SpringBoot集成Tomcat服务架构配置
知了一笑 人气:0一、Tomcat集成
使用的成本越低,内部封装越复杂;
1、依赖层级
在SpringBoot框架的web依赖包中,引入的是内嵌Tomcat组件,基于SpringBoot的版本,Tomcat集成的是9.0版本;
<!-- 1、项目工程依赖 -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId>
<version>2.2.5.RELEASE</version>
</dependency>
<!-- 2、starter-web依赖 -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-tomcat</artifactId>
<version>2.2.5.RELEASE</version>
<scope>compile</scope>
</dependency>
<!-- 3、starter-tomcat依赖 -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.tomcat.embed</groupId>
<artifactId>tomcat-embed-core</artifactId>
<version>9.0.31</version>
<scope>compile</scope>
</dependency>
2、自动化配置
在SpringBoot框架的自动配置类中,Web项目中不显式更换其他服务依赖时,默认提供了对Tomcat服务的管理;
@ConditionalOnWebApplication(type = Type.SERVLET)
@EnableConfigurationProperties(ServerProperties.class)
@Import({ ServletWebServerFactoryAutoConfiguration.BeanPostProcessorsRegistrar.class,
ServletWebServerFactoryConfiguration.EmbeddedTomcat.class})
public class ServletWebServerFactoryAutoConfiguration {
@Bean
@ConditionalOnClass(name = "org.apache.catalina.startup.Tomcat")
public TomcatServletWebServerFactoryCustomizer tomcatServletWebServerFactoryCustomizer(
ServerProperties serverProperties) {
return new TomcatServletWebServerFactoryCustomizer(serverProperties);
}
}
二、Tomcat架构
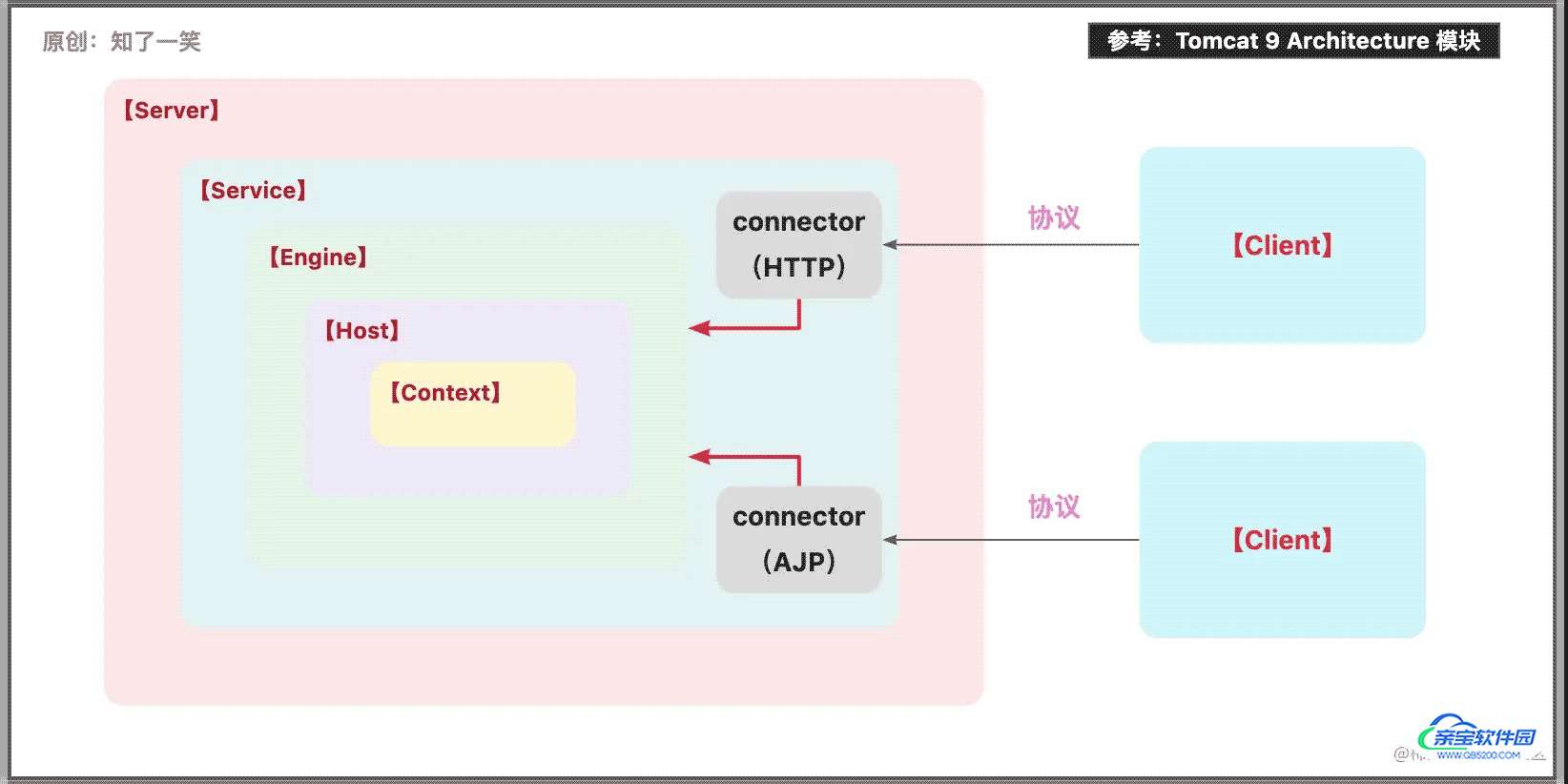
Server:代表整个Tomcat容器;
Service:服务器内部的中间组件,将一个或多个Connector绑定到一个Engine上;
Engine:表示特定服务的请求处理管道,接收Connector的请求并响应;
Host:网络主机名称;
Connector:连接器处理与客户端的通信;
Context:代表一个Web应用程序的上下文;
参考Tomcat9.0版本的核心组件描述,对于框架有大致的了解后,再去分析集成原理,会更容易把握主线逻辑;
三、Tomcat配置
1、基础配置
在配置文件中,对Tomcat做一些基础性的设置,查看下面的配置类可以知道,这些属性存在默认值;
server:
port: 8082 # 端口号
tomcat: # Tomcat组件
uri-encoding: UTF-8 # URI编码
max-threads: 100 # 最大工作线程
min-spare-threads: 10 # 最小工作线程
2、属性配置类
在服务配置中,提供多种服务器的适配,像Tomcat、Jetty、Netty、Undertow,从策略上看,配置分为公共属性以及各种服务器的适配属性;
更多配置信息,可以参考完整的源码和注释说明;
@ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "server", ignoreUnknownFields = true)
public class ServerProperties {
private Integer port;
public static class Tomcat {
private Charset uriEncoding = StandardCharsets.UTF_8;
private int maxThreads = 200;
private int minSpareThreads = 10;
}
}
3、配置加载分析

- 基于配置的属性,定制化管理Tomcat服务的信息;
public class TomcatWebServerFactoryCustomizer
implements WebServerFactoryCustomizer<ConfigurableTomcatWebServerFactory> {
@Override
public void customize(ConfigurableTomcatWebServerFactory factory) {
ServerProperties properties = this.serverProperties;
ServerProperties.Tomcat tomcatProperties = properties.getTomcat();
PropertyMapper propertyMapper = PropertyMapper.get();
customizeStaticResources(factory);
}
}
- TomcatWeb服务工厂,这里在创建WebServer时,使用的是Tomcat,需要适当的了解一下Tomcat架构;
public class TomcatServletWebServerFactory extends AbstractServletWebServerFactory
implements ConfigurableTomcatWebServerFactory, ResourceLoaderAware {
@Override
public WebServer getWebServer(ServletContextInitializer... initializers) {
Tomcat tomcat = new Tomcat();
Connector connector = new Connector(this.protocol);
connector.setThrowOnFailure(true);
tomcat.getService().addConnector(connector);
customizeConnector(connector);
tomcat.setConnector(connector);
tomcat.getHost().setAutoDeploy(false);
configureEngine(tomcat.getEngine());
prepareContext(tomcat.getHost(), initializers);
return getTomcatWebServer(tomcat);
}
}
四、周期管理方法
1、控制类
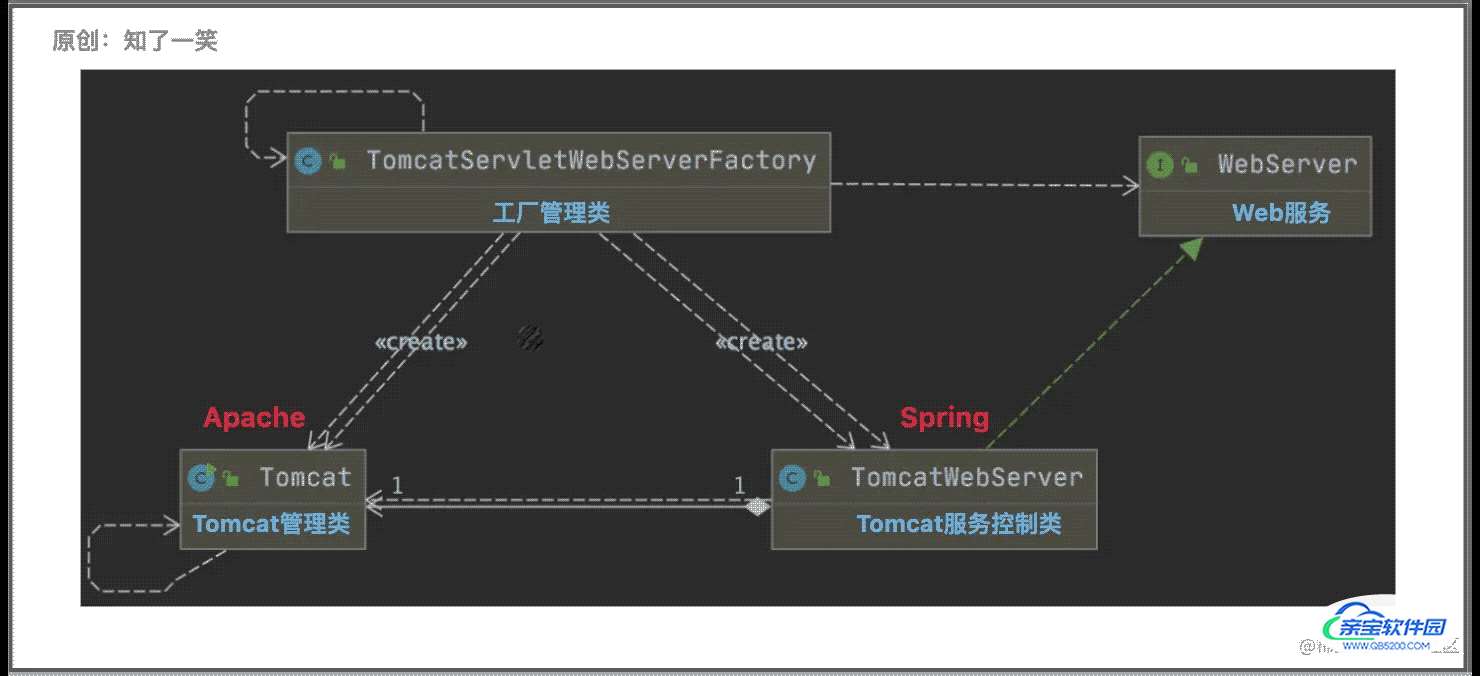
- WebServer的简单接口,只声明端口获取,服务启动和停止相关方法;
public interface WebServer {
// 获取监听的端口
int getPort();
// 服务启动
void start() throws WebServerException;
// 服务停止
void stop() throws WebServerException;
}
- SpringBoot中,Tomcat服务核心控制类,通过TomcatServletWebServerFactory工厂类创建,对Tomcat生命周期的管理提供了一层包装;
public class TomcatWebServer implements WebServer {
private final Tomcat tomcat;
private final Map<Service, Connector[]> serviceConnectors = new HashMap<>();
}
- Apache组件中,轻量级Tomcat启动器,提供了Tomcat基础配置,比如默认的Port和HostName,以及生命周期管理的方法,TomcatWebServer类中调用的就是该API中的具体方法;
public class Tomcat {
protected Server server;
protected int port = 8080;
protected String hostname = "localhost";
// 初始化服务
public void init() throws LifecycleException {
getServer();
server.init();
}
// 启动服务
public void start() throws LifecycleException {
getServer();
server.start();
}
// 停止服务
public void stop() throws LifecycleException {
getServer();
server.stop();
}
}
2、核心方法
2.1 初始化,初始化时,调用Apache-Tomcat类中启动方法;
public class TomcatWebServer implements WebServer {
/**
* 初始化方法
*/
private void initialize() throws WebServerException {
// 控制台日志
logger.info("Tomcat initialized with port(s): " + getPortsDescription(false));
synchronized (this.monitor) {
// 调用Apache-Tomcat类中启动方法
this.tomcat.start();
}
}
}
2.2 启动,在初始化的方法中,调用的Tomcat启动方法,这里对状态进行校验并输出日志;
public class TomcatWebServer implements WebServer {
/**
* 启动方法
*/
public void start() throws WebServerException {
synchronized (this.monitor) {
if (this.started) {
return;
}
checkThatConnectorsHaveStarted();
// 启动状态的标识
this.started = true;
// 控制台日志
logger.info("Tomcat started on port(s): " + getPortsDescription(true) + " with context path '"
+ getContextPath() + "'");
}
}
}
2.3 停止,在组件生命周期的常规管理逻辑中,停止服务之后进行销毁动作的执行,其中自然涉及到多个状态标识的转换;
public class TomcatWebServer implements WebServer {
/**
* 停止方法
*/
public void stop() throws WebServerException {
synchronized (this.monitor) {
// 状态变化
boolean wasStarted = this.started;
this.started = false;
// Tomcat服务停止
stopTomcat();
this.tomcat.destroy();
}
}
}
参考源码
编程文档:
https://gitee.com/cicadasmile/butte-java-note
应用仓库:
加载全部内容