OpenCV 车道实时检测 使用OpenCV对车道进行实时检测的实现代码实例
cofisher 人气:0项目介绍
下图中的两条线即为车道:
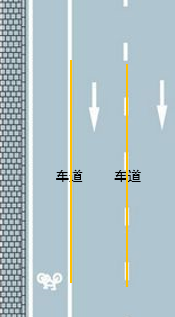
我们的任务就是通过 OpenCV 在一段视频(或摄像头)中实时检测出车道并将其标记出来。其效果如下图所示:

这里使用的代码来源于磐怼怼大神,此文章旨在对其代码进行解释。
实现步骤
1、将视频的所有帧读取为图片;
2、创建掩码并应用到这些图片上;
3、图像阈值化;
4、用霍夫线变换检测车道;
5、将车道画到每张图片上;
6、将所有图片合并为视频。
代码实现
1、导入需要的库
import os import re import cv2 import numpy as np from tqdm import notebook import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
其中 tqdm.notebook 是用来显示进度条的。
2、将图片(视频的每一帧)加载进来
这里我们已经将视频的每一帧读取为图片了,并将它们都放进 frames 文件夹。
# 获取帧的文件名
col_frames = os.listdir('frames/') # 读取 frames 文件夹下的所有图片
col_frames.sort(key=lambda f: int(re.sub('\D', '', f))) # 按名称对图片进行排序
# 加载帧
col_images=[]
for i in notebook.tqdm(col_frames):
img = cv2.imread('frames/'+i)
col_images.append(img) # 将所有图片添加进 col_images 列表
3、选择一张图片进行处理
3.1 选定一张图片
# 指定一个索引 idx = 457 # plot frame plt.figure(figsize=(10,10)) plt.imshow(col_images[idx][:,:,0], cmap= "gray") plt.show()

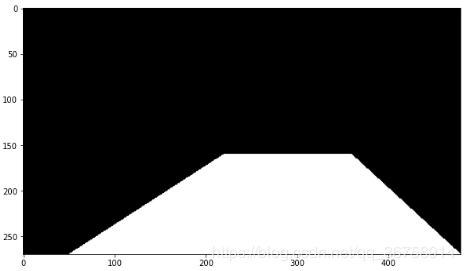
3.2 创建掩码
# 创建0矩阵 stencil = np.zeros_like(col_images[idx][:,:,0]) # 指定多边形的坐标 polygon = np.array([[50,270], [220,160], [360,160], [480,270]]) # 用1填充多边形 cv2.fillConvexPoly(stencil, polygon, 1) # 画出多边形 plt.figure(figsize=(10,10)) plt.imshow(stencil, cmap= "gray") plt.show()
3.3 将掩码应用到图片上
# 应用该多边形作为掩码 img = cv2.bitwise_and(col_images[idx][:,:,0], col_images[idx][:,:,0], mask=stencil) # 画出掩码后的图片 plt.figure(figsize=(10,10)) plt.imshow(img, cmap= "gray") plt.show()
这里的按位与操作 cv2.bitwise_and() 可以参考OpenCV 之按位运算举例解析一文。

3.4 图像阈值化
# 应用图像阈值化 ret, thresh = cv2.threshold(img, 130, 145, cv2.THRESH_BINARY) # 画出图像 plt.figure(figsize=(10,10)) plt.imshow(thresh, cmap= "gray") plt.show()
其中 cv2.threshold 函数的用法可以参考Opencv之图像阈值一文。
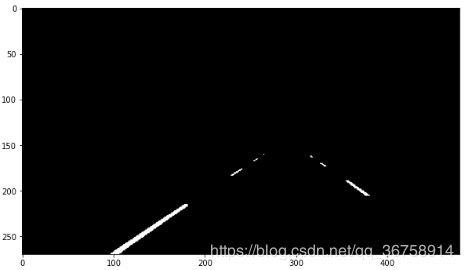
3.5 霍夫线变换检测车道
lines = cv2.HoughLinesP(thresh, 1.0, np.pi/180, 30, maxLineGap=200) # 创建原始帧的副本 dmy = col_images[idx][:,:,0].copy() # 霍夫线 for line in lines: x1, y1, x2, y2 = line[0] # 提取出霍夫线的坐标 cv2.line(dmy, (x1, y1), (x2, y2), (255, 0, 0), 3) # 将霍夫线画在帧上 # 画出帧 plt.figure(figsize=(10,10)) plt.imshow(dmy, cmap= "gray") plt.show()
cv2.HoughLinesP() 函数介绍:
lines = HoughLinesP(image, rho, theta, threshold, minLineLength=None, maxLineGap=None)
输入:
- image: 必须是二值图像;
- rho: 线段以像素为单位的距离精度,double类型的,推荐用1.0
- theta: 线段以弧度为单位的角度精度,推荐用numpy.pi/180
- threshod: 累加平面的阈值参数,int类型,超过设定阈值才被检测出线段,值越大,基本上意味着检出的线段越长,检出的线段个数越少。
- minLineLength:线段以像素为单位的最小长度。
- maxLineGap:同一方向上两条线段判定为一条线段的最大允许间隔,超过了设定值,则把两条线段当成一条线段。
输出:
lines:一个三维矩阵,其形状符合 (m, 1, n),其中 m 表示直线个数,n 表示每条直线的两端坐标。

4、对每张图片进行上一步骤的处理后写入视频
4.1 定义视频格式
# 输出视频路径 pathOut = 'roads_v2.mp4' # 视频每秒的帧数 fps = 30.0 # 视频中每一帧的尺寸 height, width = img.shape size = (width,height) # 写入视频 out = cv2.VideoWriter(pathOut,cv2.VideoWriter_fourcc(*'DIVX'), fps, size)
4.2 处理所有图片并写入视频文件
for img in notebook.tqdm(col_images):
# 应用帧掩码
masked = cv2.bitwise_and(img[:,:,0], img[:,:,0], mask=stencil)
# 应用图像阈值化
ret, thresh = cv2.threshold(masked, 130, 145, cv2.THRESH_BINARY)
# 应用霍夫线变换
lines = cv2.HoughLinesP(thresh, 1, np.pi/180, 30, maxLineGap=200)
dmy = img.copy()
#画出检测到的线
try:
for line in lines:
x1, y1, x2, y2 = line[0]
cv2.line(dmy, (x1, y1), (x2, y2), (255, 0, 0), 3)
out.write(dmy)
except TypeError:
out.write(img)
out.release()
完整代码
import os
import re
import cv2
import numpy as np
from tqdm import notebook
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
col_frames = os.listdir('frames/')
col_frames.sort(key=lambda f: int(re.sub('\D', '', f)))
col_images=[]
for i in notebook.tqdm(col_frames):
img = cv2.imread('frames/'+i)
col_images.append(img)
stencil = np.zeros_like(col_images[0][:,:,0])
polygon = np.array([[50,270], [220,160], [360,160], [480,270]])
cv2.fillConvexPoly(stencil, polygon, 1)
pathOut = 'roads_v2.mp4'
fps = 30.0
height, width = img.shape
size = (width,height)
out = cv2.VideoWriter(pathOut,cv2.VideoWriter_fourcc(*'DIVX'), fps, size)
for img in notebook.tqdm(col_images):
masked = cv2.bitwise_and(img[:,:,0], img[:,:,0], mask=stencil)
ret, thresh = cv2.threshold(masked, 130, 145, cv2.THRESH_BINARY)
lines = cv2.HoughLinesP(thresh, 1, np.pi/180, 30, maxLineGap=200)
dmy = img.copy()
try:
for line in lines:
x1, y1, x2, y2 = line[0]
cv2.line(dmy, (x1, y1), (x2, y2), (255, 0, 0), 3)
out.write(dmy)
except TypeError:
out.write(img)
out.release()
加载全部内容