android学习笔记之View的滑动
呼啸 人气:0前言
其实不管是哪种滑动方式,基本思想都是类似的:当点击事件传递到View时,系统记下触摸点的坐标,手指移动的时候,系统记下移动后的坐标,并计算出偏移量,并通过偏移量来修改View的坐标。
下面我们来讲下几种滑动方法:
1.layout方法
大家知道,绘制View的时候会调用onlayout方法来设置要显示的位置。因此我们也可以通过修改view的left,top,right,bottom这4个属性来控制view的坐标。接下来我们来自定义一个View,通过layout方法来实现滑动:
package com.example.myapplication.views
import android.content.Context
import android.util.AttributeSet
import android.view.MotionEvent
import android.view.View
class CustomView @JvmOverloads constructor(
context: Context,
attrs:AttributeSet? = null,
defStyleAttr:Int= 0
) :View(
context,attrs,defStyleAttr){
private var lastX:Int = 0
private var lastY:Int = 0
override fun onTouchEvent(event: MotionEvent): Boolean {
//获取手指触摸点的横坐标和纵坐标
val x = event.x.toInt()
val y = event.y.toInt()
when(event.action) {
MotionEvent.ACTION_DOWN -> {
lastX = x
lastY = y
}
MotionEvent.ACTION_MOVE -> {
//计算移动距离
val offsetX = x -lastX
val offsetY = y -lastY
//调用layout方法来重新放置他的位置
layout(left+offsetX,top+offsetY,right + offsetX, bottom + offsetY)
}
}
return true
}
}然后我们把他放到XML里去使用:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:orientation="vertical">
<com.example.myapplication.views.CustomView
android:id="@+id/view_my"
android:layout_width="100dp"
android:layout_height="100dp"
android:layout_gravity="center_horizontal"
android:background="@mipmap/cai"/>
</LinearLayout>看下效果:

这个移动的效果实现。
2.接下来,我们看看offsetLeftAndRight()与offsetTopAndBottom()方法
这两种方法和layout方法差不多,我们稍加修改就可以。我们替换下ACTION_MOVE中的代码块:
MotionEvent.ACTION_MOVE -> {
//计算移动距离
val offsetX = x -lastX
val offsetY = y -lastY
//对left和right进行偏移
offsetLeftAndRight(offsetX)
//对top和bottom进行偏移
offsetTopAndBottom(offsetY)
// //调用layout方法来重新放置他的位置
// layout(left+offsetX,top+offsetY,right + offsetX, bottom + offsetY)
}仍然能够实现。
3.第三个方法:LayoutParams(改变布局参数)
LayoutParams主要保存了一个View的布局参数,因此我们可以通过LayoutParams来改变View的布局参数。从而达到改变View位置的效果。我们同样替换下ACTION_MOVE中的代码块:
MotionEvent.ACTION_MOVE -> {
//计算移动距离
val offsetX = x -lastX
val offsetY = y -lastY
val layoutParams = layoutParams as LinearLayout.LayoutParams
layoutParams.leftMargin = left + offsetX
layoutParams.topMargin = top + offsetY
setLayoutParams(layoutParams)
// //对left和right进行偏移
// offsetLeftAndRight(offsetX)
// //对top和bottom进行偏移
// offsetTopAndBottom(offsetY)
// //调用layout方法来重新放置他的位置
// layout(left+offsetX,top+offsetY,right + offsetX, bottom + offsetY)
}
}不过经过我实验,这个有挺大的偏差,总是靠右边。什么原因?
4.接下来,看看使用第四种方法,使用动画来滑动。
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<set xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:fillAfter="true">
<translate android:fromXDelta="0"
android:toXDelta="300"
/>
</set>使用代码调用:
findViewById<View>(R.id.view_my).animation = AnimationUtils.loadAnimation(this,R.anim.translate)
需要注意的是,view动画,并不能改变view的位置参数。所以我们点击Button并不会触发,因为他的负控件要先判断点击事件是否在子view的位置参数范围内才会分发给他,当我们点击原来的位置的时候,才会响应。如果我们想让他在移动后的位置响应,也就是说更改view的位置参数,那么可以使用属性动画。
val customView = findViewById<View>(R.id.view_my)
findViewById<Button>(R.id.btn_move).setOnClickListener {
ObjectAnimator.ofFloat(customView,"translationX",0f,300f).setDuration(1000).start()
}5.接下来我们看看第五种方法,scrollTo与ScrollBy
scrollTo(x,y)表示移动到一个具体的坐标点,而scrollBy(dx,dy)表示移动的增量为dx,dy,其实我们看源码就知道scorllBy最终也是计算出最终坐标,最终调用scrollTo的。我们可以看下源码:
public void scrollBy(int x, int y) {
scrollTo(mScrollX + x, mScrollY + y);
}需要注意的是,scrollTo和ScrollBy是移动的内容。我们如果设置了Bacgroud会发现看不出效果。可以改下:
<com.example.myapplication.views.CustomView
android:id="@+id/view_my"
android:layout_width="100dp"
android:layout_height="100dp"
android:layout_gravity="center_horizontal"
android:foreground="@mipmap/cai"/> findViewById<Button>(R.id.btn_move).setOnClickListener {
customView.scrollBy(50,100)
// ObjectAnimator.ofFloat(customView,"translationX",0f,300f).setDuration(1000).start()
}使用foreground。接着看下效果:

最开始是这样的,然后我们点击下按钮,变成了这样:
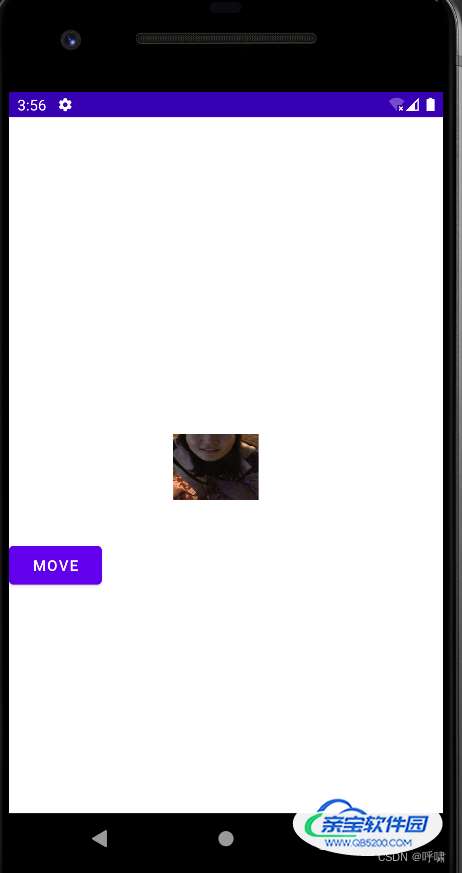
是不是发现了神奇的现象。再点击一次:
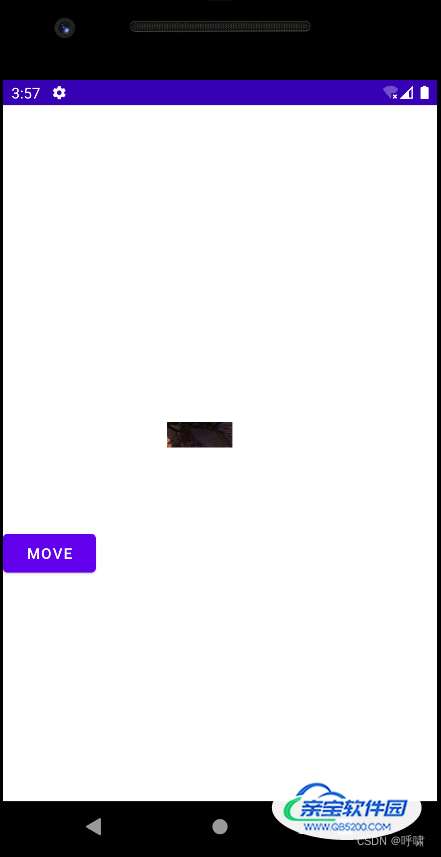
好家伙,快看不到了。什么原因呢?这里有两个奇怪的现象,第一个是他似乎移动的方向是相反的,第二个是是越来越小。准确说,是好像并不是缩小,而是只能看到局部。
这是因为参照物的不同导致的。假设,我们把手机屏幕比喻为放大镜。下面的内容当作报纸。我们调用这个方法,实际是使放大镜相对于这个view,往下移动了,放大镜看不到的地方不并是不存在了。所以他才看起来像是往左上移动了。然后,因为我们是内容在移动,所以View本身并没有移动,所以他的前景色就看不到了。
我们如果希望能做到随手指移动,可以在move方法里这样修改:
MotionEvent.ACTION_MOVE -> {
//计算移动距离
val offsetX = x -lastX
val offsetY = y -lastY
val parentView = parent as View
parentView.scrollBy(-offsetX,-offsetY)
}这里,取相反的值,岗刚说了,是因为参考物,会导致视觉相反。而要取他的parent,是因为这个view就属于他的parent的内容。所以,他就可以进行相关的动作。
6.来看第六种方法Scroller
我们在使用scrollTo/scrollBy方法进行滑动的时候,这个过程是瞬间就完成的。所以体验就不是太好。我们可以使用scroller来实现有过度效果的滑动。但是scroller本身是不能实现View的滑动,它需要与View的computeScroller 方法配合才能实现弹性滑动效果。来看代码实现:
首先,定义个成员变量:
private val mScroller = Scroller(context)
接下来,我们重写computeScroll方法,系统会绘制View的时候,在draw方法里调用该方法。
我们先在CustomView里定义个方法:
fun smoothScrollTo(destX:Int, destY:Int){
val scrollX = scrollX
val delta = destX - scrollX
mScroller.startScroll(scrollX,0,delta,2,2000)
invalidate()
}这个方法是提供给外部调用的,参数是想偏移的X和Y。
scrollX是目前已经滑动值,拿目的要偏移的减去已经滑动的,就是还剩下的。调用scroller.startScroll()方法。设置一个duration。我们调用invalidate()就开始重绘。这个时候就会调用view的computeScroller方法。这里面我们调用父空间viewGroup的scroollTo方法,来获取当前的一小段滑动值,然后行成小的滑动。接着调用invalidate()方法不断的重绘。
override fun computeScroll() {
super.computeScroll()
if (mScroller.computeScrollOffset()) {
(parent as View).scrollTo(mScroller.currX,mScroller.currY)
invalidate()
}
}最后,我们在activity里调用:
customView.smoothScrollTo(-400,0)
向右边平移400。
总结
加载全部内容