python连接读写操作redis的完整代码实例
zhangphil 人气:0python读写操作redis数据库
redis有16个逻辑数据库(编号db0到db15),每个逻辑数据库数据是隔离的,默认db0。选择第n个逻辑数据库,命令select n ,python连接时可指定数据库编号(0~15)。
为python安装支持库:
pip install redis
连接redis
第一种方式,直连:
import redis def redis_opt(): redis_conn = redis.Redis(host='127.0.0.1', port=6379, password='', db=6) print(redis_conn.client_id())
第二种方式,连接池:
import redis def redis_opt(): redis_pool = redis.ConnectionPool(host='127.0.0.1', port=6379, password='', db=6) redis_conn = redis.Redis(connection_pool=redis_pool) print(redis_conn.client_id())
对redis数据库进行读写操作
import redis
def redis_opt():
redis_pool = redis.ConnectionPool(host='127.0.0.1', port=6379, password='', db=6)
redis_conn = redis.Redis(connection_pool=redis_pool)
key = 'data'
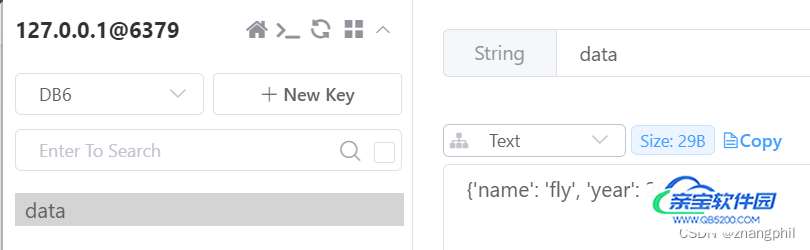
my_data = {"name": 'fly', 'year': 2022}
redis_conn.set(key, str(my_data))
print(redis_conn.get(key))如图:
更新操作:
key = 'data'
my_data = {'name': 'fly', 'year': 2022}
redis_conn.set(key, str(my_data))
my_data = {'name': 'phil', 'year': 2020}
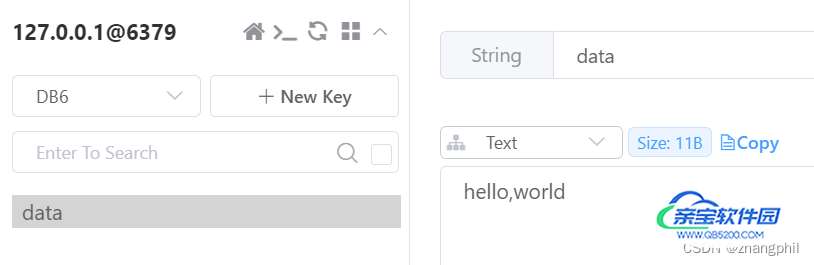
redis_conn.getset(key, str(my_data))追加操作:
redis_pool = redis.ConnectionPool(host='127.0.0.1', port=6379, password='', db=6) redis_conn = redis.Redis(connection_pool=redis_pool) key = 'data' redis_conn.set(key, 'hello,') redis_conn.append(key, 'world')
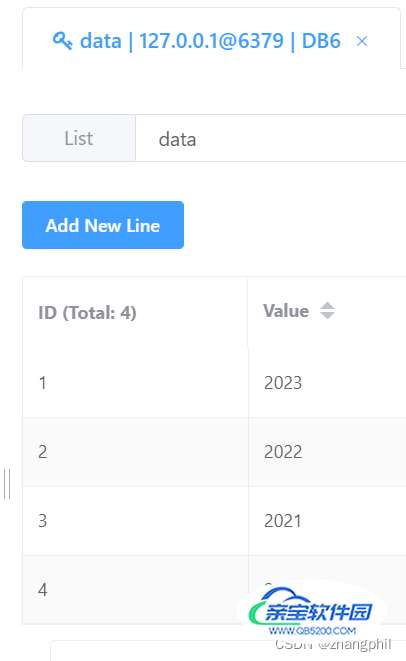
lpush 列表左侧追加值
key = 'data' redis_conn.lpush(key, 2020, 2021, 2022) redis_conn.lpush(key, 2023)
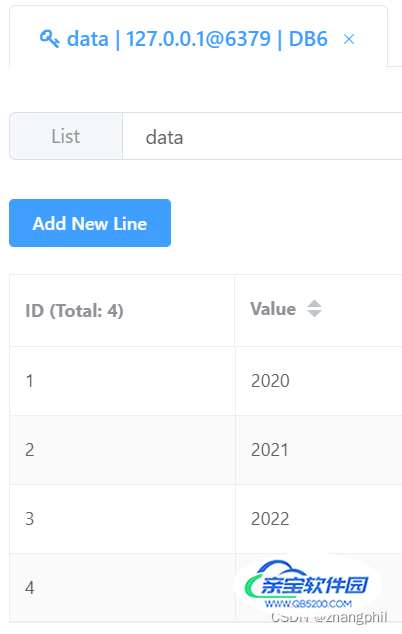
如果换成右侧追加,相当于尾部追加:
key = 'data' redis_conn.rpush(key, 2020, 2021, 2022) redis_conn.rpush(key, 2023)
lpushx(name, value),如果键name存在时候才追加,否则不会追加。
根据特定值位置位置插入新值
key = 'data' redis_conn.rpush(key, 2020, 2021, 2022) redis_conn.rpush(key, 2023) print(redis_conn.llen(key)) # 列表长度 # AFTER,之后。BEFORE之前。 v = redis_conn.linsert(name=key, where='AFTER', refvalue=2020, value='1999') print(v)
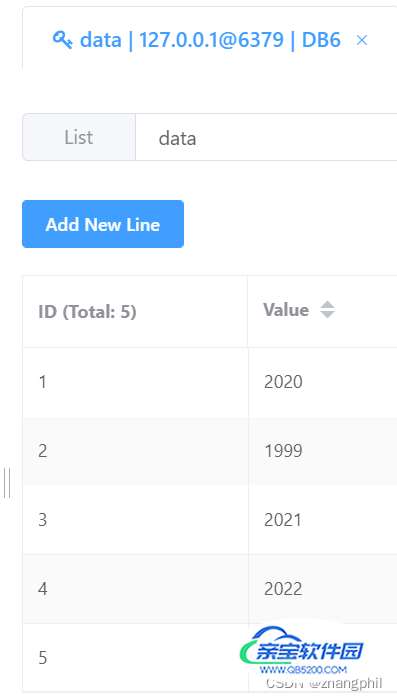
根据索引位置插入新值:
key = 'data' redis_conn.rpush(key, 2020, 2021, 2022) redis_conn.rpush(key, 2023) print(redis_conn.llen(key)) # 列表长度 v = redis_conn.lset(name=key, index=2, value='1999') print(v)
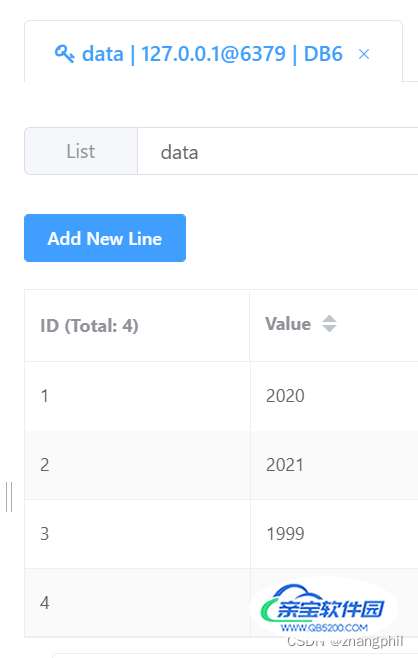
根据列表索引起始位置获取值
key = 'data' redis_conn.rpush(key, 2020, 2021, 2022) redis_conn.rpush(key, 2023) print(redis_conn.llen(key)) # 列表长度 v = redis_conn.lrange(name=key, start=1, end=3) print(v)
输出:
4 [b'2021', b'2022', b'2023']
删除列表左侧的一个值
lpop(name)
从左向右删除列表中n个相同的值
lrem(name, value, num)
如果是从右向作,需要把num的值改为负数即可,比如-3,从右向左删掉3个重复的value。
删除列表范围之外所有值
ltrim(name, start, end)
列表中最右边的值删除并放入到新列表中的最左边
rpoplpush(src, dst) brpoplpush(src, dst, timeout=0)
存储哈希Map键值
key = 'data' redis_conn.hset(key, 'name', 'fly') redis_conn.hset(key, 'year', 2022) print(redis_conn.hget(key, 'year'))
输出:
b'2022'
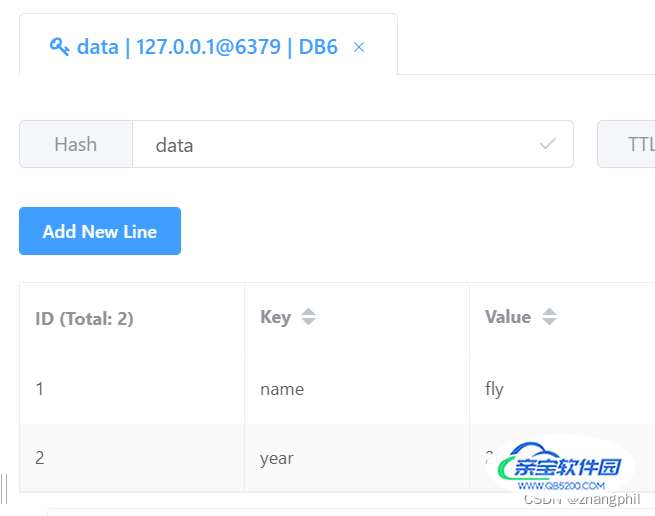
以下注意name和key的区分。name是作为在redis中的“大键”,key是在redis中存储名为name的数据块中的键。
存储打包的哈希键值对
my_name = 'my_data'
my_key = 'my_key'
val = {'name': 'fly', 'year': 2022}
json_val = json.dumps(val)
redis_conn.hset(name=my_name, key=my_key, value=json_val)
print(redis_conn.hgetall(my_name))
print(redis_conn.hkeys(my_name))
print(redis_conn.hvals(my_name))输出:
{b'my_key': b'{"name": "fly", "year": 2022}'}
[b'my_key']
[b'{"name": "fly", "year": 2022}']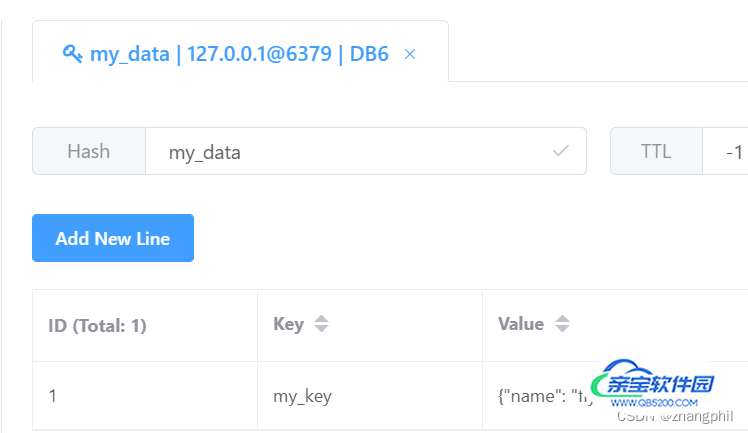
删除键值对
my_name = 'my_data'
my_key = 'my_key'
val = {'name': 'fly', 'year': 2022}
json_val = json.dumps(val)
redis_conn.hset(name=my_name, key=my_key, value=json_val)
print(redis_conn.hgetall(my_name))
print(redis_conn.hkeys(my_name))
print(redis_conn.hvals(my_name))
print(redis_conn.hexists(name=my_name, key=my_key))
print(redis_conn.hdel(my_name, my_key)) #删除my_name数据块里面的my_key键值对设置键值的过期时间,超过时间就自动删除
my_name = 'my_data'
my_key = 'my_key'
val = {'name': 'fly', 'year': 2022}
json_val = json.dumps(val)
redis_conn.hset(name=my_name, key=my_key, value=json_val)
print(redis_conn.hgetall(my_name))
redis_conn.expire(name=my_name, time=5) # 超过5秒自动删除。全局查询redis中是否有以name存储的数据块
v = redis_conn.exists('my_name')重命名redis中的键名
rename(src, dst)
把某一键值移动到另外的redis逻辑库
move(name, db)
类型判断
type(name)
redis-sentinel哨兵模式下Python操作redis代码实例
#redis-sentinel连接
'''
启动redis服务端(6390主库):
redis-server msconf/redis-6390.conf
redis-server msconf/redis-6391.conf
redis-server msconf/redis-6392.conf
redis-server msconf/redis-6393.conf
启动哨兵功能:
redis-sentinel redis_sentinel/redis-sentinel_26390.conf
redis-sentinel redis_sentinel/redis-sentinel_26391.conf
redis-sentinel redis_sentinel/redis-sentinel_26392.conf
'''
## 导入redis sentinel包
from redis.sentinel import Sentinel
#指定sentinel的地址和端口号(连接哨兵)
sentinel=Sentinel([('192.168.160.135',26390),('192.168.160.135',26391),('192.168.160.135',26392)],socket_timeout=0.1)
#测试,获取以下主库和从库的信息:mymaster是哨兵配置文件中的指定的监控主库
print(sentinel.discover_master('mymaster'))#主库信息
print(sentinel.discover_slaves('mymaster'))#从库信息
##配置读写分离
#写节点:主库
master=sentinel.master_for('mymaster',password=123456,socket_timeout=0.1)#注意主库设置了安全模式有密码
print(master)
#读节点:从库
slave=sentinel.slave_for('mymaster',password=123456,socket_timeout=0.1)#注意从库设置了安全模式有密码
print(slave)
#读写分离测试
print(master.dbsize())
print(master.keys())
print(slave.keys())
master.set('name4',4)
print(slave.keys())
print(slave.get('name4'))redis-cluster(集群)模式下Python操作redis代码实例
# redis-cluster集群:https://github.com/Grokzen/redis-py-cluster
# pip install redis-py-cluster
from rediscluster import StrictRedisCluster
#是少要链接集群中的一台数据库,可以是多台,防止有的数据库会挂掉
startup_nodes = [{"host": "192.168.160.135", "port": "7000"}, {"host": "192.168.160.135", "port": "7001"},
{"host": "192.168.160.135", "port": "7002"}, {"host": "192.168.160.135", "port": "7003"},
{"host": "192.168.160.135", "port": "7004"}, {"host": "192.168.160.135", "port": "7005"} ]
rc = StrictRedisCluster(startup_nodes=startup_nodes,password=123456, decode_responses=True)
rc.set('name1',1234)
print(rc.keys())
print(rc.dbsize())
print(rc.get('name1'))以上就是python连接读写操作redis的完整代码实例的详细内容,更多关于python读写redis的代码实例的资料请关注其它相关文章!,希望大家以后多多支持!
加载全部内容