PyQt中使用QProcess运行一个进程的示例代码
smart_cat 人气:0一、前言
设计应用程序时,有时不希望将一个不太相关的功能集成到程序中,或者是因为该功能与当前设计的应用程序联系不大,或者是因为该功能已经可以使用现成的程序很好地实现了,这时就可以在当前的应用程序中调用外部的程序来实现该功能,这就会使用到进程。Qt应用程序可以很容易地启动一个外部应用程序,而且Qt也提供了很多种进程间通信的方法。
二、运行一个进程
Qt的QProcess类用来启动一个外部程序并与其通信。要启动一个程序,可以使用start()函数,然后将程序名称和运行这个程序说要使用的命令行参数作为该函数的参数。执行完start()后,QProcess进入Starting状态,当程序已经运行后,QProcess就会进入Running状态并发射started信号。当进程退出后,QProcess重新进入NotRunning状态(初始状态)并发射finished信号。
发射的finished信号提供了进程的退出代码和退出状态,也可以调用exitCode()来获取上一个结束的进程的退出代码,使用exitStatus()来获取它的退出状态。任何时间发生了错误,QProcess都会发射error信号,也可以调用error()来查看错误的类型和上次发生的错误。使用state()可以查看当前进程的状态。
三、启动进程的例子
本例中通过按下按钮,启动了windows系统自带的记事本程序,即notepad.exe, 因为它在windows的系统目录下,该目录已经加在了系统的PATH环境变量中,所以不需要特别指定路径。
运行程序,然后单击按钮,就可以启动记事本程序,可以看到,使用QProcess运行一个外部程序是很简单的。
from PyQt5.QtWidgets import QApplication, QWidget, QPushButton, QHBoxLayout, QMessageBox
from PyQt5.QtCore import QProcess
import sys
class MyWidget(QWidget):
def __init__(self):
super().__init__()
self.__process = QProcess()
self.__btn = QPushButton('start notepad')
self.__init_ui()
# 关联button clicked信号和对应的槽函数
self.__btn.clicked.connect(self.__btn_clicked_handler)
self.__process.started.connect(self.__process_started_handler)
self.__process.finished.connect(self.__process_finished_handler)
def __init_ui(self):
my_layout = QHBoxLayout()
my_layout.addWidget(self.__btn)
self.setLayout(my_layout)
def __btn_clicked_handler(self):
'''
处理button的clicked信号,打开notepad.exe
'''
self.__process.start('notepad.exe')
def __process_started_handler(self):
'''
处理QProcess的started信号
'''
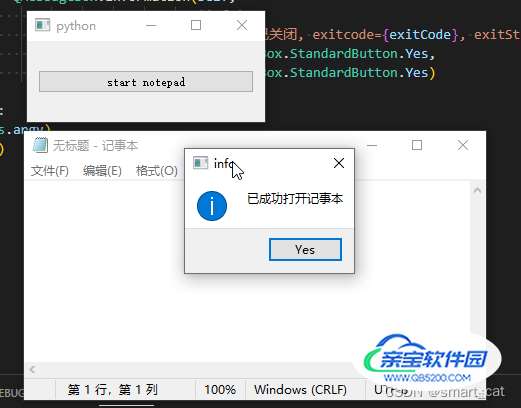
start_msg_box = QMessageBox.information(self,
'info',
'已成功打开记事本',
QMessageBox.StandardButton.Yes,
QMessageBox.StandardButton.Yes)
def __process_finished_handler(self, exitCode, exitStatus):
'''
处理QProcess的finished信号,获取退出状态
'''
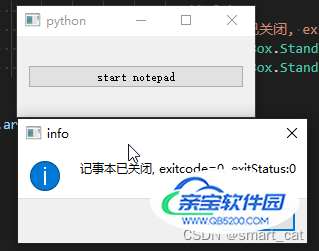
finished_msg_box = QMessageBox.information(self,
'info',
f'记事本已关闭, exitcode={exitCode}, exitStatus:{exitStatus}',
QMessageBox.StandardButton.Yes,
QMessageBox.StandardButton.Yes)
if __name__ == '__main__':
app = QApplication(sys.argv)
my_widget = MyWidget()
my_widget.show()
sys.exit(app.exec_())运行效果如下,
加载全部内容