Java ArrayList与Vector和LinkedList的使用及源码分析
芝麻干 人气:0ArrayList是List接口实现类中的其中一个(重点):
- 数组结构实现,查询快,增删慢
- jdk1.2版本,运行效率快、线程不安全。
ArrayList的使用:和之前使用的类似。
直接看代码:
主类:
package com.collections.test;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Iterator;
import java.util.ListIterator;
public class Demo02 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ArrayList arrayList = new ArrayList();
Student s1 = new Student("aaa",18);
Student s2 = new Student("bbb",19);
Student s3 = new Student("ccc",20);
// 添加
arrayList.add(s1);
arrayList.add(s2);
arrayList.add(s3);
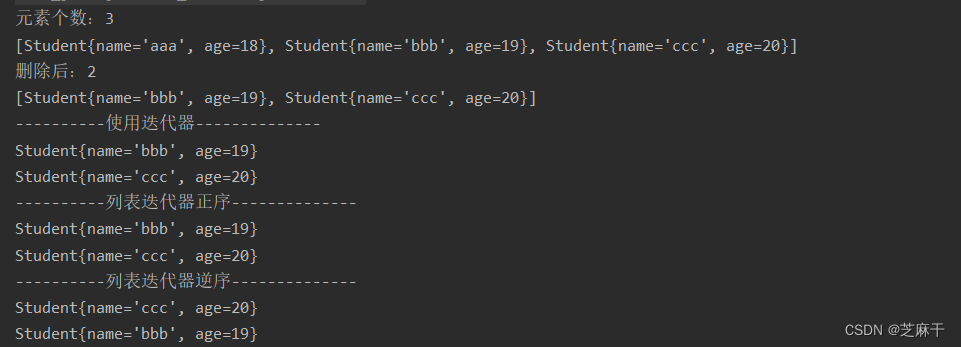
System.out.println("元素个数:"+arrayList.size());
System.out.println(arrayList.toString());
// 删除
// arrayList.remove(s1);
// 重写equal方法,使equal方法比较的是属性后,可以进行如下删除
arrayList.remove(new Student("aaa",18));
System.out.println("删除后:"+arrayList.size());
System.out.println(arrayList.toString());
// 遍历
// 使用迭代器
System.out.println("----------使用迭代器--------------");
Iterator it = arrayList.iterator();
while (it.hasNext()){
Student s = (Student) it.next();
System.out.println(s);
}
System.out.println("----------列表迭代器正序--------------");
// 列表迭代器
ListIterator listIterator = arrayList.listIterator();
while (listIterator.hasNext()){
Student s = (Student) listIterator.next();
System.out.println(s);
}
System.out.println("----------列表迭代器逆序--------------");
while (listIterator.hasPrevious()){
Student s = (Student) listIterator.previous();
System.out.println(s);
}
}
}Student类:重写了equal方法,使比较方法变为属性之间的比较。
package com.collections.test;
import java.util.Objects;
public class Student {
private String name;
private int age;
public Student() {
}
public Student(String name, int age) {
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public int getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setAge(int age) {
this.age = age;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Student{" +
"name='" + name + '\'' +
", age=" + age +
'}';
}
@Override
public boolean equals(Object obj) {
// 1.判断是不是同一类型
if(this==obj){
return true;
}
if(obj==null){
return false;
}
// 3.判断是否是Student类型
if(obj instanceof Student){
// 强制类型转换
Student s = (Student)obj;
if(s.age == this.age && s.name == this.name){
return true;
}
}
return false;
}
}删除和添加可以直接输入属性添加了。
运行结果:
ArrayList源码分析:
1.进入ArrayList源码中,先记住几个变量。
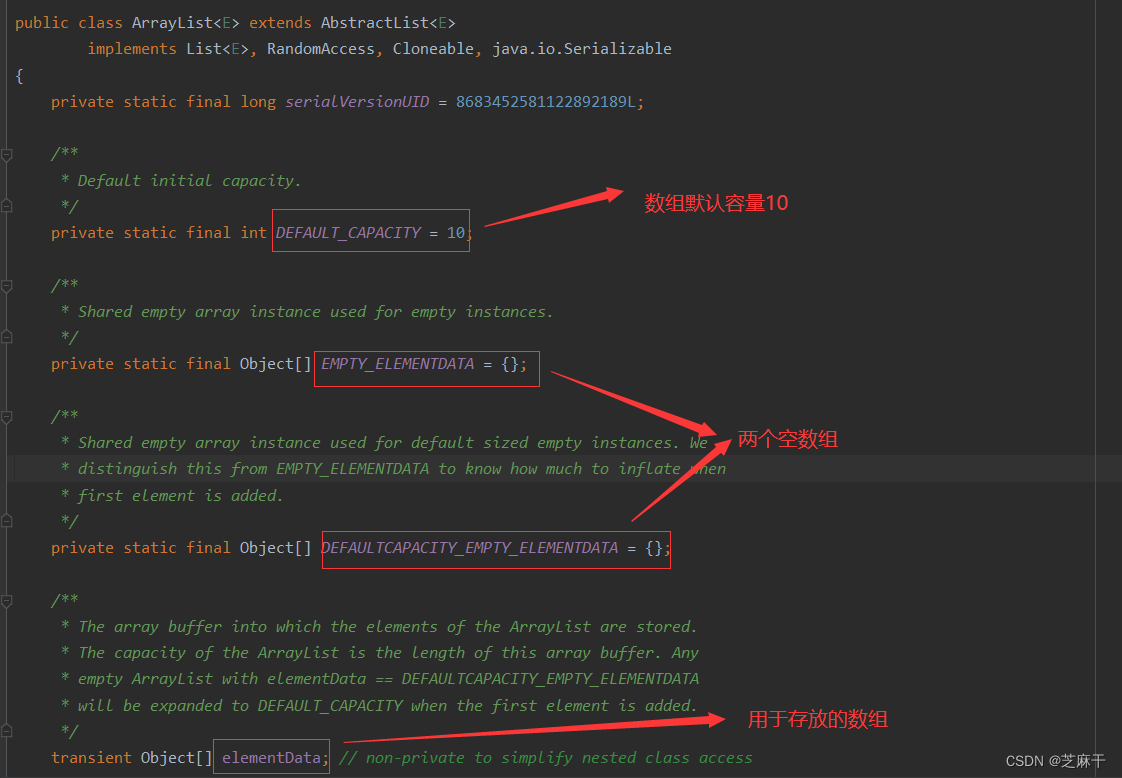
往下还有个size,表示元素个数。
重点记住三个:
默认容量DEFAULT_CAPACITY = 10、存放元素的数组:elemtData 和 实际元素个数size()
往下翻:
因为我们引用的是无参构造方法,有参就跳过,直接看无参的。

也就是说,当没有向集合中添加任何元素时,集合容量为0
当我们添加元素时,也就是add()方法,会是什么情况?进入到add源码中查看。
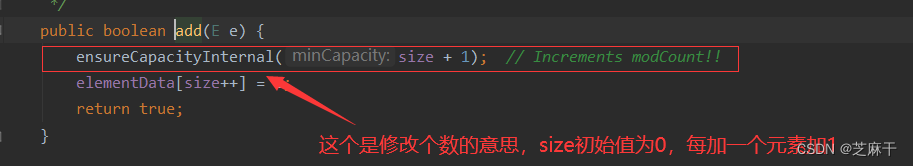
我们再进入到这方法中来看:
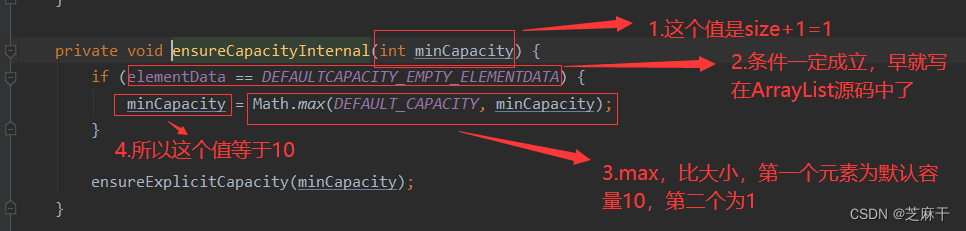
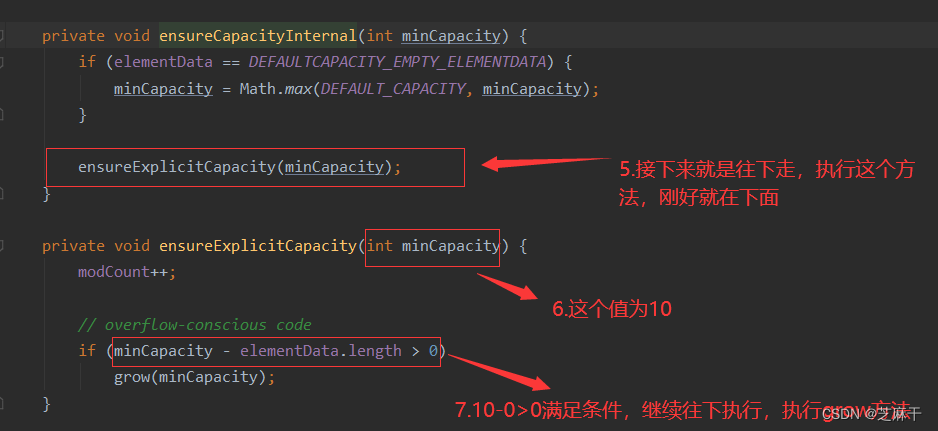
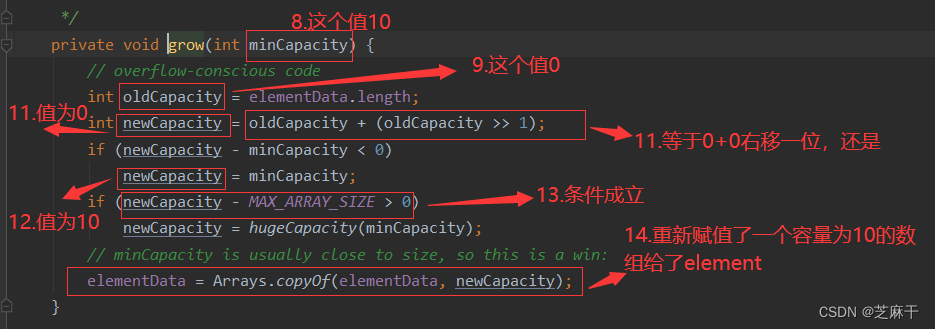
也就是说,当向集合中添加了1个元素时,集合容量就变为10。
如果添加了超过10个元素,会进行扩容,还是和上述方法一样,一步一步看下来,会发现:
当输入第11个元素时,容量最后会变成15,也就是说,每次扩容会是原来的1.5倍。 其实就是上述第11步的右移一位,相当于加上了原来值的二分之一,也就是1.5倍。
总结一下:
如果集合中没有元素时,容量为0,如果添加了一个元素,集合会是默认容量10,如果超出容量大小,会进行扩容,每次容量时原来的1.5倍。
源码查看:ctrl+鼠标左键。
Vector的使用:
直接看代码:
package com.collections;
import java.util.Enumeration;
import java.util.Vector;
//Vector集合的使用
//存储方式:数组
public class Demo04 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Vector vector = new Vector();
// 添加
vector.add("苹果");
vector.add("梨子");
vector.add("西瓜");
System.out.println("元素个数为:"+vector.size());
// 枚举器遍历
Enumeration elements = vector.elements();
while (elements.hasMoreElements()){
String s = (String) elements.nextElement();
System.out.println(s);
}
System.out.println("-----------------------------------");
// 其他方法firstElement 第一个元素 lastElement最后一个元素 elementAt()位置遍历
System.out.println(vector.firstElement());
System.out.println(vector.lastElement());
System.out.println(vector.elementAt(2));
}
}LinkedList的使用:
package com.collections.test;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Iterator;
import java.util.LinkedList;
import java.util.ListIterator;
//LinkList的使用
public class Demo03 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
LinkedList linkedList = new LinkedList();
Student s1 = new Student("aaa",18);
Student s2 = new Student("bbb",19);
Student s3 = new Student("ccc",20);
// 添加
linkedList.add(s1);
linkedList.add(s2);
linkedList.add(s3);
System.out.println("元素个数:"+linkedList.size());
System.out.println(linkedList.toString());
// 删除
// linkedList.remove(s1);
System.out.println("删除后:"+linkedList.size());
System.out.println(linkedList.toString());
// 遍历
// for 循环
System.out.println("----------for循环--------------");
for (int i = 0; i <linkedList.size() ; i++) {
System.out.println(linkedList.get(i));
}
System.out.println("----------增强for循环--------------");
for (Object o:linkedList) {
System.out.println(o);
}
// 使用迭代器
System.out.println("----------使用迭代器--------------");
Iterator it = linkedList.iterator();
while (it.hasNext()){
Student s = (Student) it.next();
System.out.println(s);
}
System.out.println("----------列表迭代器正序--------------");
// 列表迭代器
ListIterator listIterator = linkedList.listIterator();
while (listIterator.hasNext()){
Student s = (Student) listIterator.next();
System.out.println(s);
}
System.out.println("----------列表迭代器逆序--------------");
while (listIterator.hasPrevious()){
Student s = (Student) listIterator.previous();
System.out.println(s);
}
}
}加载全部内容