next-redux-wrapper使用细节及源码分析
拾光者 人气:0引言
前几天写了一篇文章讲解了 wrapper 概念,本篇文章主要从源码分析它的实现过程,去更好的理解服务端使用 redux 的注意事项。
- 分析版本:8.1.0
- 仓库地址:github.com/kirill-kons…
先附上一份主要代码结构图:
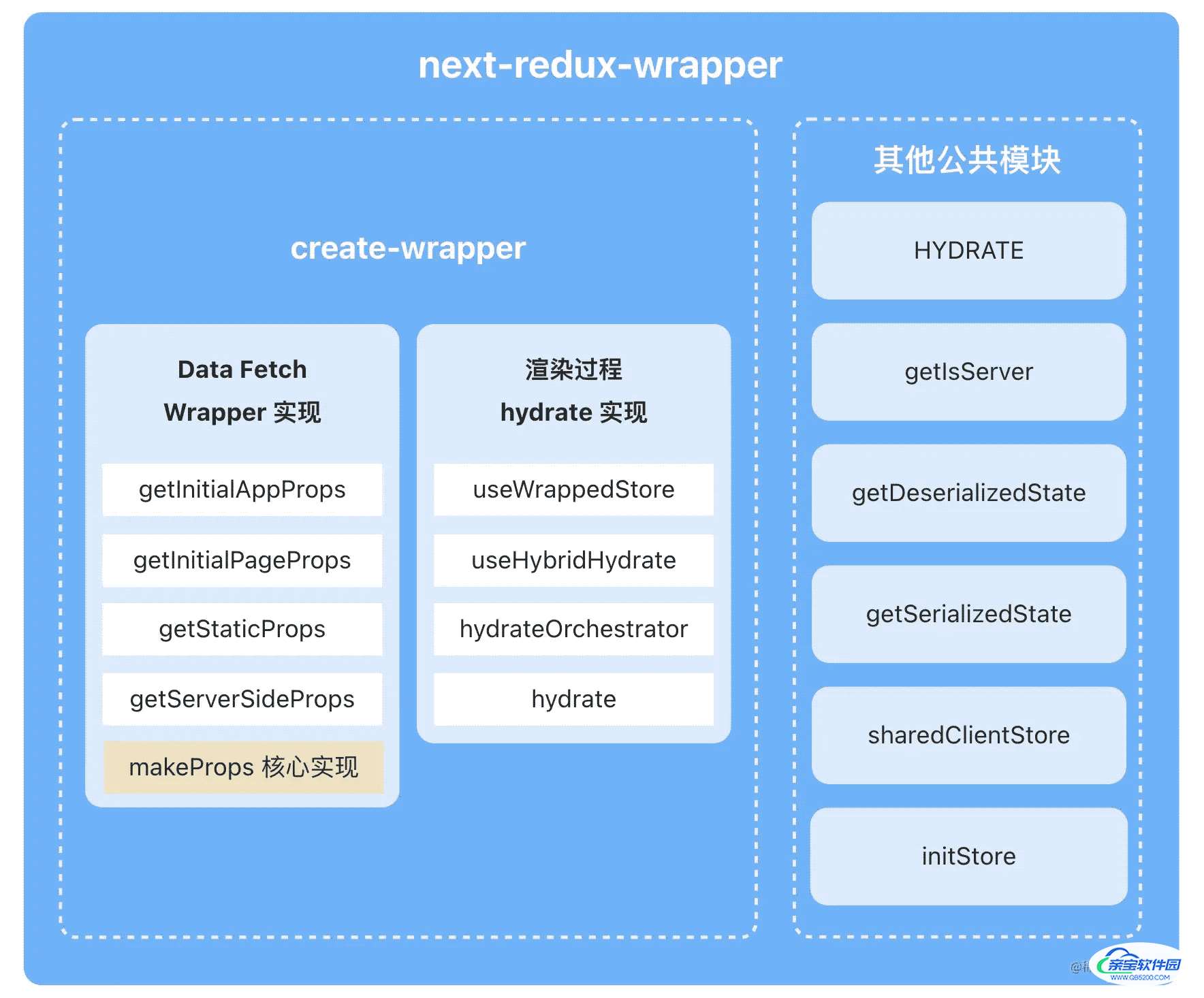
目录结构
. ├── lerna.json ├── package.json ├── packages │ ├── configs │ ├── demo │ ├── demo-page │ ├── demo-redux-toolkit │ ├── demo-saga │ ├── demo-saga-page │ └── wrapper └── yarn.lock
可以明显的看出来这是一个用 lerna 管理的 monorepo 仓库
demo-* 开头的是案例库,而configs 库也是为案例库服务的,那么只用管 wrapper 库即可。
wrapper 结构:
packages/wrapper ├── jest.config.js jest 配置 ├── next-env.d.ts ├── package.json ├── src │ └── index.tsx 核心实现代码 ├── tests 测试代码 │ ├── client.spec.tsx │ ├── server.spec.tsx │ └── testlib.tsx ├── tsconfig.es6.json └── tsconfig.json
核心代码都在 packages/wrapper/src/index.tsx文件,下面开始分析。
代码结构
把大部分代码的具体实现去掉,然后留下整体代码的顶层声明:
// 用于客户端 hydrate 的时发送初始化指令用的 action key
export const HYDRATE = '__NEXT_REDUX_WRAPPER_HYDRATE__';
// 用于判断是否是服务器
const getIsServer = () => typeof window === 'undefined';
// 用于反序列化 State,类似解密函数
const getDeserializedState = <S extends Store>(initialState: any, {deserializeState}: Config<S> = {}) =>
deserializeState ? deserializeState(initialState) : initialState;
// 用于序列化 State,类似加密函数
const getSerializedState = <S extends Store>(state: any, {serializeState}: Config<S> = {}) =>
serializeState ? serializeState(state) : state;
// 客户端存储 store 用的变量
let sharedClientStore: any;
// 初始化 redux store
const initStore = <S extends Store>({makeStore, context = {}}: InitStoreOptions<S>): S => {
// ...
};
// 创建 wrapper
export const createWrapper = <S extends Store>(makeStore: MakeStore<S>, config: Config<S> = {}) => {
// ...
return {
getServerSideProps,
getStaticProps,
getInitialAppProps,
getInitialPageProps,
// 以前的函数,忽略掉,不建议使用了
withRedux,
useWrappedStore,
};
};
// 以前的函数,忽略掉,不建议使用了
export default <S extends Store>(makeStore: MakeStore<S>, config: Config<S> = {}) => {
// ...
return createWrapper(makeStore, config).withRedux;
};
代码分析:
HYDRATE,常量,用于客户端react执行hydrate的时发送初始化指令用的 action key。getIsServer用于判断是否是服务器.getDeserializedState用于反序列化State,类似解密函数,依赖外部使用方传入。getSerializedState用于序列化State,类似加密函数,依赖外部使用方传入。sharedClientStore变量,用于客户端存储redux store用的,用在initStore中。initStore初始化redux store,主要是处理 服务端 和 客户端 在创建时缓存的位置问题。createWrapper创建 wrapper 核心default默认导出函数,以前的函数,忽略掉,不建议使用了,主要使用createWrapper函数返回的withRedux函数,因此本篇文章不进行讲解withRedux函数。
一共就 8 个声明,其中只暴露了 HYDRATE 、 createWrapper 和默认导出函数,忽略掉默认导出函数。
下面进行对 createWrapper 函数的分析。
核心实现
createWrapper 整体实现概览
// 创建 wrapper
export const createWrapper = <S extends Store>(makeStore: MakeStore<S>, config: Config<S> = {}) => {
// 几个 wrapper 函数的实际核心实现函数
const makeProps = async (): Promise<WrapperProps> => {/** ... */};
// 页面级 getInitialProps 函数的包裹函数
const getInitialPageProps = (callback) => async (context) => {/** ... */};
// 应用级 getInitialProps 函数的包裹函数
const getInitialAppProps = (callback) => async (context) => {/** ... */};
// getStaticProps 函数的包裹函数
const getStaticProps = (callback) => async (context) => {/** ... */};
// getServerSideProps 函数的包裹函数
const getServerSideProps = (callback) => async (context) => await getStaticProps(callback)(context);
// hydrate 处理函数,调用 store.dispatch 发起初始化
const hydrate = (store: S, state: any) => {
if (!state) {
return;
}
store.dispatch({
type: HYDRATE,
payload: getDeserializedState<S>(state, config),
} as any);
};
// hydrate 处理中间数据的函数(用于分析处理各种情况)
const hydrateOrchestrator = (store: S, giapState: any, gspState: any, gsspState: any, gippState: any) => {
//...
};
// redux hydrate 执行 hook
const useHybridHydrate = (store: S, giapState: any, gspState: any, gsspState: any, gippState: any) => {
// ...
};
// 用于在应用中关联 store 的 hook。一般用在 App 组件
// giapState stands for getInitialAppProps state
const useWrappedStore = <P extends AppProps>(incomingProps: P, displayName = 'useWrappedStore'): {store: S; props: P} => {
// ...
return {store, props: {...initialProps, ...resultProps}};
};
return {
getServerSideProps,
getStaticProps,
getInitialAppProps,
getInitialPageProps,
useWrappedStore,
};
};
可以把 createWrapper 函数的内容分两类:
- Next.js 数据获取函数的包裹函数实现。
- Next.js 渲染页面内容 时的处理实现。
从 数据获取 到 渲染页面内容 本身就有一个前后顺序,这里也按照这个顺序来分析。
createWrapper 中 数据获取函数 的包裹函数实现分析
callback 函数说明,就是我们调用 wrapper.[wrapperFunctionName] 函数时传递的参数。
比如:
App.getInitialProps = wrapper.getInitialAppProps(({ store }) => async (ctx) => {
// ...
});
callback 就是 ({ store }) => async (ctx) => {} 这部分代码.
我们来看几个 数据获取函数 的代码:
// 页面级 getInitialProps 函数的包裹函数
const getInitialPageProps =
<P extends {} = any>(callback: PageCallback<S, P>): GetInitialPageProps<P> =>
async (
context: NextPageContext | any, // legacy
) => {
// context 中会存储 store — 避免双重包装,因为有可能上层组件也调用了 `getInitialPageProps` 或者 `getInitialAppProps` 函数。
if ('getState' in context) {
// 有缓存的 store ,直接给 callback 传入的 store
return callback && callback(context as any);
}
// 调用 makeProps 执行开发者传入要执行的函数
return await makeProps({callback, context, addStoreToContext: true});
};
// 应用级 getInitialProps 函数的包裹函数
const getInitialAppProps =
<P extends {} = any>(callback: AppCallback<S, P>): GetInitialAppProps<P> =>
async (context: AppContext) => {
// 调用 makeProps 执行开发者传入要执行的函数
const {initialProps, initialState} = await makeProps({callback, context, addStoreToContext: true});
// 每个 `数据获取函数` 最后需要的返回函数类型不一样,因此需要处理成 Next.js 需要的类型
return {
...initialProps,
initialState,
};
};
// getStaticProps 函数的包裹函数
const getStaticProps =
<P extends {} = any>(callback: GetStaticPropsCallback<S, P>): GetStaticProps<P> =>
async context => {
// 调用 makeProps 函数时,相比 getInitialPageProps 和 getInitialAppProps 缺少了 addStoreToContext 参数
const {initialProps, initialState} = await makeProps({callback, context});
return {
...initialProps,
props: {
...initialProps.props,
initialState,
},
} as any;
};
// getServerSideProps 函数的包裹函数
const getServerSideProps =
<P extends {} = any>(callback: GetServerSidePropsCallback<S, P>): GetServerSideProps<P> =>
async context =>
await getStaticProps(callback as any)(context); // 返回参数和static一样,因此直接调用 getStaticProps 函数即可
我们可以看出几个函数的主要区别点在于 参数类型(也就是context 类型) 和 返回值类型 不一致,这也是 Next.js 不同数据获取函数 的区别之一。
getInitialPageProps 需要注意有可能上层组件也调用了 getInitialPageProps 或者 getInitialAppProps 函数。 因此需要判断是否把 store 存储到了 context 中,是的话,需要直接从 context 中获取。(注释是这样的,这里有点问题,待验证)
getInitialAppProps 和 getInitialPageProps 实现类似,只是只需要执行一次,不用考虑缓存,还有就是 返回值类型 不一样
getStaticProps 调用 makeProps 函数时,相比 getInitialPageProps 和 getInitialAppProps 缺少了 addStoreToContext 参数,返回值也不一样。
getServerSideProps 返回参数和 getStaticProps 一样,因此直接调用 getStaticProps 函数即可。
接下来就是几个数据获取的 wrapper 函数 的实际核心实现,也就是 makeProps 函数:
// 数据获取的 `wrapper 函数` 的实际核心
const makeProps = async ({
callback,
context,
addStoreToContext = false,
}: {
callback: Callback<S, any>;
context: any;
addStoreToContext?: boolean;
}): Promise<WrapperProps> => {
// 服务端初始化 store
const store = initStore({context, makeStore});
if (config.debug) {
console.log(`1. getProps created store with state`, store.getState());
}
// Legacy stuff - 把 store 放入 context 中
if (addStoreToContext) {
if (context.ctx) {
context.ctx.store = store;
} else {
context.store = store;
}
}
// 这里实现了 callback 双层函数执行,先传递 store 给 callback 生成新的函数
const nextCallback = callback && callback(store);
// 再用新的函数传递 context 参数,获取 initialProps
const initialProps = (nextCallback && (await nextCallback(context))) || {};
if (config.debug) {
console.log(`3. getProps after dispatches has store state`, store.getState());
}
const state = store.getState();
return {
initialProps,
// 在服务端可以对 state 数据加密,防止被轻易解析
initialState: getIsServer() ? getSerializedState<S>(state, config) : state,
};
};
makeProps 函数主要初始化 store ,然后把 store 传递给 callback 函数并执行获取到一个函数,这个函数传入 context 再次执行,就可以获取到对应 数据获取函数 的返回值,处理后进行返回即可。
其中需要注意下面几点:
callback函数必须返回一个函数,否则其返回的initialProps会被是空对象- 调用
createWrapper时传递参数中的debug参数在这里会起作用 - 把
store放入context是一个遗留的处理方式,后续可能会去掉。但并没说明后续处理方式。 - 返回的
initialState在服务端可能自定义加密方法。
createWrapper 中 渲染页面内容 时的处理实现分析
服务端把数据获取后,下面就要进行的步骤是:渲染页面内容。
有几个概念需要先理清楚,不然会直接看前面几个函数的实现会很懵逼。
giapState:对应getInitialAppProps处理后的stategspState:对应getStaticProps处理后的stategsspState:对应getServerSideProps处理后的stategippState:对应getInitialPageProps处理后的state
useWrappedStore hook
// 用于在应用中关联 store 的hook。
const useWrappedStore = <P extends AppProps>(incomingProps: P, displayName = 'useWrappedStore'): {store: S; props: P} => {
// createWrapper 给 incomingProps 添加了 WrapperProps 类型,因为它们不是从 P 类型获取,因此在这里进行强制赋予类型
const {initialState: giapState, initialProps, ...props} = incomingProps as P & WrapperProps;
// getStaticProps state
const gspState = props?.__N_SSG ? props?.pageProps?.initialState : null;
// getServerSideProps state
const gsspState = props?.__N_SSP ? props?.pageProps?.initialState : null;
// getInitialPageProps state
const gippState = !gspState && !gsspState ? props?.pageProps?.initialState ?? null : null;
// debug 打印代码,删除掉了
if (config.debug) {}
// 获取store,initStore 会缓存 store ,有则直接缓存,没有则进行初始化。
const store = useMemo<S>(() => initStore<S>({makeStore}), []);
// state 初始化
useHybridHydrate(store, giapState, gspState, gsspState, gippState);
// 后续余state 无关,主要是去掉
let resultProps: any = props;
// 顺序很重要! Next.js 中 page 的 getStaticProps 应该覆盖 pages/_app 中的 props
// @see https://github.com/zeit/next.js/issues/11648
if (initialProps && initialProps.pageProps) {
resultProps.pageProps = {
...initialProps.pageProps, // this comes from wrapper in _app mode
...props.pageProps, // this comes from gssp/gsp in _app mode
};
}
// 防止props中的 initialState被到处传递,为了数据安全,清除掉 initialState
if (props?.pageProps?.initialState) {
resultProps = {...props, pageProps: {...props.pageProps}};
delete resultProps.pageProps.initialState;
}
// 处理 getInitialPageProps 的数据, 清除掉 initialProps
if (resultProps?.pageProps?.initialProps) {
resultProps.pageProps = {...resultProps.pageProps, ...resultProps.pageProps.initialProps};
delete resultProps.pageProps.initialProps;
}
return {store, props: {...initialProps, ...resultProps}};
};
useWrappedStore hook 主要做了以下几件事:
- 从
App props中获取数据,并进行分类 - 初始化
store:服务端不会再初始化,会从缓存获取,客户端则会在这里初始化。 - 处理数据覆盖排序及清除
wrapper函数注入的自定义数据字段:initialProps和initialState。
initStore
// 初始化 redux store
const initStore = <S extends Store>({makeStore, context = {}}: InitStoreOptions<S>): S => {
const createStore = () => makeStore(context);
if (getIsServer()) {
// 服务端则存储到 req.__nextReduxWrapperStore 参数 中进行服用
const req: any = (context as NextPageContext)?.req || (context as AppContext)?.ctx?.req;
if (req) {
// ATTENTION! THIS IS INTERNAL, DO NOT ACCESS DIRECTLY ANYWHERE ELSE
// @see https://github.com/kirill-konshin/next-redux-wrapper/pull/196#issuecomment-611673546
if (!req.__nextReduxWrapperStore) {
req.__nextReduxWrapperStore = createStore(); // Used in GIP/GSSP
}
return req.__nextReduxWrapperStore;
}
return createStore();
}
// Memoize the store if we're on the client
// 客户端则存储到 sharedClientStore 上
if (!sharedClientStore) {
sharedClientStore = createStore();
}
return sharedClientStore;
};
initStore 函数中,服务端利用每次请求都会新生成的对象 req 来缓存服务端请求上下文的 store,客户端利用 sharedClientStore 变量来存储。
useHybridHydrate hook
// hydrate 初始化前置逻辑处理
const useHybridHydrate = (store: S, giapState: any, gspState: any, gsspState: any, gippState: any) => {
const {events} = useRouter();
const shouldHydrate = useRef(true);
// 客户端路由改变的时候好应该重新初始化。
useEffect(() => {
const handleStart = () => {
shouldHydrate.current = true;
};
events?.on('routeChangeStart', handleStart);
return () => {
events?.off('routeChangeStart', handleStart);
};
}, [events]);
// 这里写了一大堆注释,就是表面 useMemo 里面进行 hydrate 并不会导致页面重新不断渲染,主要是当作 constructor 来使用
useMemo(() => {
if (shouldHydrate.current) {
hydrateOrchestrator(store, giapState, gspState, gsspState, gippState);
shouldHydrate.current = false;
}
}, [store, giapState, gspState, gsspState, gippState]);
};
useHybridHydrate 函数主要用于处理 初始化 state 的前置逻辑,主要使用 useMemo 来尽早调用 hydrateOrchestrator 函数初始化 state , 并使用监听路由的方式来处理客户端路由切换时需要重新初始化的问题。
hydrateOrchestrator
// hydrate 处理中间数据的函数(用于分析处理各种情况)
const hydrateOrchestrator = (store: S, giapState: any, gspState: any, gsspState: any, gippState: any) => {
if (gspState) {
// `getStaticProps` 并不能和其他数据获取函数同时存在在一个页面,但可能存在 `getInitialAppProps`,这时候只会在构建的时候执行,因此需要覆盖 `giapState`
hydrate(store, giapState);
hydrate(store, gspState);
} else if (gsspState || gippState || giapState) {
// 处理优先级问题,getServerSideProps > getInitialPageProps > getInitialAppProps
hydrate(store, gsspState ?? gippState ?? giapState);
}
};
hydrateOrchestrator 函数主要用于处理获取state的覆盖和优先级问题:
getStaticProps并不能和其他数据获取函数同时存在在一个页面,但可能存在getInitialAppProps,这时候只会在构建的时候执行,因此需要覆盖giapState。- 非
SSG情况,优先级getServerSideProps>getInitialPageProps>getInitialAppProps
hydrate
// hydrate 处理函数,触发服务端渲染过程中的数据 HYDRATE
const hydrate = (store: S, state: any) => {
if (!state) {
return;
}
store.dispatch({
type: HYDRATE,
payload: getDeserializedState<S>(state, config),
} as any);
};
hydrate 函数就是用于发起 HYDRATE action 的。
总结
本文主要从 目录结构 分析,然后再到 代码结构分析,最好再分析重点代码实现,这样一步一步的去读源码,可以让思路更加清晰。
读源码之前,有使用经验也是一个很重要的点,这样才能带着疑问和思考去读,让阅读源码更有意思
加载全部内容