vue2.x双向数据绑定原理解析
不叫猫先生 人气:0前言
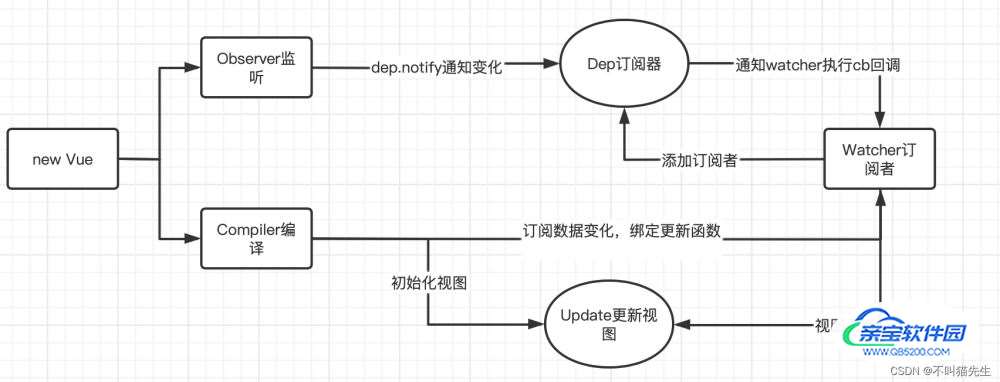
双向数据绑定原理主要运用了发布订阅模式来实现的,通过Object.defineProperty对数据劫持,触发getter,setter方法。数据变化时通知订阅者watcher触发回调视图更新。主要有四个重要的角色:
- 监听器Observer:劫持并监听所有属性,如果有变动的,就通知订阅者。
- 订阅器 Dep:收集订阅者,对监听器 Observer 和 订阅者 Watcher 进行统一管理
- 订阅者Watcher:收到属性的变化通知并执行相应的函数,从而更新视图。
- 解析器Compile:扫描和解析每个节点的相关指令,并根据初始化模板数据以及初始化相应的订阅器
一、index.html文件
写一个简易的vue代码,实例化Vue
<script type="module">
import { Vue } from "./vue.js "
let vm = new Vue({
el: document.querySelector('#app'),
data: {
message: "Hello,luyu",
num: "33"
},
methods: {
increase() {
this.num++;
},
}
})
</script>
<div id="app">
<h1>{{message}}</h1>
<h2>{{num}}</h2>
<input type="text" v-model="message">
<input type="text" v-model="num">
<button v-on:click="increase">【+】</button>
</div>二、vue.js文件
在vue的原型对象添加_init方法进行初始化,主要干这几件事:
- 接受传过来的
options,并声明$options,$el,$data,$methods - proxy代理,代理什么?
this.$data代理为this,这样我们直接就可以this.变量值 - observer对data数据进行监听,变成响应式数据
- compiler编译代码
export function Vue(options = {}) {
this._init(options)
}
Vue.prototype._init = function (options) {
this.$options = options;
//假设这里就是一个el,已经querySelector
this.$el = options.el;
this.$data = options.data;
this.$methods = options.methods;
// beforeCreate--initState--initData
proxy(this, this.$data)
//observer()
observer(this.$data)//对data监听,对data中数据变成响应式
new Compiler(this);
}1.proxy代理发生了什么?
proxy接收两个参数,一个是this(vue实例化对象),一个是需要代理的对象(this.$data),举个例子来说就是不使用this. $options.message了,直接使用 this.message获取数据。主要通过Object.defineProperty数据劫持,触发属性的getter或者setter方法。当然数据为NaN时,则不继续执行,故需要写一个方法进行判断。
// 把this.$data 代理到 this
function proxy(target, data) {
Object.keys(data).forEach(key => {
Object.defineProperty(target, key, {
enumerable: true,
configurable: true,
get() {
return data[key]
},
set(newValue) {
//需要考虑NaN的情况,故需要修改以下代码
// if (data[key] !== newValue) data[key] = newValue
if (!isSameVal(data[key], newValue)) data[key] = newValue;
},
})
})
}
function isSameVal (val,newVal){
//如果新值=旧值或者新值、旧值有一个为NaN,则不继续执行
return val === newVal || (Number.isNaN(val)) && (Number.isNaN(newVal))
}2.observer监听数据
对data数据进监听,考虑到数据有嵌套,如果数据类型为object则需要递归循环遍历监听数据,一个非常出名的监听方法为defineReactive,接收三个参数,一个数据data,一个属性key,一个数值data[key]。那么observer监听数据主要做了什么事?
- 初始化:递归循环数据,批量进行响应式处理
- 获取数据时:收集依赖,每一个响应式数据都有一个依赖,把依赖添加到dep中。
- 修改数据时:新增加的数据也不是响应式的,所以需要walk一下,将新增加的数据变成响应式。比如:this.A={name:'zhangsan'},然后修改后变成this.A = {age:18},刚开始A的值已经做过响应式了,但是修改后的值没有,所以需要进行walk一下。另外数据修改更新后,需要通知watcher进行页面更新渲染。
function observer(data) {
new Observer(data)
}
// 对data监听,把数据变成响应式
class Observer {
constructor(data) {
this.walk(data)
}
//批量对数据进行监听
walk(data) {
if (data && typeof data === 'object') {
Object.keys(data).forEach(key => this.defineReactive(data, key, data[key]))
}
}
//把每一个data里面的数据收集起来
defineReactive(obj, key, value) {
let that = this;
this.walk(value);//递归
let dep = new Dep();
Object.defineProperty(obj, key, {
configurable: true,
enumerable: true,
get() {
// 4一旦获取数据,把watcher收集起来,给每一个数据加一个依赖的收集
//5num中的dep,就有了这个watcher
console.log(Dep.target, 'Dep.target')
Dep.target && dep.add(Dep.target)
return value
},
set(newValue) {
if (!isSameVal(value, newValue)) {
value = newValue;
//添加的新值也不是响应式的,所以需要调用walk
that.walk(newValue);
//有了watcher之后,修改时就可以调用update方法
//6 重新set时就通知更新
dep.notify()
}
}
})
}
}
3.订阅者Watcher
数据改变需要通知视图层进行更新,更新仅需要调用Watcher中的update方法,然后执行cb(视图更新回调函数)。Watcher干了啥事?
- 初始化:获取vue实例vm,属性key,回调cb。注册全局变量Dep.target=this,this即Watcher本身,缓存vm[key],this._old=vm[key]表达式会执行属性key的getter方法,getter方法为该属性添加依赖,放到dep中,每一个属性都会有一个依赖。
- 数据更新时:调用update方法,执行回调cb
// watcher和dep的组合就是发布订阅者模式
// 视图更新
// 数据改变,视图才会更新,需要去观察
// 1 new Watcher(vm, 'num', () => { 更新视图上的num显示 })
class Watcher {
constructor(vm, key, cb) {
this.vm = vm;
this.key = key;
this.cb = cb;//试图更新的函数
Dep.target = this;//2.全局变量,放的就是Watcher自己
//
console.log(vm[key], 'vm[key]')
this.__old = vm[key];//3.一旦进行了这句赋值。就会触发这个值得getter,会执行Observer中的get方法
Dep.target = null;
}
//执行所有的cb函数
update() {
let newVal = this.vm[this.key];
if (!isSameVal(newVal, this.__old)) this.cb(newVal)
}
}4.订阅器Dep
属性变化可能是多个,所以就需要一个订阅器来收集这些订阅者。Dep主要完成什么工作?
- 初始化:new set 初始化watchers
- 获取数据时:当Dep.target && dep.add(Dep.target)成立时,执行add,收集订阅者。其中Dep.target指的是Watcher本身,Watcher中含有update方法。
- 数据更新时:调用notify方法,所有的watcher都执行update方法
// 每一个数据都要有一个 dep 的依赖
class Dep {
constructor() {
this.watchers = new Set();
}
add(watcher) {
console.log(watcher, 'watcher')
if (watcher && watcher.update) this.watchers.add(watcher)
}
//7让所有的watcher执行update方法
notify() {
console.log('333333')
console.log(this.watchers, 'watchers')
this.watchers.forEach(watc => watc.update())
}
}5.编译器Compiler
编译器主要的工作是递归编译#app下的所有节点内容。主要做了以下几件事:
- 初始化:获取vm,并对挂载元素进行处理,分为文本节点处理,元素节点处理
- 文本节点处理:当挂载节点是文本节点的话,判断node.textContent是否有{{}},RegExp.$1取出双括号包裹的属性名。然后通过replace进行正则替换,用vm[key]取代之前的node.textContent内容。
- 元素节点处理:当挂载节点是元素节点的话,可能会有多个,所以需要循环处理。匹配到以v-开头的指令时获取它的值value,然后进行update更新,本文里的更新有两种,一种是针对以v-开头属性值为model,另一种是针对v-开头的属性值为click。
- model:先对node.value进行赋值,然后再对赋的值进行响应式处理
- click:注册监听函数,执行click事件。
初始化编译器流程图如下所示:

数据修改时,因为初始化已经对数据做了响应式处理,所以当修改数据时,首先会走observer中的get方法,由于初始化已经对该数据进行监听,添加了watcher,并且此时Dep.target为null,所以不会再次收集订阅者信息,而是去通知视图进行更新,走了set中的notify,notify去通知所有的watcher去执行update方法。流程图如下所示:

class Compiler {
constructor(vm) {
this.el = vm.$el;
this.vm = vm;
this.methods = vm.$methods;
// console.log(vm.$methods, 'vm.$methods')
this.compile(vm.$el)
}
compile(el) {
let childNodes = el.childNodes;
//childNodes为类数组
Array.from(childNodes).forEach(node => {
if (node.nodeType === 3) {
this.compileText(node)
} else if (node.nodeType === 1) {
this.compileElement(node)
}
//递归
if (node.childNodes && node.childNodes.length) this.compile(node)
})
}
//文本节点处理
compileText(node) {
//匹配出来 {{massage}}
let reg = /\{\{(.+?)\}\}/;
let value = node.textContent;
if (reg.test(value)) {
let key = RegExp.$1.trim()
// 开始时赋值
node.textContent = value.replace(reg, this.vm[key]);
//添加观察者
new Watcher(this.vm, key, val => {
//数据改变时的更新
node.textContent = val;
})
}
}
//元素节点
compileElement(node) {
//简化,只做v-on,v-model的匹配
if (node.attributes.length) {
Array.from(node.attributes).forEach(attr => {
let attrName = attr.name;
if (attrName.startsWith('v-')) {
//v-指令匹配成功可能是是v-on,v-model
attrName = attrName.indexOf(':') > -1 ? attrName.substr(5) : attrName.substr(2)
let key = attr.value;
this.update(node, key, attrName, this.vm[key])
}
})
}
}
update(node, key, attrName, value) {
console.log('更新')
if (attrName == "model") {
node.value = value;
new Watcher(this.vm, key, val => node.value = val);
node.addEventListener('input', () => {
this.vm[key] = node.value;
})
} else if (attrName == 'click') {
// console.log(this.methods,'key')
node.addEventListener(attrName, this.methods[key].bind(this.vm))
}
}
}
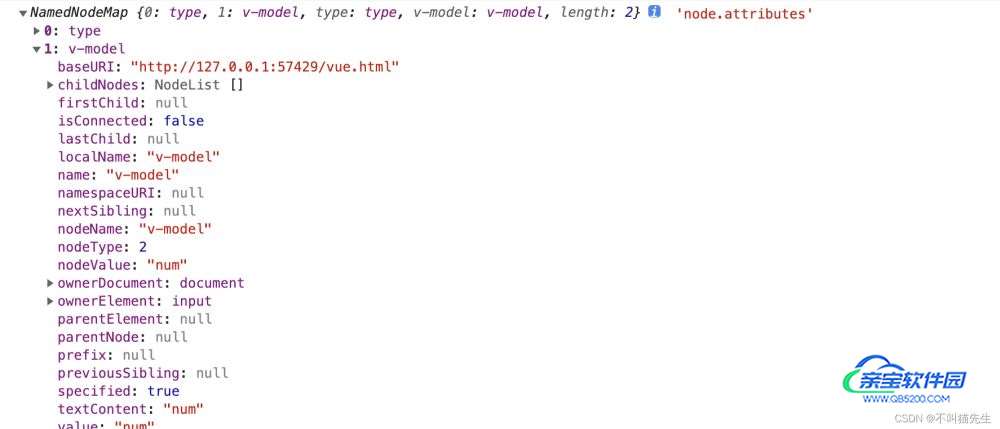
元素节点中node.attributes如下:
//以下面代码为例 <input type="text" v-model="num">
三、文中用到的js基础
1.reg.exec
reg.exec用来检索字符串中的正则表达式的匹配,每次匹配完成后,reg.lastIndex被设定为匹配命中的结束位置。
reg.exec传入其它语句时,lastIndex不会自动重置为0,需要手动重置 reg.exec匹配结果可以直接从其返回值读取
let reg=/jpg|jpg|jpeg/gi
let str='jpg'
if(reg.test(str)){
// true
}
if(reg.test(str)){
// false
}
if(reg.test(str)){
// true
}
if(reg.test(str)){
// false
}(/jpg|jpg|jpeg/gi).test(str) // true (/jpg|jpg|jpeg/gi).test(str) // true (/jpg|jpg|jpeg/gi).test(str) // true
2.reg.test
测试字符串是否与正则表达式匹配
3.RegExp.$x
保存了最近1次exec或test执行产生的子表达式命中匹配。该特性是非标准的,请尽量不要在生产环境中使用它
4.startsWith
用于检测字符串是否以指定的子字符串开始。如果是以指定的子字符串开头返回 true,否则 false,该方法对大小写敏感。
var str = "Hello world, welcome to the Runoob.";
var n = str.startsWith("Hello");//true四、源码
地址:链接跳转
加载全部内容
 爱之家商城
爱之家商城 氢松练
氢松练 Face甜美相机
Face甜美相机 花汇通
花汇通 走路宝正式版
走路宝正式版 天天运动有宝
天天运动有宝 深圳plus
深圳plus 热门免费小说
热门免费小说