可以获父组件实例,然后通过这个实例就可以访问父组件的属性和方法,它还有一个兄弟root,可以获取根组件实例。
代码示例:
// 获父组件的数据 this.$parent.foo // 写入父组件的数据 this.$parent.foo = 2 // 访问父组件的计算属性 this.$parent.bar // 调用父组件的方法 this.$parent.baz() //在子组件传给父组件例子中,可以使用this.$parent.getNum(100)传值给父组件。
七.sessionStorage传值
sessionStorage 是浏览器的全局对象,存在它里面的数据会在页面关闭时清除 。运用这个特性,我们可以在所有页面共享一份数据。
代码示例:
// 保存数据到 sessionStorage
sessionStorage.setItem('key', 'value');
// 从 sessionStorage 获取数据
let data = sessionStorage.getItem('key');
// 从 sessionStorage 删除保存的数据
sessionStorage.removeItem('key');
// 从 sessionStorage 删除所有保存的数据
sessionStorage.clear();
注意:里面存的是键值对,只能是字符串类型,如果要存对象的话,需要使用 let objStr = JSON.stringify(obj) 转成字符串然后再存储(使用的时候 let obj = JSON.parse(objStr) 解析为对象)。
推荐一个库 good-storage ,它封装了sessionStorage ,可以直接用它的API存对象
//localStorage storage.set(key,val) storage.get(key, def) //sessionStorage storage.session.set(key, val) storage.session.get(key, val)
八.路由传值
使用问号传值
A页面跳转B页面时使用 this. r o u t e r . p u s h ( ' / B ? n a m e = d a n s e e k ' ) B 页 面 可 以 使 用 t h i s . router.push('/B?name=danseek') B页面可以使用 this. router.push('/B?name=danseek')B页面可以使用this.route.query.name 来获取A页面传过来的值
上面要注意router和route的区别
使用冒号传值
配置如下路由:
{
path: '/b/:name',
name: 'b',
component: () => import( '../views/B.vue')
},
在B页面可以通过 this.$route.params.name 来获取路由传入的name的值
使用父子组件传值
由于router-view本身也是一个组件,所以我们也可以使用父子组件传值方式传值,然后在对应的子页面里加上props,因为type更新后没有刷新路由,所以不能直接在子页面的mounted钩子里直接获取最新type的值,而要使用watch
<router-view :type="type"></router-view>
// 子页面
props: ['type']
watch: {
type(){
// console.log("在这个方法可以时刻获取最新的数据:type=",this.type)
},
},
九.祖传孙 $attrs
正常情况下需要借助父亲的props作为中间过渡,但是这样在父亲组件就会多了一些跟父组件业务无关的属性,耦合度高,借助$attrs可以简化些,而且祖跟孙都无需做修改
祖组件:
<template>
<section>
<parent name="grandParent" sex="男" age="88" hobby="code" @sayKnow="sayKnow"></parent>
</section>
</template>
<script>
import Parent from './Parent'
export default {
name: "GrandParent",
components: {
Parent
},
data() {
return {}
},
methods: {
sayKnow(val){
console.log(val)
}
},
mounted() {
}
}
</script>
父组件
<template>
<section>
<p>父组件收到</p>
<p>祖父的名字:{{name}}</p>
<children v-bind="$attrs" v-on="$listeners"></children>
</section>
</template>
<script>
import Children from './Children'
export default {
name: "Parent",
components: {
Children
},
// 父组件接收了name,所以name值是不会传到子组件的
props:['name'],
data() {
return {}
},
methods: {},
mounted() {
}
}
</script>
子组件
<template>
<section>
<p>子组件收到</p>
<p>祖父的名字:{{name}}</p>
<p>祖父的性别:{{sex}}</p>
<p>祖父的年龄:{{age}}</p>
<p>祖父的爱好:{{hobby}}</p>
<button @click="sayKnow">我知道啦</button>
</section>
</template>
<script>
export default {
name: "Children",
components: {},
// 由于父组件已经接收了name属性,所以name不会传到子组件了
props:['sex','age','hobby','name'],
data() {
return {}
},
methods: {
sayKnow(){
this.$emit('sayKnow','我知道啦')
}
},
mounted() {
}
}
</script>
十.孙传祖使用$listeners
文字内容同第九个
祖组件
<template>
<div id="app">
<children-one @eventOne="eventOne"></children-one>
{{ msg }}
</div>
</template>
<script>
import ChildrenOne from '../src/components/children.vue'
export default {
name: 'App',
components: {
ChildrenOne,
},
data() {
return {
msg: ''
}
},
methods: {
eventOne(value) {
this.msg = value
}
}
}
</script>
父组件
<template>
<div>
<children-two v-on="$listeners"></children-two>
</div>
</template>
<script>
import ChildrenTwo from './childrenTwo.vue'
export default {
name: 'childrenOne',
components: {
ChildrenTwo
}
}
</script>
子组件
<template>
<div>
<button @click="setMsg">点击传给祖父</button>
</div>
</template>
<script>
export default {
name: 'children',
methods: {
setMsg() {
this.$emit('eventOne', '123')
}
}
}
</script>
十一.promise传参
promise 中 resolve 如何传递多个参数
//类似与这样使用,但实际上后面两个参数无法获取
promise = new Promise((resolve,reject)=>{
let a = 1
let b = 2
let c = 3
resolve(a,b,c)
})
promise.then((a,b,c)=>{
console.log(a,b,c)
})
resolve() 只能接受并处理一个参数,多余的参数会被忽略掉。
如果想多个用数组,或者对象方式。。
数组
promise = new Promise((resolve,reject)=>{
resolve([1,2,3])
})
promise.then((arr)=>{
console.log(arr[0],arr[1],arr[2])
})
对象
promise = new Promise((resolve,reject)=>{
resolve({a:1,b:2,c:3})
})
promise.then(obj=>{
console.log(obj.a,obj.b,obj.c)
})
十二.全局变量
定义一个全局变量,在有值的组件直接赋值,在需要的组件内直接使用就可以了,具体的话看我这篇博客就可以,
博客链接点击就好 全局变量 篇
加载全部内容