解读Integer类的parseInt和valueOf的区别
bai_student 人气:0Integer类的parseInt和valueOf区别
我们平时应该都用过或者见过parseInt和valueOf这两个方法。一般我们是想把String类型的字符数字转成int类型。从这个功能层面来说,这两个方法都一样,都可以胜任这个功能。
但是,我们进入源码,看下Integer类下这两个方法
我们看parseInt()这个方法是如何实现的
public static int parseInt(String s) throws NumberFormatException {
return parseInt(s,10);
}我们再看valueOf()是如何实现的
public static Integer valueOf(String s) throws NumberFormatException {
return Integer.valueOf(parseInt(s, 10));
}从代码,我们起码看到了两点:返回结果类型不一样,parseInt方法返回的是int基本类型,valueOf方法返回的是Integer的包装类型
valueOf方法实际上是调用了parseInt方法,也就是说,如果我们仅仅只需要得到字符串类型字符数值对应的整数数值,那我们大可不必调用valueOf,因为这样得到整形数值之后还要做一个装箱的操作,将int封装为Integer。
写代码测试效率:
public class StringDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
String str = "123";
long startTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
for(int i = 0;i<100000000;i++){
Integer.parseInt(str);
}
long endTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println(endTime-startTime);
}
}如下代码:
public class StringDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
String str = "123";
long startTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
for(int i = 0;i<100000000;i++){
Integer.valueOf(str);
}
long endTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println(endTime-startTime);
}
}分别测试三遍,得到的时间如下,可以看到paraseInt()的效率更好。
| 方法 | 第一次时长 | 第二次时长 | 第三次时长 |
|---|---|---|---|
| parseInt() | 2946 | 2965 | 2952 |
| valueOf() | 3124 | 3117 | 3126 |
Integer的parseInt与value of原理
我一直使用Integer的转换,包括Long,枚举等,从来没有注意它是怎么实现的,最近有个业务组转换报错了,想看看是如何实现的。据笔者猜测:ASCII码转换?这是常用的计量,什么大写变小写都是这样实现的。下面看看如何实现的吧
1. demo构建
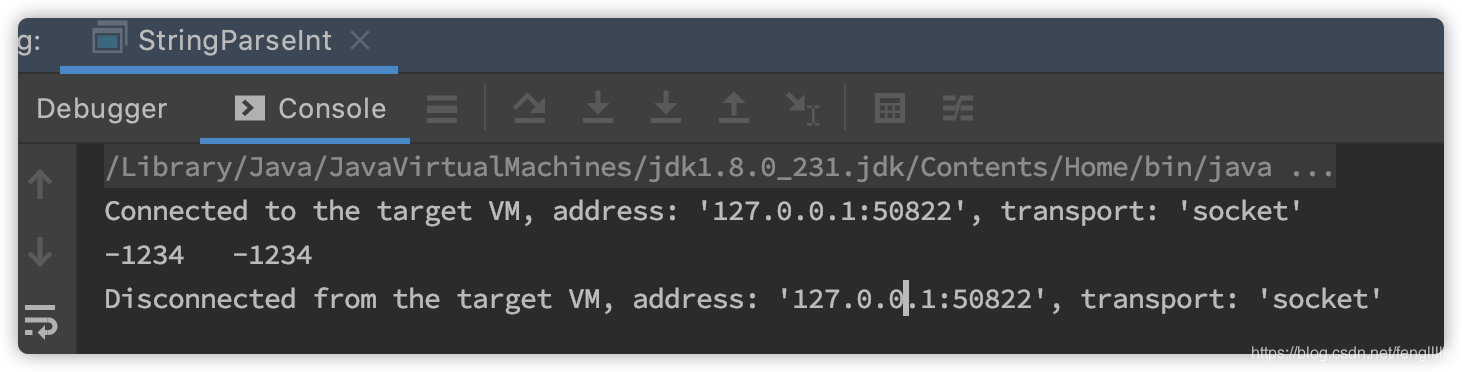
public class StringParseInt {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String str = "-1234";
int i = Integer.parseInt(str);
int y = Integer.valueOf(str);
System.out.println(i + "\t" + y);
}
}输出都正常,关键是看怎么实现的
2. Integer的实现方式
2.1 value of
public static Integer valueOf(String s) throws NumberFormatException {
return Integer.valueOf(parseInt(s, 10));
}本质还是parseInt,从这点看与parseInt没有区别;但是这里有装箱,如果接收值是int建议直接使用parseInt,省去装箱的过程。
public static Integer valueOf(int i) {
if (i >= IntegerCache.low && i <= IntegerCache.high)
return IntegerCache.cache[i + (-IntegerCache.low)];
return new Integer(i);
}如果在缓存数组,直接使用,看看缓存数组怎么来的
private static class IntegerCache {
//下限固定-128
static final int low = -128;
//上限没有初始化
static final int high;
//核心缓存数组
static final Integer cache[];
//类加载初始化
static {
// high value may be configured by property
//初始127上限
int h = 127;
//VM参数java.lang.Integer.IntegerCache.high可以配置Integer的最大上限
String integerCacheHighPropValue =
sun.misc.VM.getSavedProperty("java.lang.Integer.IntegerCache.high");
if (integerCacheHighPropValue != null) {
try {
//我没设置的值,如果不是int字符串型就会报错,然后被捕获
int i = parseInt(integerCacheHighPropValue);
//取大,对比127;也就是至少是127
i = Math.max(i, 127);
// Maximum array size is Integer.MAX_VALUE
// 上面官方注释很明显了,这里减128再减1是因为low是-128
h = Math.min(i, Integer.MAX_VALUE - (-low) -1);
} catch( NumberFormatException nfe) {
// If the property cannot be parsed into an int, ignore it.
}
}
high = h;
//创建缓存数组,如果设置java.lang.Integer.IntegerCache.high,不宜设置过大,过大很占连续空间
cache = new Integer[(high - low) + 1];
int j = low;
//初始化缓存
for(int k = 0; k < cache.length; k++)
cache[k] = new Integer(j++);
// range [-128, 127] must be interned (JLS7 5.1.7)
//断言至少127,JLS7
assert IntegerCache.high >= 127;
}
private IntegerCache() {}
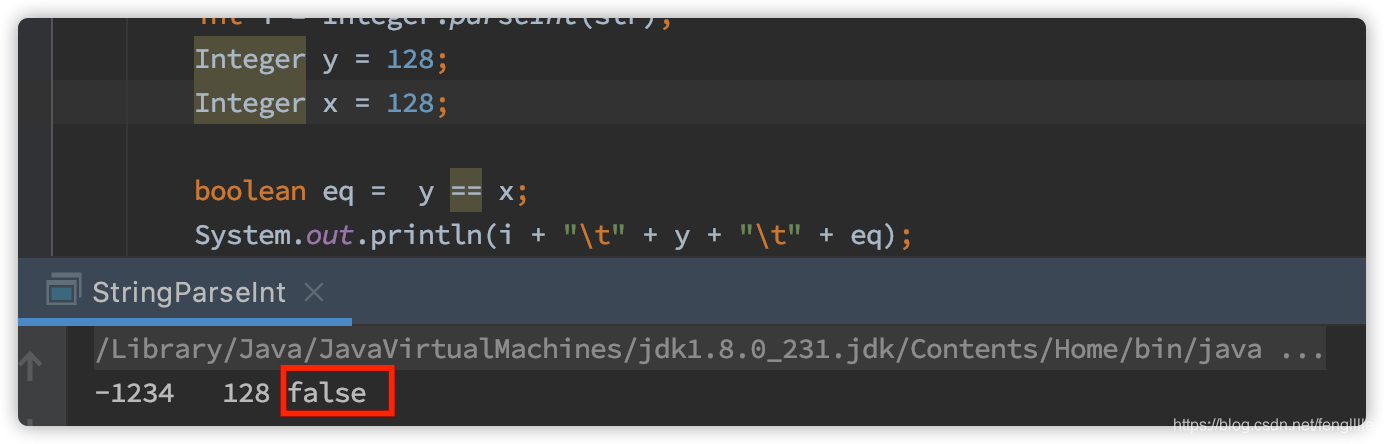
}从源码看Integer内部类装载时,会初始化一个缓存空间,存储Integer对象。很多面试时就会被这个坑了,初始化的缓存对象地址取值是一致的,可以使用==作对比;然后超过这个范围的Integer就不能了,要使用Integer的eq方法
public boolean equals(Object obj) {
if (obj instanceof Integer) {
return value == ((Integer)obj).intValue();
}
return false;
}因为自动装箱,实际上使用的value of方法,默认情况下,-128~127使用缓存对象。
2.2 parseInt
/**
* 这段注释尤为重要,定义了符号位,定义了10进制数字
* Parses the string argument as a signed decimal integer. The
* characters in the string must all be decimal digits, except
* that the first character may be an ASCII minus sign {@code '-'}
* ({@code '\u005Cu002D'}) to indicate a negative value or an
* ASCII plus sign {@code '+'} ({@code '\u005Cu002B'}) to
* indicate a positive value. The resulting integer value is
* returned, exactly as if the argument and the radix 10 were
* given as arguments to the {@link #parseInt(java.lang.String,
* int)} method.
*
* @param s a {@code String} containing the {@code int}
* representation to be parsed
* @return the integer value represented by the argument in decimal.
* @exception NumberFormatException if the string does not contain a
* parsable integer.
*/
public static int parseInt(String s) throws NumberFormatException {
return parseInt(s,10);
}重点来哦,String能转为int的本质,这里需要传一个核心参数,Integer给我们默认了10进制,其他类型也是相同,比如Long
public static long parseLong(String s) throws NumberFormatException {
return parseLong(s, 10);
}因为转换后的就是10进制的数字,可供使用。
进一步分析parseInt(String s, int radix);radix即进制的意思。
public static int parseInt(String s, int radix)
throws NumberFormatException
{
/*
* WARNING: This method may be invoked early during VM initialization
* before IntegerCache is initialized. Care must be taken to not use
* the valueOf method.
*/
//字符串不能为null,没有判断空字符串
if (s == null) {
throw new NumberFormatException("null");
}
//进制不能小于2,至少要2进制
if (radix < Character.MIN_RADIX) {
throw new NumberFormatException("radix " + radix +
" less than Character.MIN_RADIX");
}
//进制不能大于36
if (radix > Character.MAX_RADIX) {
throw new NumberFormatException("radix " + radix +
" greater than Character.MAX_RADIX");
}
int result = 0;
//正负标记,默认正
boolean negative = false;
//字符串长度
int i = 0, len = s.length();
int limit = -Integer.MAX_VALUE;
int multmin;
int digit;
//干活了
if (len > 0) {
//首位字符
char firstChar = s.charAt(0);
//这里玩了个计谋,0字符的ASCII是48,后面的数字包括ABCDEF的ASCII都比0大;
//其中 + 43; - 45
//只有带符号位的会判断,其他就默认正数
if (firstChar < '0') { // Possible leading "+" or "-"
//负数
if (firstChar == '-') {
negative = true;
limit = Integer.MIN_VALUE;
//非负即正,因为小于'0'
} else if (firstChar != '+')
throw NumberFormatException.forInputString(s);
if (len == 1) // Cannot have lone "+" or "-" 注释说明白了
throw NumberFormatException.forInputString(s);
i++;
}
multmin = limit / radix;
while (i < len) {
// Accumulating negatively avoids surprises near MAX_VALUE
// 拿到字符,转换为ASCII数字并按进制转为数字
digit = Character.digit(s.charAt(i++),radix);
//不能带符号位,前面已经验证了
if (digit < 0) {
throw NumberFormatException.forInputString(s);
}
//最小限制,但是这里是一个负数
if (result < multmin) {
throw NumberFormatException.forInputString(s);
}
//由于是从高位向低位,所以需要进制;字符每往后走,需要乘进制
result *= radix;
//同样最小验证,可能在某些地方有用,暂时没看出来
if (result < limit + digit) {
throw NumberFormatException.forInputString(s);
}
//这里使用反向进位,为了照顾字符从前往后,也可以字符从后往前正向进位
result -= digit;
}
} else {
throw NumberFormatException.forInputString(s);
}
//负数正数校正,上面的算法是反向进位
return negative ? result : -result;
}这里说一下Character.digit(s.charAt(i++),radix)
public static int digit(char ch, int radix) {
return digit((int)ch, radix);
}digit就是数字的意思,这里直接把char字符强转int类型,即ASCII数字,然后按照进制转换成相应的数字
小结:类型转换其实是字符的ASCII的解析符号位,并按字符转为数字,然后使用逆向负进位方式生成数字,最后修正符号得出我们想要的结果。算法符合了字符串解析的顺序,不符合人类的思维习惯。
以上为个人经验,希望能给大家一个参考,也希望大家多多支持。
加载全部内容