浅析Node.js查找字符串功能
人气:0需求如下:
整个目录下大概有40几M,文件无数,由于时间久了, 记不清那个字符串具体在哪个文件,于是。强大,亮瞎双眼的Node.js闪亮登场:
windows下安装Node.js和安装普通软件毫无差别,装完后打开Node.js的快捷方式,或者直接cmd,你懂的。
创建findString.js
var path = require("path");
var fs = require("fs");
var filePath = process.argv[2];
var lookingForString = process.argv[3];
recursiveReadFile(filePath);
function recursiveReadFile(fileName){
if(!fs.existsSync(fileName)) return;
if(isFile(fileName)){
check(fileName);
}
if(isDirectory(fileName)){
var files = fs.readdirSync(fileName);
files.forEach(function(val,key){
var temp = path.join(fileName,val);
if(isDirectory(temp)) recursiveReadFile(temp);
if (isFile(temp)) check(temp);
})
}
}
function check(fileName){
var data = readFile(fileName);
var exc = new RegExp(lookingForString);
if(exc.test(data))
console.log(fileName);
}
function isDirectory(fileName){
if(fs.existsSync(fileName)) return fs.statSync(fileName).isDirectory();
}
function isFile(fileName){
if(fs.existsSync(fileName)) return fs.statSync(fileName).isFile();
}
function readFile(fileName){
if(fs.existsSync(fileName)) return fs.readFileSync(fileName,"utf-8");
}
两个参数:第一个参数为“文件夹名称” 第二个参数为“你要查找的字符串”
如图:
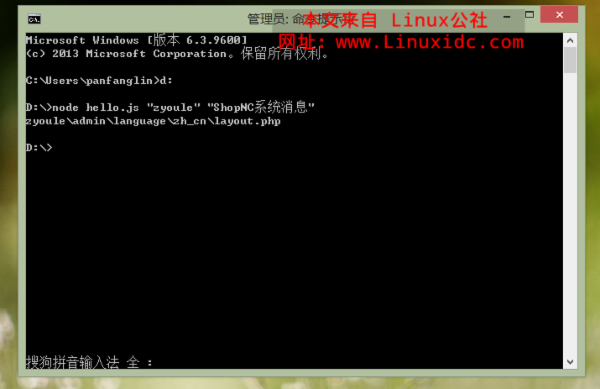
打印出文件路径,完事,收工。速度实在是彪悍,亮瞎双眼。。。如果采用java全文搜索,你惨了...
Nodejs查找,读写文件
(1),路径处理
1.首先,我们需要注意的文件路径的规范化,nodejs给我们提供了Path模块,normolize方法能帮我们规范化路径:
var path = require('path');
path.normalize('/foo/bar/nor/faz/..'); -> /foo/bar/nor
2.当然还有join合并路径:
var path = require('path');
path.join('/foo', 'bar', 'baz/asdf', 'quux', '..'); ->/foo/bar/baz/asdf
3.解析路径
var path = require('path');
path.resolve('/foo/bar', './baz'); ->/foo/bar/baz
path.resolve('/foo/bar', '/tmp/file/'); ->/tmp/file
4.在两个相对路径间查找相对路径
var path = require('path');
path.relative('https://img.qb5200.com/download-x/data/orandea/test/aaa', 'https://img.qb5200.com/download-x/data/orandea/impl/bbb'); ->../../impl/bbb
5.抽离路径
var path = require('path');
path.dirname('/foo/bar/baz/asdf/quux.txt'); ->/foo/bar/baz/asdf
=================
var path = require('path');
path.basename('/foo/bar/baz/asdf/quux.html') ->quux.html
甚至你还还可以将后缀名去掉,只需要在basename中传入第二个参数,参数为后缀名,例如:
var path = require('path');
path.basename('/foo/bar/baz/asdf/quux.html', '.html'); ->quux
当然文件路径中可能会存在各种不同的文件,我们不可能硬编码后缀来得到我们想要的结果,
所以有一个方法能帮我们得到后缀名:
path.extname('/a/b/index.html'); // => '.html'
path.extname('/a/b.c/index'); // => ''
path.extname('/a/b.c/.'); // => ''
path.extname('/a/b.chttps://img.qb5200.com/download-x/d.'); // => '.'
(2),文件处理
var fs = require('fs');
1.判断文件是否存在
fs.exists(path, function(exists) {});
上面的接口为异步操作的,因此有回调函数,在回调中可以处理我们的各种操作,如果需要同步操作可以用下面的方法:
fs.existsSync(path);
2.读取文件状态信息
fs.stat(path, function(err, stats) {
if (err) { throw err;}
console.log(stats);
});
控制台输出states的内容大致如下:
{ dev: 234881026,
ino: 95028917,
mode: 33188,
nlink: 1,
uid: 0,
gid: 0,
rdev: 0,
size: 5086,
blksize: 4096,
blocks: 0,
atime: Fri, 18 Nov 2011 22:44:47 GMT,
mtime: Thu, 08 Sep 2011 23:50:04 GMT,
ctime: Thu, 08 Sep 2011 23:50:04 GMT }
同时,stats还具有一些方法,比如:
stats.isFile();
stats.isDirectory();
stats.isBlockDevice();
stats.isCharacterDevice();
stats.isSymbolicLink();
stats.isFifo();
stats.isSocket();
.读写文件
fs.open('/path/to/file', 'r', function(err, fd) {
// todo
});
第二个参数为操作类型:
r : 只读
r+ : 读写
w : 重写文件
w+ : 重写文件,如果文件不存在则创建
a : 读写文件,在文件末尾追加
a+ : 读写文件,如果文件不存在则创建
下面为一个读取文件的小例子:
var fs = require('fs');
fs.open('./nodeRead.html', 'r', function opened(err, fd) {
if (err) { throw err }
var readBuffer = new Buffer(1024),
bufferOffset = 0,
bufferLength = readBuffer.length,
filePosition = 100;
fs.read(fd,
readBuffer,
bufferOffset,
bufferLength,
filePosition,
function read(err, readBytes) {
if (err) { throw err; }
console.log('just read ' + readBytes + ' bytes');
if (readBytes > 0) {
console.log(readBuffer.slice(0, readBytes));
}
});
});
下面为一个写文件的小例子:
var fs = require('fs');
fs.open('./my_file.txt', 'a', function opened(err, fd) {
if (err) { throw err; }
var writeBuffer = new Buffer('hello, world!'),
bufferPosition = 0,
bufferLength = writeBuffer.length, filePosition = null;
fs.write( fd,
writeBuffer,
bufferPosition,
bufferLength,
filePosition,
function(err, written) {
if (err) { throw err; }
console.log('wrote ' + written + ' bytes');
});
});
对于文件的读写操作,我们不应该忘记在这些操作都完成之后执行关闭操作,即close(); 下面是一个封装的方法,其中就包括了文件的后期关闭操作,使用起来方便:
var fs = require('fs');
function openAndWriteToSystemLog(writeBuffer, callback) {
fs.open('./my_file', 'a', function(err, fd) {
if (err) { return callback(err); }
function notifyError(err) {
fs.close(fd, function() {
callback(err);
});
}
var bufferOffset = 0,
bufferLength = writeBuffer.length,
filePosition = null;
fs.write( fd, writeBuffer, bufferOffset, bufferLength, filePosition,function(err, written) {
if (err) { return notifyError(err); }
fs.close(fd, function() {
callback(err);
});
});
});
}
openAndWriteToSystemLog(new Buffer('writing this string'),function(err) {
if (err) {
console.log("error while opening and writing:", err.message);
return;
}
console.log('All done with no errors');
});
加载全部内容