Lombok SpringBoot和IDEA Lombok为啥这么牛逼?SpringBoot和IDEA官方都要支持它
人气:0最近 IDEA 2020最后一个版本发布了 ,已经内置了Lombok插件,SpringBoot 2.1.x之后的版本也在Starter中内置了Lombok依赖。为什么他们都要支持Lombok呢?今天我来讲讲Lombok的使用,看看它有何神奇之处!
Lombok简介
Lombok是一款Java代码功能增强库,在Github上已有9.8k+Star。它会自动集成到你的编辑器和构建工具中,从而使你的Java代码更加生动有趣。通过Lombok的注解,你可以不用再写getter、setter、equals等方法,Lombok将在编译时为你自动生成。
Lombok集成
首先我们需要在IDEA中安装好Lombok插件,如果你使用的是最新版IDEA 2020.3,则Lombok插件已经内置,无需安装。
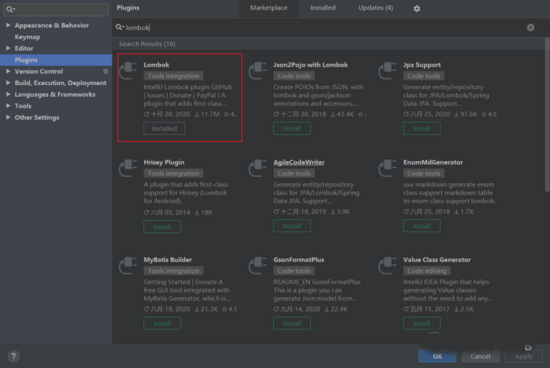
之后在项目的pom.xml文件中添加Lombok依赖,SpringBoot 2.1.x版本后无需指定Lombok版本,SpringBoot在 spring-boot-dependencies 中已经内置。
<!--lombok依赖--> <dependency> <groupId>org.projectlombok</groupId> <artifactId>lombok</artifactId> <optional>true</optional> </dependency>
Lombok使用
Lombok中有很多注解,这些注解使得我们可以更加方便的编写Java代码,下面介绍下这些注解的使用。
val
使用val注解可以取代任意类型作为局部变量,这样我们就不用写复杂的ArrayList和Map.Entry类型了,具体例子如下。
/**
* Created by macro on 2020/12/16.
*/
public class ValExample {
public static void example() {
//val代替ArrayList<String>和String类型
val example = new ArrayList<String>();
example.add("Hello World!");
val foo = example.get(0);
System.out.println(foo.toLowerCase());
}
public static void example2() {
//val代替Map.Entry<Integer,String>类型
val map = new HashMap<Integer, String>();
map.put(0, "zero");
map.put(5, "five");
for (val entry : map.entrySet()) {
System.out.printf("%d: %s\n", entry.getKey(), entry.getValue());
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
example();
example2();
}
}
当我们使用了val注解后,Lombok会从局部变量的初始化表达式推断出具体类型,编译后会生成如下代码。
public class ValExample {
public ValExample() {
}
public static void example() {
ArrayList<String> example = new ArrayList();
example.add("Hello World!");
String foo = (String)example.get(0);
System.out.println(foo.toLowerCase());
}
public static void example2() {
HashMap<Integer, String> map = new HashMap();
map.put(0, "zero");
map.put(5, "five");
Iterator var1 = map.entrySet().iterator();
while(var1.hasNext()) {
Entry<Integer, String> entry = (Entry)var1.next();
System.out.printf("%d: %s\n", entry.getKey(), entry.getValue());
}
}
}
@NonNull
在方法上使用@NonNull注解可以做非空判断,如果传入空值的话会直接抛出NullPointerException。
/**
* Created by macro on 2020/12/16.
*/
public class NonNullExample {
private String name;
public NonNullExample(@NonNull String name){
this.name = name;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
new NonNullExample("test");
//会抛出NullPointerException
new NonNullExample(null);
}
}
编译后会在构造器中添加非空判断,具体代码如下。
public class NonNullExample {
private String name;
public NonNullExample(@NonNull String name) {
if (name == null) {
throw new NullPointerException("name is marked non-null but is null");
} else {
this.name = name;
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
new NonNullExample("test");
new NonNullExample((String)null);
}
}
@Cleanup
当我们在Java中使用资源时,不可避免地需要在使用后关闭资源。使用@Cleanup注解可以自动关闭资源。
/**
* Created by macro on 2020/12/16.
*/
public class CleanupExample {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
String inStr = "Hello World!";
//使用输入输出流自动关闭,无需编写try catch和调用close()方法
@Cleanup ByteArrayInputStream in = new ByteArrayInputStream(inStr.getBytes("UTF-8"));
@Cleanup ByteArrayOutputStream out = new ByteArrayOutputStream();
byte[] b = new byte[1024];
while (true) {
int r = in.read(b);
if (r == -1) break;
out.write(b, 0, r);
}
String outStr = out.toString("UTF-8");
System.out.println(outStr);
}
}
编译后Lombok会生成如下代码。
public class CleanupExample {
public CleanupExample() {
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
String inStr = "Hello World!";
ByteArrayInputStream in = new ByteArrayInputStream(inStr.getBytes("UTF-8"));
try {
ByteArrayOutputStream out = new ByteArrayOutputStream();
try {
byte[] b = new byte[1024];
while(true) {
int r = in.read(b);
if (r == -1) {
String outStr = out.toString("UTF-8");
System.out.println(outStr);
return;
}
out.write(b, 0, r);
}
} finally {
if (Collections.singletonList(out).get(0) != null) {
out.close();
}
}
} finally {
if (Collections.singletonList(in).get(0) != null) {
in.close();
}
}
}
}
@Getter/@Setter
有了@Getter/@Setter注解,我们再也不用编写getter/setter方法了。试想下之前即使我们使用IDEA自动生成getter/setter方法,如果类属性的类型和名称改了,又要重新生成getter/setter方法也是一件很麻烦的事情。
/**
* Created by macro on 2020/12/17.
*/
public class GetterSetterExample {
@Getter
@Setter
private String name;
@Getter
@Setter(AccessLevel.PROTECTED)
private Integer age;
public static void main(String[] args) {
GetterSetterExample example = new GetterSetterExample();
example.setName("test");
example.setAge(20);
System.out.printf("name:%s age:%d",example.getName(),example.getAge());
}
}
编译后Lombok会生成如下代码。
public class GetterSetterExample {
private String name;
private Integer age;
public GetterSetterExample() {
}
public String getName() {
return this.name;
}
public void setName(final String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public Integer getAge() {
return this.age;
}
protected void setAge(final Integer age) {
this.age = age;
}
}
@ToString
把所有类属性都编写到toString方法中方便打印日志,是一件多么枯燥无味的事情。使用@ToString注解可以自动生成toString方法,默认会包含所有类属性,使用@ToString.Exclude注解可以排除属性的生成。
/**
* Created by macro on 2020/12/17.
*/
@ToString
public class ToStringExample {
@ToString.Exclude
private Long id;
private String name;
private Integer age;
public ToStringExample(Long id,String name,Integer age){
this.id =id;
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
ToStringExample example = new ToStringExample(1L,"test",20);
//自动实现toString方法,输出ToStringExample(name=test, age=20)
System.out.println(example);
}
}
编译后Lombok会生成如下代码。
public class ToStringExample {
private Long id;
private String name;
private Integer age;
public ToStringExample(Long id, String name, Integer age) {
this.id = id;
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
}
public String toString() {
return "ToStringExample(name=" + this.name + ", age=" + this.age + ")";
}
}
@EqualsAndHashCode
使用@EqualsAndHashCode注解可以自动生成hashCode和equals方法,默认包含所有类属性,使用@EqualsAndHashCode.Exclude可以排除属性的生成。
/**
* Created by macro on 2020/12/17.
*/
@Getter
@Setter
@EqualsAndHashCode
public class EqualsAndHashCodeExample {
private Long id;
@EqualsAndHashCode.Exclude
private String name;
@EqualsAndHashCode.Exclude
private Integer age;
public static void main(String[] args) {
EqualsAndHashCodeExample example1 = new EqualsAndHashCodeExample();
example1.setId(1L);
example1.setName("test");
example1.setAge(20);
EqualsAndHashCodeExample example2 = new EqualsAndHashCodeExample();
example2.setId(1L);
//equals方法只对比id,返回true
System.out.println(example1.equals(example2));
}
}
编译后Lombok会生成如下代码。
public class EqualsAndHashCodeExample {
private Long id;
private String name;
private Integer age;
public EqualsAndHashCodeExample() {
}
public boolean equals(final Object o) {
if (o == this) {
return true;
} else if (!(o instanceof EqualsAndHashCodeExample)) {
return false;
} else {
EqualsAndHashCodeExample other = (EqualsAndHashCodeExample)o;
if (!other.canEqual(this)) {
return false;
} else {
Object this$id = this.getId();
Object other$id = other.getId();
if (this$id == null) {
if (other$id != null) {
return false;
}
} else if (!this$id.equals(other$id)) {
return false;
}
return true;
}
}
}
protected boolean canEqual(final Object other) {
return other instanceof EqualsAndHashCodeExample;
}
public int hashCode() {
int PRIME = true;
int result = 1;
Object $id = this.getId();
int result = result * 59 + ($id == null ? 43 : $id.hashCode());
return result;
}
}
@XxConstructor
使用@XxConstructor注解可以自动生成构造方法,有@NoArgsConstructor、@RequiredArgsConstructor和@AllArgsConstructor三个注解可以使用。
- @NoArgsConstructor:生成无参构造函数。
- @RequiredArgsConstructor:生成包含必须参数的构造函数,使用@NonNull注解的类属性为必须参数。
- @AllArgsConstructor:生成包含所有参数的构造函数。
/**
* Created by macro on 2020/12/17.
*/
@NoArgsConstructor
@RequiredArgsConstructor(staticName = "of")
@AllArgsConstructor
public class ConstructorExample {
@NonNull
private Long id;
private String name;
private Integer age;
public static void main(String[] args) {
//无参构造器
ConstructorExample example1 = new ConstructorExample();
//全部参数构造器
ConstructorExample example2 = new ConstructorExample(1L,"test",20);
//@NonNull注解的必须参数构造器
ConstructorExample example3 = ConstructorExample.of(1L);
}
}
编译后Lombok会生成如下代码。
public class ConstructorExample {
@NonNull
private Long id;
private String name;
private Integer age;
public ConstructorExample() {
}
private ConstructorExample(@NonNull final Long id) {
if (id == null) {
throw new NullPointerException("id is marked non-null but is null");
} else {
this.id = id;
}
}
public static ConstructorExample of(@NonNull final Long id) {
return new ConstructorExample(id);
}
public ConstructorExample(@NonNull final Long id, final String name, final Integer age) {
if (id == null) {
throw new NullPointerException("id is marked non-null but is null");
} else {
this.id = id;
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
}
}
}
@Data
@Data是一个方便使用的组合注解,是@ToString、@EqualsAndHashCode、@Getter、@Setter和@RequiredArgsConstructor的组合体。
/**
* Created by macro on 2020/12/17.
*/
@Data
public class DataExample {
@NonNull
private Long id;
@EqualsAndHashCode.Exclude
private String name;
@EqualsAndHashCode.Exclude
private Integer age;
public static void main(String[] args) {
//@RequiredArgsConstructor已生效
DataExample example1 = new DataExample(1L);
//@Getter @Setter已生效
example1.setName("test");
example1.setAge(20);
//@ToString已生效
System.out.println(example1);
DataExample example2 = new DataExample(1L);
//@EqualsAndHashCode已生效
System.out.println(example1.equals(example2));
}
}
编译后Lombok会生成如下代码。
public class DataExample {
@NonNull
private Long id;
private String name;
private Integer age;
public DataExample(@NonNull final Long id) {
if (id == null) {
throw new NullPointerException("id is marked non-null but is null");
} else {
this.id = id;
}
}
@NonNull
public Long getId() {
return this.id;
}
public String getName() {
return this.name;
}
public Integer getAge() {
return this.age;
}
public void setId(@NonNull final Long id) {
if (id == null) {
throw new NullPointerException("id is marked non-null but is null");
} else {
this.id = id;
}
}
public void setName(final String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public void setAge(final Integer age) {
this.age = age;
}
public boolean equals(final Object o) {
if (o == this) {
return true;
} else if (!(o instanceof DataExample)) {
return false;
} else {
DataExample other = (DataExample)o;
if (!other.canEqual(this)) {
return false;
} else {
Object this$id = this.getId();
Object other$id = other.getId();
if (this$id == null) {
if (other$id != null) {
return false;
}
} else if (!this$id.equals(other$id)) {
return false;
}
return true;
}
}
}
protected boolean canEqual(final Object other) {
return other instanceof DataExample;
}
public int hashCode() {
int PRIME = true;
int result = 1;
Object $id = this.getId();
int result = result * 59 + ($id == null ? 43 : $id.hashCode());
return result;
}
public String toString() {
return "DataExample(id=" + this.getId() + ", name=" + this.getName() + ", age=" + this.getAge() + ")";
}
}
@Value
使用@Value注解可以把类声明为不可变的,声明后此类相当于final类,无法被继承,其属性也会变成final属性。
/**
* Created by macro on 2020/12/17.
*/
@Value
public class ValueExample {
private Long id;
private String name;
private Integer age;
public static void main(String[] args) {
//只能使用全参构造器
ValueExample example = new ValueExample(1L,"test",20);
// example.setName("andy") //没有生成setter方法,会报错
// example.name="andy" //字段被设置为final类型,会报错
}
}
编译后Lombok会生成如下代码。
public final class ValueExample {
private final Long id;
private final String name;
private final Integer age;
public static void main(String[] args) {
new ValueExample(1L, "test", 20);
}
public ValueExample(final Long id, final String name, final Integer age) {
this.id = id;
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
}
public Long getId() {
return this.id;
}
public String getName() {
return this.name;
}
public Integer getAge() {
return this.age;
}
}
@Builder
使用@Builder注解可以通过建造者模式来创建对象,建造者模式加链式调用,创建对象太方便了!
/**
* Created by macro on 2020/12/17.
*/
@Builder
@ToString
public class BuilderExample {
private Long id;
private String name;
private Integer age;
public static void main(String[] args) {
BuilderExample example = BuilderExample.builder()
.id(1L)
.name("test")
.age(20)
.build();
System.out.println(example);
}
}
编译后Lombok会生成如下代码。
public class BuilderExample {
private Long id;
private String name;
private Integer age;
BuilderExample(final Long id, final String name, final Integer age) {
this.id = id;
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
}
public static BuilderExample.BuilderExampleBuilder builder() {
return new BuilderExample.BuilderExampleBuilder();
}
public String toString() {
return "BuilderExample(id=" + this.id + ", name=" + this.name + ", age=" + this.age + ")";
}
public static class BuilderExampleBuilder {
private Long id;
private String name;
private Integer age;
BuilderExampleBuilder() {
}
public BuilderExample.BuilderExampleBuilder id(final Long id) {
this.id = id;
return this;
}
public BuilderExample.BuilderExampleBuilder name(final String name) {
this.name = name;
return this;
}
public BuilderExample.BuilderExampleBuilder age(final Integer age) {
this.age = age;
return this;
}
public BuilderExample build() {
return new BuilderExample(this.id, this.name, this.age);
}
public String toString() {
return "BuilderExample.BuilderExampleBuilder(id=" + this.id + ", name=" + this.name + ", age=" + this.age + ")";
}
}
}
@SneakyThrows
还在手动捕获并抛出异常?使用@SneakyThrows注解自动实现试试!
/**
* Created by macro on 2020/12/17.
*/
public class SneakyThrowsExample {
//自动抛出异常,无需处理
@SneakyThrows(UnsupportedEncodingException.class)
public static byte[] str2byte(String str){
return str.getBytes("UTF-8");
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
String str = "Hello World!";
System.out.println(str2byte(str).length);
}
}
编译后Lombok会生成如下代码。
public class SneakyThrowsExample {
public SneakyThrowsExample() {
}
public static byte[] str2byte(String str) {
try {
return str.getBytes("UTF-8");
} catch (UnsupportedEncodingException var2) {
throw var2;
}
}
}
@Synchronized
当我们在多个线程中访问同一资源时,往往会出现线程安全问题,以前我们往往使用synchronized关键字修饰方法来实现同步访问。使用@Synchronized注解同样可以实现同步访问。
package com.macro.mall.tiny.example;
import lombok.*;
/**
* Created by macro on 2020/12/17.
*/
@Data
public class SynchronizedExample {
@NonNull
private Integer count;
@Synchronized
@SneakyThrows
public void reduceCount(Integer id) {
if (count > 0) {
Thread.sleep(500);
count--;
System.out.println(String.format("thread-%d count:%d", id, count));
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
//添加@Synchronized三个线程可以同步调用reduceCount方法
SynchronizedExample example = new SynchronizedExample(20);
new ReduceThread(1, example).start();
new ReduceThread(2, example).start();
new ReduceThread(3, example).start();
}
@RequiredArgsConstructor
static class ReduceThread extends Thread {
@NonNull
private Integer id;
@NonNull
private SynchronizedExample example;
@Override
public void run() {
while (example.getCount() > 0) {
example.reduceCount(id);
}
}
}
}
编译后Lombok会生成如下代码。
public class SynchronizedExample {
private final Object $lock = new Object[0];
@NonNull
private Integer count;
public void reduceCount(Integer id) {
try {
synchronized(this.$lock) {
if (this.count > 0) {
Thread.sleep(500L);
Integer var3 = this.count;
Integer var4 = this.count = this.count - 1;
System.out.println(String.format("thread-%d count:%d", id, this.count));
}
}
} catch (Throwable var7) {
throw var7;
}
}
}
@With
使用@With注解可以实现对原对象进行克隆,并改变其一个属性,使用时需要指定全参构造方法。
@With
@AllArgsConstructor
public class WithExample {
private Long id;
private String name;
private Integer age;
public static void main(String[] args) {
WithExample example1 = new WithExample(1L, "test", 20);
WithExample example2 = example1.withAge(22);
//将原对象进行clone并设置age,返回false
System.out.println(example1.equals(example2));
}
}
编译后Lombok会生成如下代码。
public class WithExample {
private Long id;
private String name;
private Integer age;
public WithExample withId(final Long id) {
return this.id == id ? this : new WithExample(id, this.name, this.age);
}
public WithExample withName(final String name) {
return this.name == name ? this : new WithExample(this.id, name, this.age);
}
public WithExample withAge(final Integer age) {
return this.age == age ? this : new WithExample(this.id, this.name, age);
}
public WithExample(final Long id, final String name, final Integer age) {
this.id = id;
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
}
}
@Getter(lazy=true)
当我们获取某一个属性比较消耗资源时,可以给@Getter添加 lazy=true 属性实现懒加载,会生成Double Check Lock 样板代码对属性进行懒加载。
/**
* Created by macro on 2020/12/17.
*/
public class GetterLazyExample {
@Getter(lazy = true)
private final double[] cached = expensive();
private double[] expensive() {
double[] result = new double[1000000];
for (int i = 0; i < result.length; i++) {
result[i] = Math.asin(i);
}
return result;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
//使用Double Check Lock 样板代码对属性进行懒加载
GetterLazyExample example = new GetterLazyExample();
System.out.println(example.getCached().length);
}
}
编译后Lombok会生成如下代码。
public class GetterLazyExample {
private final AtomicReference<Object> cached = new AtomicReference();
public GetterLazyExample() {
}
private double[] expensive() {
double[] result = new double[1000000];
for(int i = 0; i < result.length; ++i) {
result[i] = Math.asin((double)i);
}
return result;
}
public double[] getCached() {
Object value = this.cached.get();
if (value == null) {
synchronized(this.cached) {
value = this.cached.get();
if (value == null) {
double[] actualValue = this.expensive();
value = actualValue == null ? this.cached : actualValue;
this.cached.set(value);
}
}
}
return (double[])((double[])(value == this.cached ? null : value));
}
}
@Log
使用@Log注解,可以直接生成日志对象log,通过log对象可以直接打印日志。
/**
* Created by macro on 2020/12/17.
*/
@Log
public class LogExample {
public static void main(String[] args) {
log.info("level info");
log.warning("level warning");
log.severe("level severe");
}
}
编译后Lombok会生成如下代码。
public class LogExample {
private static final Logger log = Logger.getLogger(LogExample.class.getName());
public LogExample() {
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
log.info("level info");
log.warning("level warning");
log.severe("level severe");
}
}
@Slf4j
使用Lombok生成日志对象时,根据使用日志实现的不同,有多种注解可以使用。比如@Log、@Log4j、@Log4j2、@Slf4j等。
/**
* Created by macro on 2020/12/17.
*/
@Slf4j
public class LogSlf4jExample {
public static void main(String[] args) {
log.info("level:{}","info");
log.warn("level:{}","warn");
log.error("level:{}", "error");
}
}
编译后Lombok会生成如下代码。
public class LogSlf4jExample {
private static final Logger log = LoggerFactory.getLogger(LogSlf4jExample.class);
public LogSlf4jExample() {
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
log.info("level:{}", "info");
log.warn("level:{}", "warn");
log.error("level:{}", "error");
}
}
Lombok原理
如果IDEA不安装Lombok插件的话,我们打开使用Lombok的项目是无法通过编译的。装了以后IDEA才会提示我们Lombok为我们生成的方法和属性。
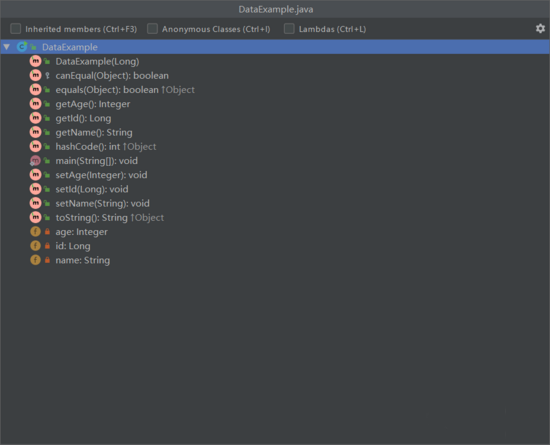
使用了@Data注解以后,查看类结构可以发现getter、setter、toString等方法。
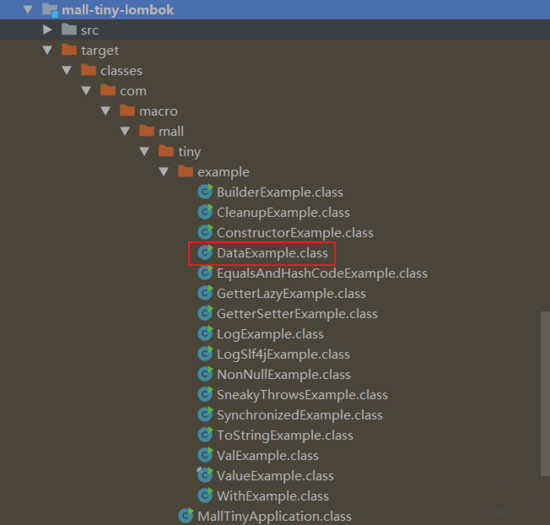
打开target目录下的 .class 文件,我们可以看到Lombok为我们生成的代码,可见Lombok是通过解析注解,然后在编译时生成代码来实现Java代码的功能增强的。
参考资料
官方文档:http://projectlombok.org/features/all
项目源码地址
https://github.com/macrozheng/mall-learning/tree/master/mall-tiny-lombok
加载全部内容