ScrollerView 上下滚动 android使用 ScrollerView 实现 可上下滚动的分类栏实例
李诗雨 人气:0想了解android使用 ScrollerView 实现 可上下滚动的分类栏实例的相关内容吗,李诗雨在本文为您仔细讲解ScrollerView 上下滚动的相关知识和一些Code实例,欢迎阅读和指正,我们先划重点:ScrollerView,上下滚动,scrollerview,滚动,下面大家一起来学习吧。
如果不考虑更深层的性能问题,我个人认为ScrollerView还是很好用的。而且单用ScrollerView就可以实现分类型的RecyclerView或ListView所能实现的效果。
下面我单单从效果展示方面考虑,使用ScrollerView实现如下图所示的可滚动的多条目分类,只是为了跟大家一起分享一下新思路。(平时:若从复用性等方面考虑,这显然是存在瑕疵的~)

特点描述:
1.可上下滚动
2.有类似于网格布局的样式
3.子条目具有点击事件
刚看到这个效果时,首先想到的是使用分类型的RecyclerView 或者 ListView ,里面再嵌套GridView来实现。
但转而又一想ScrollerView也可以滚动,只要往里面循环添加子item不就可以了吗。
实现的逻辑大致如下:
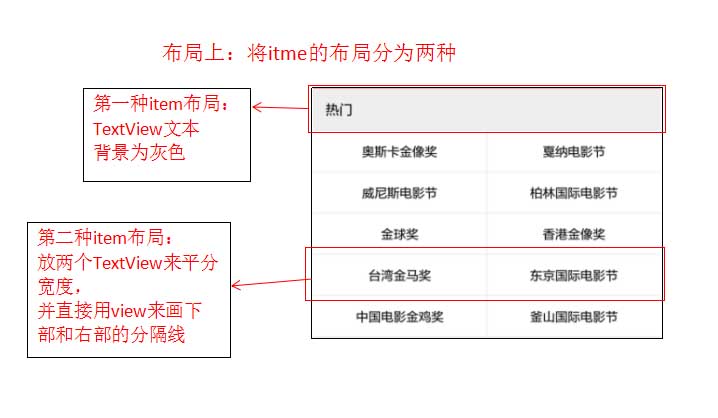
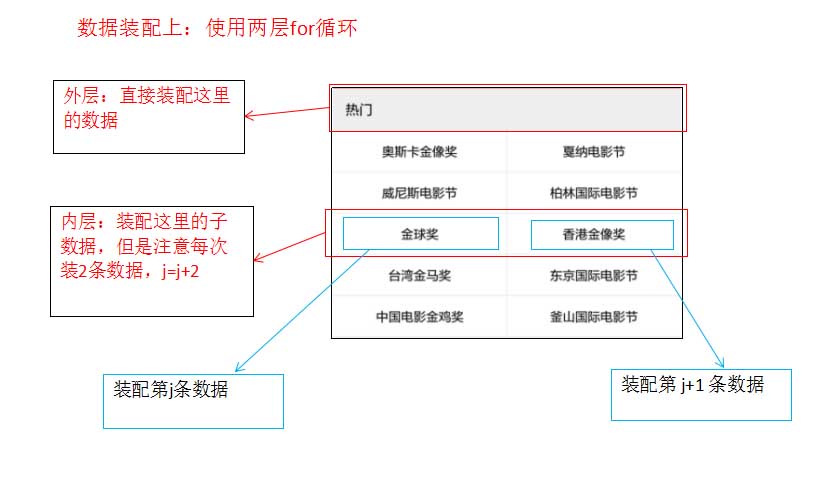
具体的实现如下:
第一步:布局里写一个ScrollerView,里面添加一个竖直的线性布局
第二步:实例化垂直线性布局
allhonor_hscroll = (LinearLayout) findViewById(R.id.allhonor_hscroll);
第三步:联网请求获取数据
setAllHonorData();
/**
* 使用okhttp
*/
public void setAllHonorData() {
OkHttpUtils
.get()
.url(url)
.build()
.execute(new StringCallback() {
@Override
public void onError(okhttp3.Call call, Exception e, int id) {
Log.e("TAG", "111");
Log.e("TAG", "onError" + e.getMessage());
}
@Override
public void onResponse(String response, int id) {
Log.e("TAG", "222");
Log.e("TAG", "onRespons" + response);
//联网成功后使用fastjson来解析数据
processData(response);
}
@Override
public void onBefore(Request request, int id) {
}
@Override
public void onAfter(int id) {
}
});
}
/**
* 使用fastjson进行解析
*
* @param json
*/
private void processData(String json) {
//使用GsonFormat生成对应的bean类
com.alibaba.fastjson.JSONObject jsonObject = JSON.parseObject(json);
String data = jsonObject.getString("data");
List<AllHonorBean.HornorBean> hornorsList = JSON.parseArray(data, AllHonorBean.HornorBean.class);
//测试是否解析数据成功
// String strTest = hornorsList.get(0).getRegion();
// Log.e("TAG", strTest);
//第四步:装配数据,使用两层for循环
}
第四步:设置两种item的布局
第一种item布局:item_allhornors0.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:background="#ffffff"
android:orientation="vertical">
<TextView
android:id="@+id/tv_allhornors_big"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:background="#11000000"
android:gravity="center_vertical"
android:paddingBottom="12dp"
android:paddingLeft="13dp"
android:paddingTop="12dp"
android:text="热门"
android:textColor="#000000"
android:textSize="14sp" />
<View
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="1dp"
android:background="#11000000" />
</LinearLayout>
第二种item布局:item_allhornors1.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:background="#ffffff"
android:orientation="vertical">
<LinearLayout
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:orientation="horizontal">
<TextView
android:id="@+id/tv_allhornors_sn0"
android:layout_width="0dp"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_weight="1"
android:clickable="true"
android:gravity="center"
android:paddingBottom="12sp"
android:paddingTop="12sp"
android:text="你好你好"
android:textColor="#000000"
android:textSize="13sp" />
<View
android:layout_width="1dp"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:background="#11000000" />
<!--注意这里的text文本一定要为空,不要设置任何内容-->
<TextView
android:id="@+id/tv_allhornors_sn1"
android:layout_width="0dp"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_weight="1"
android:clickable="true"
android:gravity="center"
android:paddingBottom="12sp"
android:paddingTop="12sp"
android:text=""
android:textColor="#000000"
android:textSize="13sp" />
</LinearLayout>
<View
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="1dp"
android:background="#11000000" />
</LinearLayout>
第五步:装配数据
if (hornorsList != null && hornorsList.size() > 0) {
//-->外层
for (int i = 0; i < hornorsList.size(); i++) {
//创建并添加第一种item布局
View globalView = View.inflate(this, R.layout.item_allhornors0, null);
TextView tv_allhornors_big = (TextView) globalView.findViewById(R.id.tv_allhornors_big);
AllHonorBean.HornorBean hornorsListBean = hornorsList.get(i);
String region = hornorsListBean.getRegion();
//外层for中直接装配数据
tv_allhornors_big.setText(region);
//将布局添加进去
allhonor_hscroll.addView(globalView);
List<AllHonorBean.HornorBean.FestivalsBean> festivalsList = hornorsListBean.getFestivals();
//-->内层,每次装两个数据
for (int j = 0; j < festivalsList.size(); j = j + 2) {
//创建并添加第二种item布局
View smallView = View.inflate(this, R.layout.item_allhornors1, null);
final TextView tv_sn0 = (TextView) smallView.findViewById(R.id.tv_allhornors_sn0);
TextView tv_sn1 = (TextView) smallView.findViewById(R.id.tv_allhornors_sn1);
//顺带在这里就直接添加点击事件的监听
if (j < festivalsList.size() - 1) {
setListener(tv_sn0, tv_sn1);
}
//装配左边的数据
honorName0 = festivalsList.get(j).getFestivalName();
tv_sn0.setText(honorName0);
//判读越界否
if (j < festivalsList.size() - 1) {
//装配右边的数据
honorName1 = festivalsList.get(j + 1).getFestivalName();
tv_sn1.setText(honorName1);
}
//添加进去
allhonor_hscroll.addView(smallView);
}
}
}
点击事件的监听:
private void setListener(final TextView tv_sn0, final TextView tv_sn1) {
//给左边的TextView 设置监听
tv_sn0.setOnClickListener(new View.OnClickListener() {
@Override
public void onClick(View view) {
Toast.makeText(MainActivity.this, "" + tv_sn0.getText(), Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show();
}
});
//给右边的TextView 设置监听
tv_sn1.setOnClickListener(new View.OnClickListener() {
@Override
public void onClick(View view) {
Toast.makeText(MainActivity.this, "" + tv_sn1.getText(), Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show();
}
});
}
完成~
再看一眼最后效果:

以上就是本文的全部内容,希望对大家的学习有所帮助,也希望大家多多支持。
加载全部内容