open 打开浏览器的过程原理示例解析
codeniu 人气:0前言
启动项目时,在本地服务器启动后会自动帮我们打开浏览器,程序是如何做到呢?又是哪些代码在起作用呢?希望通过本章节的学习,达成如下目标:
- 学习程序自动打开浏览的原理
- 学会使用 Node.js 强大的 child_process 模块
源码地址:sindresorhus/open
使用
配置 webpack 的 devServer 选项:
module.exports = {
//...
devServer: {
open: true,
},
};
告诉 dev-server 在服务器启动后打开浏览器。将其设置为 true 以打开默认浏览器。
如果你使用的是 ue-cli,则在启动命令后面添加参数 --open:
# yarn serve 不会自动打开浏览器 yarn serve # --open 参数后会自动打开浏览器 yarn serve --open
open
无论是webpack还是vue-cli,他们能够实现在浏览器中打开网页的功能,主要依赖 open 这个包。
看一下他的 slogan :
Open stuff like URLs, files, executables. Cross-platform.
打开像 URL、文件、可执行文件之类的东西。跨平台。
它有以下优点:
- 这个仓库更新维护及时
- 丰富的参数
- 安全性
- 解决了大多数 node-open 产生的问题
- 跨平台
得益于以上优点,这个包每周有两千多万的下载量:
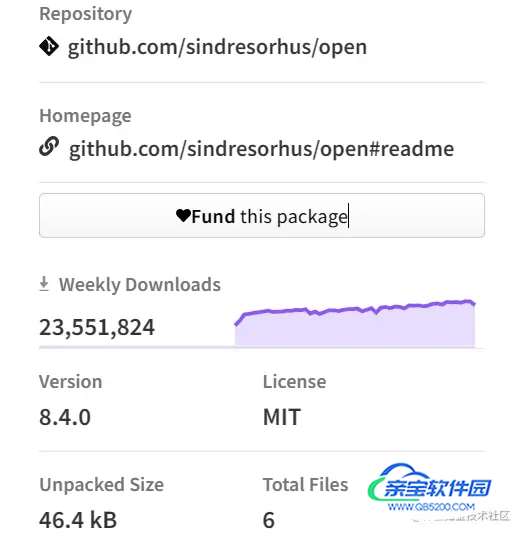
open 的实现原理
入口文件:
定位到 open 函数:
const open = (target, options) => {
if (typeof target !== 'string') {
throw new TypeError('Expected a `target`');
}
return baseOpen({
...options,
target
});
};
可以看到核心实现逻辑在 baseOpen 函数:
const path = require('path');
const childProcess = require('child_process');
const {promises: fs, constants: fsConstants} = require('fs');
const {platform, arch} = process;
const baseOpen = async options => {
options = {
wait: false,
background: false,
newInstance: false,
allowNonzeroExitCode: false,
...options
};
// ... 部分代码...
let command;
const cliArguments = [];
const childProcessOptions = {};
if (platform === 'darwin') {
command = 'open';
if (options.wait) {
cliArguments.push('--wait-apps');
}
// ...省略一些判断,
} else if (platform === 'win32' || (isWsl && !isDocker())) {
const mountPoint = await getWslDrivesMountPoint();
command = isWsl ?
`${mountPoint}c/Windows/System32/WindowsPowerShell/v1.0/powershell.exe` :
`${process.env.SYSTEMROOT}\\System32\\WindowsPowerShell\\v1.0\\powershell`;
cliArguments.push(
'-NoProfile',
'-NonInteractive',
'–ExecutionPolicy',
'Bypass',
'-EncodedCommand'
);
if (app) {
// Double quote with double quotes to ensure the inner quotes are passed through.
// Inner quotes are delimited for PowerShell interpretation with backticks.
encodedArguments.push(`"\`"${app}\`""`, '-ArgumentList');
if (options.target) {
appArguments.unshift(options.target);
}
} else if (options.target) {
encodedArguments.push(`"${options.target}"`);
}
if (appArguments.length > 0) {
appArguments = appArguments.map(arg => `"\`"${arg}\`""`);
encodedArguments.push(appArguments.join(','));
}
// Using Base64-encoded command, accepted by PowerShell, to allow special characters.
options.target = Buffer.from(encodedArguments.join(' '), 'utf16le').toString('base64');
} else {
// ...省略 其他情况
}
if (options.target) {
cliArguments.push(options.target);
}
if (platform === 'darwin' && appArguments.length > 0) {
cliArguments.push('--args', ...appArguments);
}
const subprocess = childProcess.spawn(command, cliArguments, childProcessOptions);
if (options.wait) {
return new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
subprocess.once('error', reject);
subprocess.once('close', exitCode => {
if (options.allowNonzeroExitCode && exitCode > 0) {
reject(new Error(`Exited with code ${exitCode}`));
return;
}
resolve(subprocess);
});
});
}
subprocess.unref();
return subprocess;
};
首先程序,使用 Node.js 中的 process.platform 属性来获取当前操作系统平台的值。字符串 'darwin' 用于标识 macOS。'win32' 则表示 windows操作系统了。
对不同操作系统进行不同的参数组织:
macos: 根据options中的参数一一添加到cliArguments变量中windows: 主要是获取powershell程序的路径。- wsl:根据子系统挂载点路径获取
- win:根据 process.env.SYSTEMROOT 获取操作系统的根路径
process.env.SYSTEMROOT 是一个由 Node.js 提供的全局变量,表示当前系统的根目录的路径。 在 Windows 操作系统中,根目录通常是 C:\Windows。在其他操作系统中,此变量的值可能为空或不存在。
之后使用 Node.js child_process 模块中的 childProcess.spawn 函数,以启动新的子进程并执行命令。
它将 command 和 cliArguments 变量作为参数传递给 childProcess.spawn,以及一个名为 childProcessOptions 的对象,该对象包含子进程的选项。
childProcess.spawn 函数返回一个表示已生成子进程的 ChildProcess 对象。如果 options.wait 属性为 true,则代码会返回一个新的 Promise,该Promise 对象根据子进程的回调函数做出reject或者resolve回应。
两个事件:
- 'error' 事件侦听 器会监控到发生的错误,reject.
- 'close' 事件侦听 器会在退出代码为零(或
options.allowNonzeroExitCode属性为true)时使用subprocess对象解析承诺。如果退出代码为非零且options.allowNonzeroExitCode属性为false,则 reject('错误代码')
最后使用 subprocess.unref 方法保持子进程运行,目的是为了使子进程在后台运行。
总结
总的来说,open原理是:针对不同的系统,使用Node.js的子进程 child_process 模块的spawn方法,调用系统的命令打开浏览器。
通过本章节课程的学习,学习到了如何使用 nodejs 的内置模块对操作系统类型的判断以及childProcess创建子进程的方式,更多关于open打开浏览器原理的资料请关注其它相关文章!
加载全部内容