Java集合的定义与Collection类使用详解
芝麻干 人气:1什么是集合?
概念:对象的容器,定义了对多个对象进行操作的常用方法。可实现数组的功能。
集合和数组的区别:
- 数组长度固定,集合长度不固定
- 数组可以存储基本类型和引用类型,集合只能引用类型
Collection :
Collection体系结构:
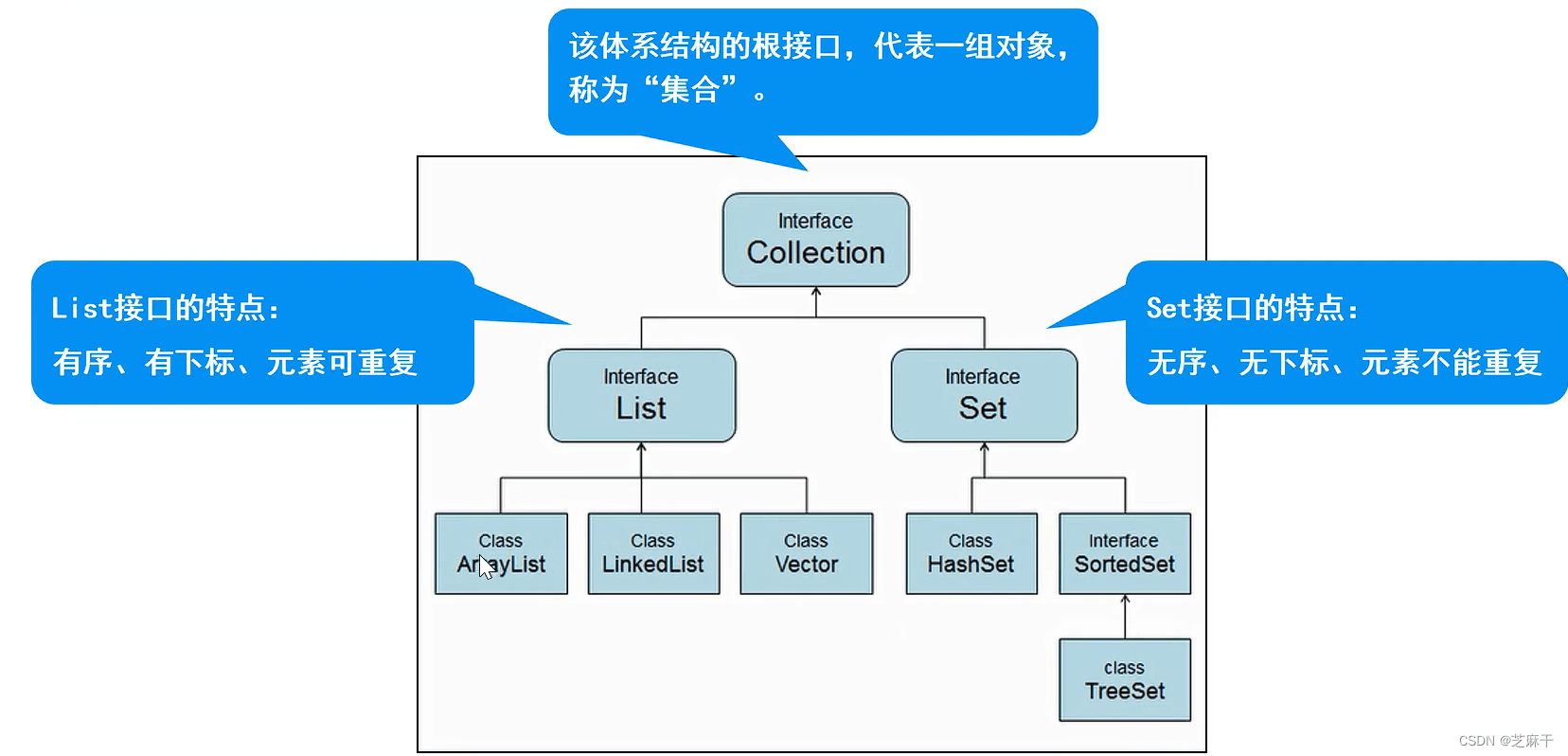
Collection的使用:包括增加元素、删除元素、遍历元素(两种方法)和判断
直接看代码:
package com.collections;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Collection;
import java.util.Iterator;
public class Demo01 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 创建集合
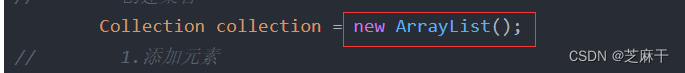
Collection collection = new ArrayList();
// 1.添加元素
collection.add("苹果");
collection.add("梨子");
collection.add("榴莲");
System.out.println(collection);
System.out.println("元素个数为:"+collection.size());
// 2.删除元素
collection.remove("榴莲");
System.out.println(collection);
System.out.println("元素个数为:"+collection.size());
// 3.遍历元素
// 3.1增强for循环
System.out.println("-------------3.1增强for循环----------------");
for (Object object:collection) {
System.out.println(object);
}
System.out.println("-------------3.2使用迭代器Iterator----------------");
// 3.2使用迭代器Iterator,本身是一个接口
// 三种方法:hasNext()判断是否有元素,next()获取下一个元素,remove()删除元素
Iterator it = collection.iterator();
while (it.hasNext()){
String s = (String)it.next();
System.out.println(s);
//it.remove();
}
System.out.println("元素个数为"+collection.size());
// 4.判断:contains
System.out.println(collection.contains("西瓜"));
// 判断是否为空
System.out.println(collection.isEmpty());
}
}注意:使用Collection是不能实例化的,但是可以通过new一个它的子类来创建对象的。
还有就是重点记住遍历元素的方法。 迭代器Iterator。
迭代器Iterator:
三种方法hasNext()、next() 还有一个remove()用于删除迭代器中的元素(在迭代器中,是不可以用collection.remove来删除元素的)
原理:
先用hasNext()判断是否有元素,如果有就下一个next(),依次类推。
使用Collection保存学生信息:
直接看代码:
Student类
package com.collections.test;
public class Student {
private String name;
private int age;
public Student() {
}
public Student(String name, int age) {
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public int getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setAge(int age) {
this.age = age;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Student{" +
"name='" + name + '\'' +
", age=" + age +
'}';
}
}主方法:
package com.collections.test;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Collection;
import java.util.Iterator;
public class Demo01 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Student s1 = new Student("aaa",18);
Student s2 = new Student("bbb",19);
Student s3 = new Student("ccc",20);
Collection collection = new ArrayList();
collection.add(s1);
collection.add(s2);
collection.add(s3);
System.out.println("元素个数为:"+collection.size());
System.out.println(collection.toString());
// collection.remove(s1);
// collection.remove(new Student("ccc",20));
System.out.println("删除后:"+collection.size());
System.out.println(collection.toString());
// 3.遍历
for (Object object:collection) {
Student s = (Student)object;
System.out.println(s);
}
System.out.println("-----------------------------------------");
// 迭代器
Iterator it = collection.iterator();
while(it.hasNext()){
Student s = (Student) it.next();
System.out.println(s);
}
}
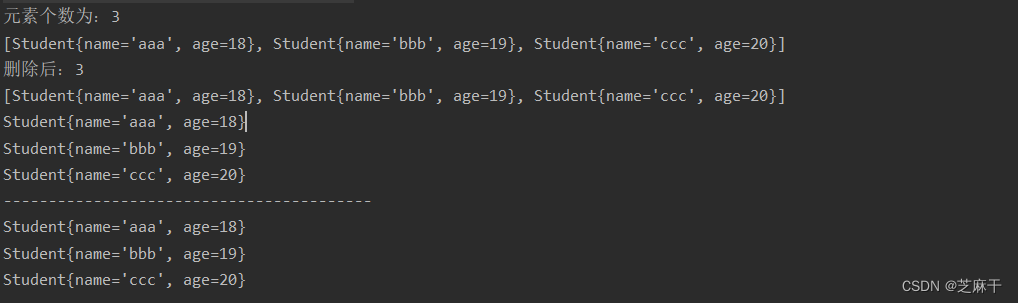
}运行结果:
加载全部内容