Python3.5 Pandas模块之Series用法实例分析
人气:1本文实例讲述了Python3.5 Pandas模块之Series用法。分享给大家供大家参考,具体如下:
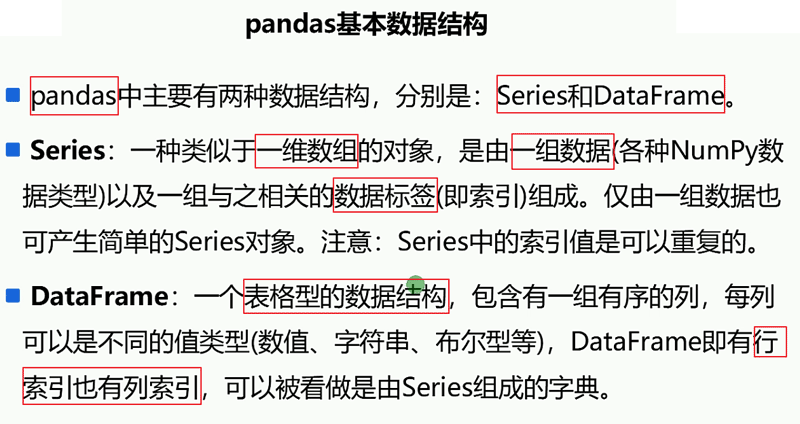
1、Pandas模块引入与基本数据结构

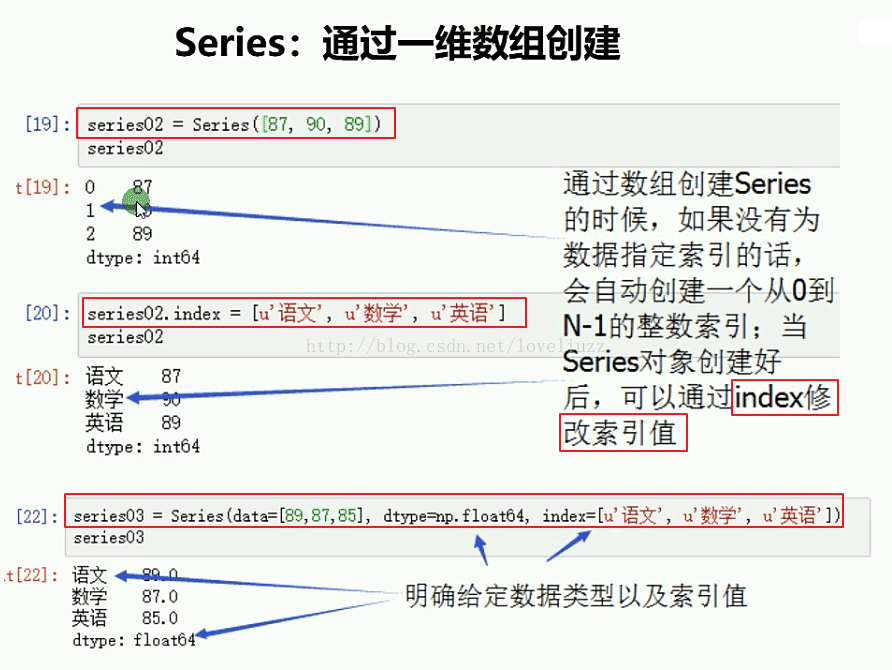
2、Series的创建

#!/usr/bin/env python
# -*- coding:utf-8 -*-
# Author:ZhengzhengLiu
#模块引入
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
from pandas import Series,DataFrame
#1.Series通过numpy一维数组创建
print("=========Series通过numpy一维数组创建==========")
arr = np.array([1,2,3,4,5])
s1 = pd.Series(arr)
print(s1)
print(s1.index)
print(s1.values)
#2.Series直接通过一维数组创建
print("=========Series直接通过一维数组创建==========")
s2 = pd.Series([10.5,20,38,40])
print(s2)
#修改索引值
s2.index = ['a','b','c','d']
print(s2)
#Series通过一维数组创建,可以在创建的同时自定义索引值,
# 也可以之后通过赋值的形式去修改
print("=========Series创建的同时自定义索引值和数据类型==========")
s3 = pd.Series(data=[89,78,90,87],dtype=np.float64,
index=['语文','数学','英语','科学'])
print(s3)
#3.Series通过字典创建,字典的键对应索引,值对应数据
print("=========Series通过字典创建==========")
dict = {'a':1,'b':2,"c":3,"d":4}
s4 = pd.Series(dict)
print(s4)
运行结果:
=========Series通过numpy一维数组创建==========
0 1
1 2
2 3
3 4
4 5
dtype: int32
RangeIndex(start=0, stop=5, step=1)
[1 2 3 4 5]
=========Series直接通过一维数组创建==========
0 10.5
1 20.0
2 38.0
3 40.0
dtype: float64
a 10.5
b 20.0
c 38.0
d 40.0
dtype: float64
=========Series创建的同时自定义索引值和数据类型==========
语文 89.0
数学 78.0
英语 90.0
科学 87.0
dtype: float64
=========Series通过字典创建==========
a 1
b 2
c 3
d 4
dtype: int64
3、Series值的获取

#模块引入
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
from pandas import Series,DataFrame
#4.Series值的获取
print("=========Series值的获取==========")
s2 = pd.Series([10.5,20,38,40])
#修改索引值
s2.index = ['a','b','c','d']
print(s2)
print(s2[0]) #方括号+下标值的形式获取Series值
print(s2["a"]) #方括号+索引的形式获取Series值
运行结果:
=========Series值的获取==========
a 10.5
b 20.0
c 38.0
d 40.0
dtype: float64
10.5
10.5
4、Series运算

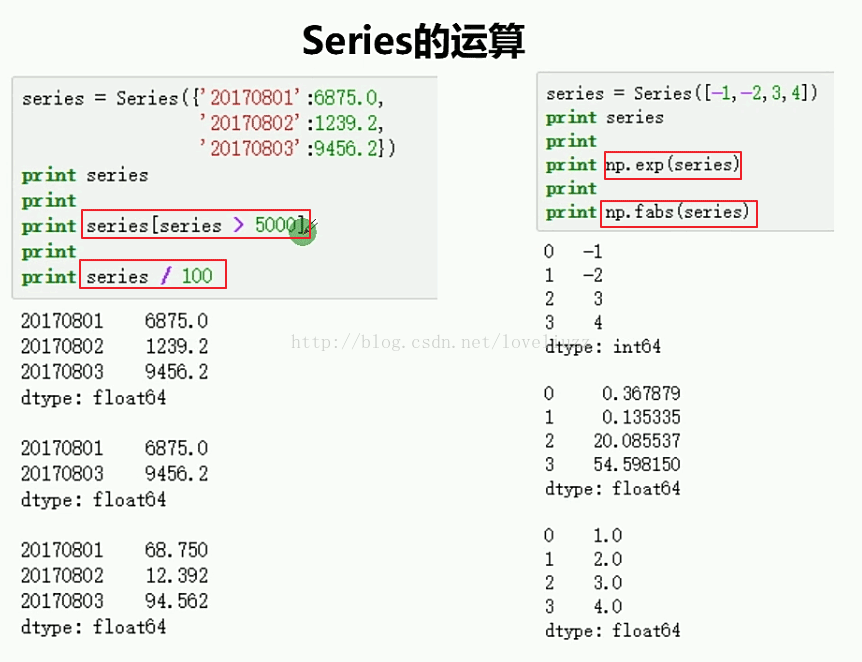
#模块引入
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
from pandas import Series,DataFrame
#5.Series值的运算
#Series中元素级别的运算结果,包含索引值并且键值关系保持不变
print("=========Series值的运算==========")
s6 = pd.Series({'a':1,'b':2,"c":3,"d":4})
print(s6)
print("=========打印Series大于2的值==========")
print(s6[s6>2])
print("=========打印Series的值除以2==========")
print(s6/2)
#numpy中的通用函数在Series中也支持
s7= pd.Series([1,2,-3,-4])
print(np.exp(s7))
运行结果:
=========Series值的运算==========
a 1
b 2
c 3
d 4
dtype: int64
=========打印Series大于2的值==========
c 3
d 4
dtype: int64
=========打印Series的值除以2==========
a 0.5
b 1.0
c 1.5
d 2.0
dtype: float64
0 2.718282
1 7.389056
2 0.049787
3 0.018316
dtype: float64
5、Series缺失值检验


#模块引入
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
from pandas import Series,DataFrame
#6.Series缺失值检验
scores = Series({"a":88,"b":79,"c":98,"d":100})
print(scores)
new = ["a","b","e","c","d"]
scores = Series(scores,index=new)
print(scores)
print("======过滤出为缺失值的项=======")
print(scores.isnull()) #NAN值返回True
#print(pd.isnull(scores)) #与上面一句等价
print("======过滤出为非缺失值的项=======")
print(pd.notnull(scores)) #非NAN值返回True
运行结果:
a 88
b 79
c 98
d 100
dtype: int64
a 88.0
b 79.0
e NaN
c 98.0
d 100.0
dtype: float64
======过滤出为缺失值的项=======
a False
b False
e True
c False
d False
dtype: bool
======过滤出为非缺失值的项=======
a True
b True
e False
c True
d True
dtype: bool
6、Series自动对齐
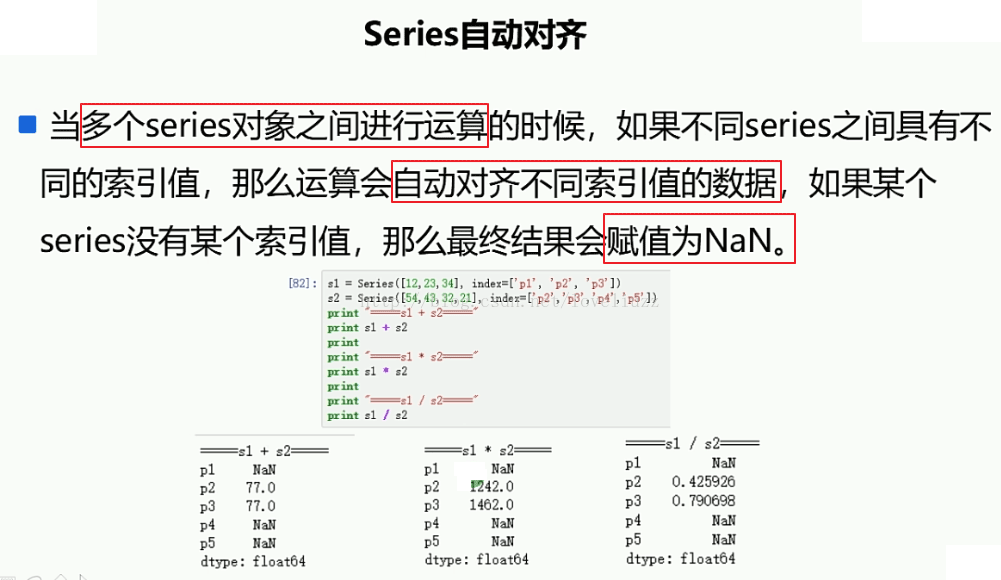
#模块引入
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
from pandas import Series,DataFrame
#7.Series自动对齐
s8 = Series([12,28,46],index=["p1","p2","p3"])
s9 = Series([2,4,6,8],index=["p2","p3","p4","p5"])
print("=======s8=======")
print(s8)
print("=======s9=======")
print(s9)
print("=======s8+s9=======")
print(s8+s9)
运行结果:
=======s8=======
p1 12
p2 28
p3 46
dtype: int64
=======s9=======
p2 2
p3 4
p4 6
p5 8
dtype: int64
=======s8+s9=======
p1 NaN
p2 30.0
p3 50.0
p4 NaN
p5 NaN
dtype: float64
7、Series及其索引的name属性
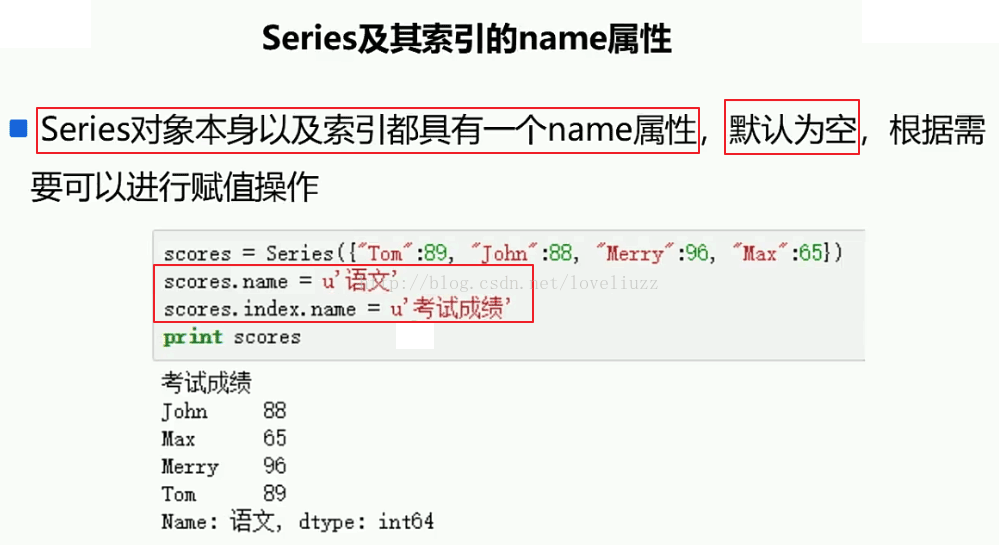
#模块引入
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
from pandas import Series,DataFrame
#8.Series及其name属性
s10 = Series({"jack":18,"amy":20,"lili":23,"susan":15})
print(s10)
print("=======设置name属性后=======")
s10.name = "年龄" #数据名称标签
s10.index.name = "姓名" #索引名称标签
print(s10)
运行结果:
amy 20
jack 18
lili 23
susan 15
dtype: int64
=======设置name属性后=======
姓名
amy 20
jack 18
lili 23
susan 15
Name: 年龄, dtype: int64
希望本文所述对大家Python程序设计有所帮助。
您可能感兴趣的文章:
加载全部内容