利用Rust编写一个简单的字符串时钟
啊哈彭 人气:01、简介
用rust写的一个简单的练手的demo,一个字符串时钟,在终端用字符串方式显示当前时间。本质是对图片取灰度,然后每个像素按灰度门限用星号代替灰度值,就把图片变为由星号组成的字符型图案。把时间字符串的每个字符按照字母和数字图片的样式转换为字符,然后拼接字符图案就实现了字符时钟的效果。
主要用到的知识有:rust操作时间、字符串、vector,字符串和vector的转换、string,以及让人恼火的生命周期。对比python,rust的列表入门难度可以说是地狱级的,一会borrow、一会move,晕头转向。

2、用到的知识点
2.1 取utc时间
时间库使用chrono = "0.4",获取秒数等时间。
let five_seconds = Duration::new(5, 0);
let five_seconds_and_five_nanos = five_seconds + Duration::new(0, 10);
assert_eq!(five_seconds_and_five_nanos.as_secs(), 5);
assert_eq!(five_seconds_and_five_nanos.subsec_nanos(), 10);
let five_seconds = Duration::from_secs(5);
assert_eq!(five_seconds, Duration::from_millis(5_000));
assert_eq!(five_seconds, Duration::from_micros(5_000_000));
assert_eq!(five_seconds, Duration::from_nanos(5_000_000_000));
let ten_seconds = Duration::from_secs(10);
let seven_nanos = Duration::from_nanos(7);
let total = ten_seconds + seven_nanos;
assert_eq!(total, Duration::new(10, 7));
获取实时utc时间。
let local:DateTime<Local>= Local::now();
println!("{:?}", local.format("%Y-%m-%d %H:%M:%S").to_string());
println!("{:?}", local.format("%a %b %e %T %Y").to_string());
println!("{:?}", local.format("%c").to_string());
println!("{:?}", local.to_string());
println!("{:?}", local.to_rfc2822());
println!("{:?}", local.to_rfc3339());
let dt = Local.with_ymd_and_hms(2020 as i32, 12, 05, 12, 0, 9).unwrap();
println!("{:?}", dt.format("%Y-%m-%d %H:%M:%S").to_string());
println!("{:?}", dt.format("%a %b %e %T %Y").to_string());
println!("{:?}", dt.format("%c").to_string());
println!("{:?}", dt.to_string());
println!("{:?}", dt.to_rfc2822());
println!("{:?}", dt.to_rfc3339());
输出为:
"2022-12-25 23:20:03"
"Sun Dec 25 23:20:03 2022"
"Sun Dec 25 23:20:03 2022"
"2022-12-25 23:20:03.499293300 +08:00"
"Sun, 25 Dec 2022 23:20:03 +0800"
"2022-12-25T23:20:03.499293300+08:00"
"2020-12-05 12:00:09"
"Sat Dec 5 12:00:09 2020"
"Sat Dec 5 12:00:09 2020"
"2020-12-05 12:00:09 +08:00"
"Sat, 05 Dec 2020 12:00:09 +0800"
"2020-12-05T12:00:09+08:00"
获取当前时间,如下格式化为20:15:23类似的格式。
let curdate = Local::now();
let datecollect = curdate.format("%H:%M:%S").to_string();
2.2 图片变换为像素图案
1、读取图片
先准备每个数字的图片,然后读取图片,转换为灰度表示。

let cur_dir = std::env::current_dir().unwrap().
into_os_string().into_string().unwrap();
let _path = if number == ':' {
format!("{}/number_pic/{}.png", &cur_dir, "maohao")
}
else{
format!("{}/number_pic/{}.png", &cur_dir, number)
};
// println!("imagepath = {}", _path);
let gray_pic = image::open(_path).unwrap()
.resize(nwidth, nheight, image::imageops::FilterType::Nearest)
.into_luma8();
初始化pix_clock结构体,解析需要用到的10个数字和冒号时间分隔字符。
pub struct pix_clock {
words : HashMap<char, Vec<String>>,
}
impl pix_clock {
pub fn new() -> pix_clock {
let mut dict_result = HashMap::new();
let numbers = vec!['0', '1', '2', '3', '4', '5', '6', '7', '8', '9', ':'];
for value in numbers {
let result = get_num_pic(value);
dict_result.insert(value, result);
// println!("num={} {:#?}", value, dict_result[&value]);
}
return pix_clock {
words: dict_result,
};
}
}
2、图片按像素灰度转换为字符图案
每行作为1个string字符串,按行处理,读取完一行后把当前行的字符串push到列表,然后清空行变量,准备解析下一行的像素。每行都解析完成后,pix_data就形成了一个由nheight行,每行nwidth个字符构成的列表。
let mut pix_data: Vec<String> = vec![];
let mut line = String::from("");
for (index, tmp) in gray_pic.to_vec().iter().enumerate() {
if index % nwidth as usize == 0 {
if line.len()>0 {
let line2 = line.clone();
pix_data.push(line2);
}
line.clear();
}
if tmp > &gap_value {
line.push_str("*");
}
else {
line.push_str(" ");
}
}
以数字3为例:println!("result data {} {:#?}", number, &pix_data);// 输出数据为:
result data 3 [
"*************",
"*************",
"****** ******",
"*** ***",
"*** ***",
"*** *** **",
"******** **",
"******* ***",
"**** ***",
"**** ***",
"******* **",
"******** **",
"********* **",
"** *** **",
"** ***",
"*** ***",
"***** *****",
"*************",
"*************",
]
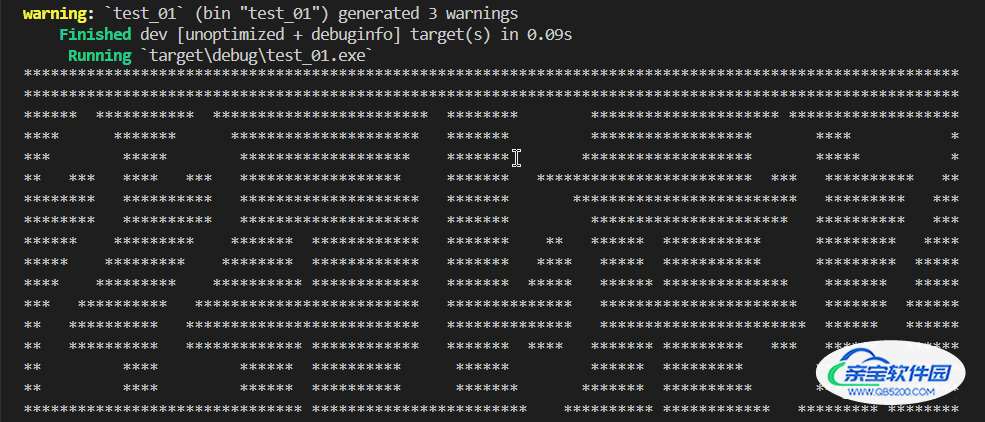
2.3 字符方式显示当前时间
上一步已经完成了单个数字转换为字符图案,由于时间字符串由多位数字构成,所以需要拼接图案。例如20:15:23,就由6个数字和2个冒号组成,所以字符串“20:15:23”就需要按行合并。
1)合并每个数组的团案,而高度不变。
let time_str = datestr.chars(); // 把字符串解析为char型字符
let mut final_vector: Vec<String> = vec![];
for _index in 0..self.words.get(&'0').unwrap().len() { // 合并后的图案高度不变,即行数不变
final_vector.push("".to_string()); // 每行的字符串变长了,先预留空String来接收每行字符
}
2)按行合并每个字符,拼接字符串的图案
for value in time_str { //遍历时间字符串的每个字符
let value_pix = self.words.get(&value).unwrap(); //获取单个字符的图案
let mut index = 0;
for x in value_pix.iter() {
final_vector[index].push_str(&x); # 每个字符相同行的字符串合并为一个大字符串
index += 1;
}
}
for temp in final_vector { // 合并后的字符串,高度不变(即行数不变)
println!("{}", format!("{}", temp)); // 打印合并后的字符串,按行显示
}
println!("");
2.4 时间刷新
按秒刷新,每秒计算一次图案字符串,然后清屏后显示,实现时间跑秒的感觉。
fn main() {
let pix_clock = pix_clock::new();
let delay = time::Duration::from_secs(1);
loop {
let curdate = Local::now();
let datecollect = curdate.format("%H:%M:%S").to_string();
pix_clock.beautifyshow(&datecollect);
thread::sleep(delay);
Clear(ClearType::All);
}
}
加载全部内容