Spring boot异步任务原理全面分析
fenglllle 人气:0前言
我们经常在需要提升性能或者项目架构解耦的过程中,使用线程池异步执行任务,经常使用ThreadPoolExecutor创建线程池。那么Spring对异步任务是如何处理的呢?
1. spring 异步任务
估计或多或少了解过一些,比如@EnableAsync可以开启异步任务,@Async用于注解说明当前方法是异步执行,下面使用demo看看Spring的异步任务如何执行。
pom依赖,其实仅依赖Spring core context 就可以了,这里演示,另外spring boot还要许多好玩的特性。
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId>
<version>2.1.3.RELEASE</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-test</artifactId>
<version>2.1.3.RELEASE</version>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
</dependencies>main & controller
@RestController
@SpringBootApplication
public class AsyncMain {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(AsyncMain.class, args);
}
@Autowired
private TaskService taskService;
@RequestMapping(value = "/async-task", method = RequestMethod.GET)
public String asyncMapping(){
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getThreadGroup() + "http-------" + Thread.currentThread().getName());
taskService.doTask();
return "exec http ok--------------";
}
}异步任务服务
@EnableAsync
@Service
public class TaskService {
@Async
public String doTask(){
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getThreadGroup() + "-------" + Thread.currentThread().getName());
return "do task done";
}
}运行main方法,访问localhost:8080/async-task,控制台可以看到:

可以看到线程的name是task-1,而http访问的线程是http-nio-xxx。说明任务异步执行了。然而Spring的异步任务是如何执行的呢,我们也并未创建线程池,难道Spring替我们创建了?
2. Spring boot异步任务执行过程分析
首先,需要执行异步任务,必须创建线程池,那我们来揪出Spring创建的线程池,从启动日志可以看出

Spring默认给我们创建了applicationTaskExecutor的ExecutorService的线程池。
通过源码分析,Spring boot的starter已经给我们设置了默认的执行器
/**
* {@link EnableAutoConfiguration Auto-configuration} for {@link TaskExecutor}.
*
* @author Stephane Nicoll
* @author Camille Vienot
* @since 2.1.0
*/
@ConditionalOnClass(ThreadPoolTaskExecutor.class)
@Configuration
@EnableConfigurationProperties(TaskExecutionProperties.class)
public class TaskExecutionAutoConfiguration {
/**
* Bean name of the application {@link TaskExecutor}.
*/
public static final String APPLICATION_TASK_EXECUTOR_BEAN_NAME = "applicationTaskExecutor";
private final TaskExecutionProperties properties;
private final ObjectProvider<TaskExecutorCustomizer> taskExecutorCustomizers;
private final ObjectProvider<TaskDecorator> taskDecorator;
public TaskExecutionAutoConfiguration(TaskExecutionProperties properties,
ObjectProvider<TaskExecutorCustomizer> taskExecutorCustomizers,
ObjectProvider<TaskDecorator> taskDecorator) {
this.properties = properties;
this.taskExecutorCustomizers = taskExecutorCustomizers;
this.taskDecorator = taskDecorator;
}
@Bean
@ConditionalOnMissingBean
public TaskExecutorBuilder taskExecutorBuilder() {
TaskExecutionProperties.Pool pool = this.properties.getPool();
TaskExecutorBuilder builder = new TaskExecutorBuilder();
builder = builder.queueCapacity(pool.getQueueCapacity());
builder = builder.corePoolSize(pool.getCoreSize());
builder = builder.maxPoolSize(pool.getMaxSize());
builder = builder.allowCoreThreadTimeOut(pool.isAllowCoreThreadTimeout());
builder = builder.keepAlive(pool.getKeepAlive());
builder = builder.threadNamePrefix(this.properties.getThreadNamePrefix());
builder = builder.customizers(this.taskExecutorCustomizers);
builder = builder.taskDecorator(this.taskDecorator.getIfUnique());
return builder;
}
@Lazy
@Bean(name = { APPLICATION_TASK_EXECUTOR_BEAN_NAME,
AsyncAnnotationBeanPostProcessor.DEFAULT_TASK_EXECUTOR_BEAN_NAME })
@ConditionalOnMissingBean(Executor.class)
public ThreadPoolTaskExecutor applicationTaskExecutor(TaskExecutorBuilder builder) {
return builder.build();
}
}追根溯源:在Spring boot的autoconfigure中已经定义了默认实现
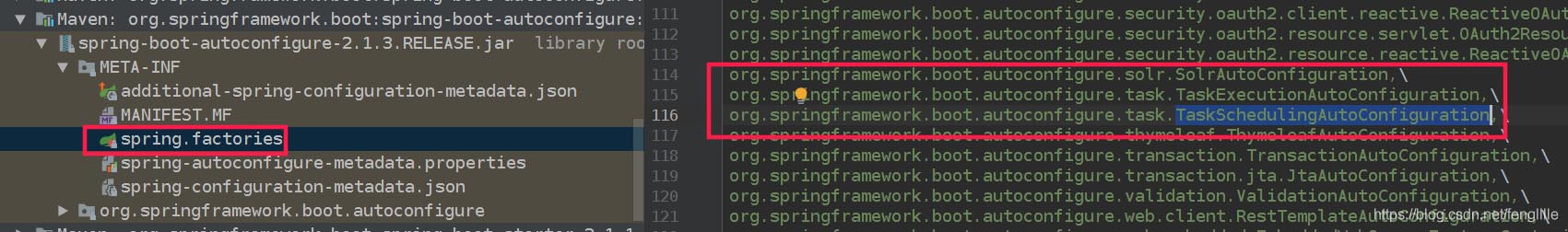
Spring为我们定义了两种实现,如上图所示,根据Spring boot的配置定律,我们可以通过配置来定义异步任务的参数
@ConfigurationProperties("spring.task.execution")
public class TaskExecutionProperties {
private final Pool pool = new Pool();
/**
* Prefix to use for the names of newly created threads.
*/
private String threadNamePrefix = "task-";
public Pool getPool() {
return this.pool;
}
public String getThreadNamePrefix() {
return this.threadNamePrefix;
}
public void setThreadNamePrefix(String threadNamePrefix) {
this.threadNamePrefix = threadNamePrefix;
}
public static class Pool {
/**
* Queue capacity. An unbounded capacity does not increase the pool and therefore
* ignores the "max-size" property.
*/
private int queueCapacity = Integer.MAX_VALUE;
/**
* Core number of threads.
*/
private int coreSize = 8;
/**
* Maximum allowed number of threads. If tasks are filling up the queue, the pool
* can expand up to that size to accommodate the load. Ignored if the queue is
* unbounded.
*/
private int maxSize = Integer.MAX_VALUE;
/**
* Whether core threads are allowed to time out. This enables dynamic growing and
* shrinking of the pool.
*/
private boolean allowCoreThreadTimeout = true;
/**
* Time limit for which threads may remain idle before being terminated.
*/
private Duration keepAlive = Duration.ofSeconds(60);省略get set方法,spring boot的配置以spring.task.execution开头,参数的设置参考如上源码的属性设置。
各位可以自行尝试,当然因为Spring bean的定义方式,我们可以复写bean来达到自定义的目的
@Lazy
@Bean(name = { APPLICATION_TASK_EXECUTOR_BEAN_NAME,
AsyncAnnotationBeanPostProcessor.DEFAULT_TASK_EXECUTOR_BEAN_NAME })
@ConditionalOnMissingBean(Executor.class)
public ThreadPoolTaskExecutor applicationTaskExecutor(TaskExecutorBuilder builder) {
return builder.build();
}比如:
@Configuration
@EnableAsync
public class TaskAsyncConfig {
@Bean
public Executor initExecutor(){
ThreadPoolTaskExecutor executor = new ThreadPoolTaskExecutor();
//定制线程名称,还可以定制线程group
executor.setThreadFactory(new ThreadFactory() {
private final AtomicInteger threadNumber = new AtomicInteger(1);
@Override
public Thread newThread(Runnable r) {
Thread t = new Thread(Thread.currentThread().getThreadGroup(), r,
"async-task-" + threadNumber.getAndIncrement(),
0);
return t;
}
});
executor.setCorePoolSize(10);
executor.setMaxPoolSize(20);
executor.setKeepAliveSeconds(5);
executor.setQueueCapacity(100);
// executor.setRejectedExecutionHandler(null);
return executor;
}
}重启,访问localhost:8080/async-task,证明我们写的Executor已经覆盖系统默认了。
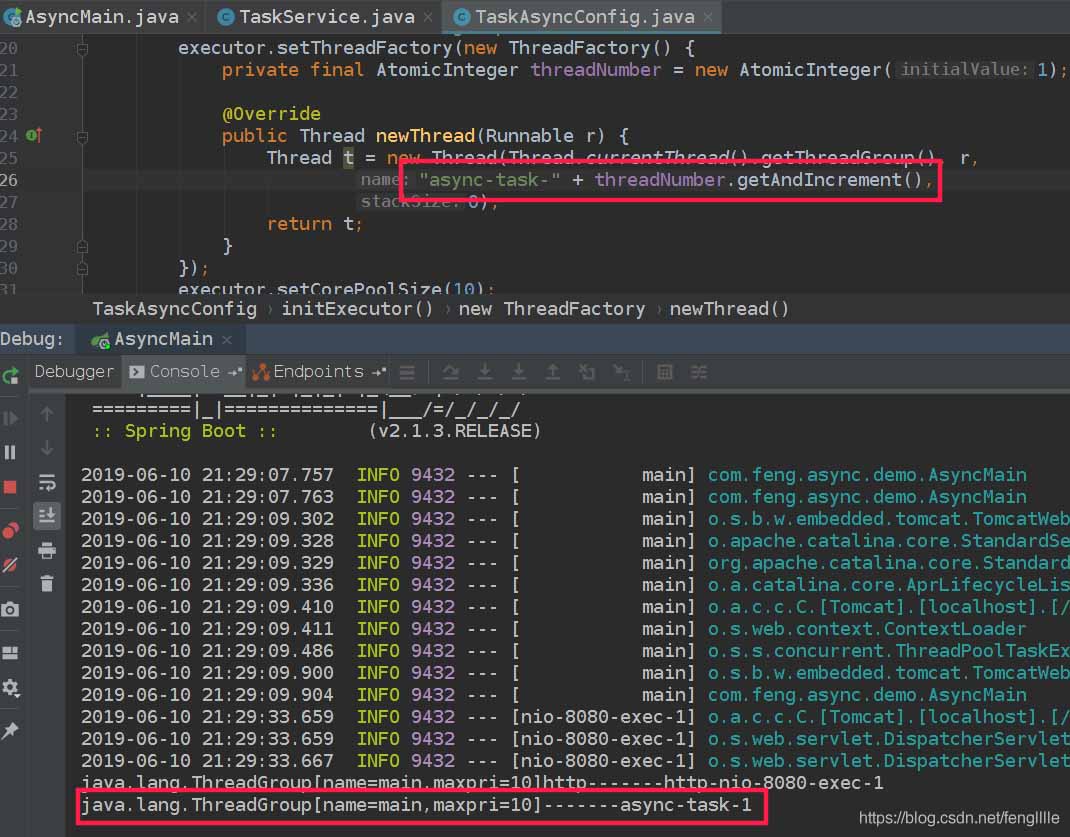
3. Spring 异步任务执行过程分析
方法断点跟踪

执行异步任务使用Spring CGLib动态代理AOP实现

可以看出动态代理后使用AsyncExecutionInterceptor来处理异步逻辑,执行submit方法

同理可以看出,默认的taskExecutor使用BeanFactory中获取。

默认使用SimpleAsyncUncaughtExceptionHandler处理异步异常。下面我们来试试
@EnableAsync
@Service
public class TaskService {
@Async
public String doTask(){
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getThreadGroup() + "-------" + Thread.currentThread().getName());
throw new RuntimeException(" I`m a demo test exception-----------------");
}
}默认会打印logger.error("Unexpected exception occurred invoking async method: " + method, ex);日志
public class SimpleAsyncUncaughtExceptionHandler implements AsyncUncaughtExceptionHandler {
private static final Log logger = LogFactory.getLog(SimpleAsyncUncaughtExceptionHandler.class);
@Override
public void handleUncaughtException(Throwable ex, Method method, Object... params) {
if (logger.isErrorEnabled()) {
logger.error("Unexpected exception occurred invoking async method: " + method, ex);
}
}
}运行测试

4. Spring 自定义Executor与自定义异步异常处理
需要实现AsyncConfigurer接口,可以看到Spring要我们配合EnableAsync与Configuration注解同时使用
/**
* Interface to be implemented by @{@link org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration
* Configuration} classes annotated with @{@link EnableAsync} that wish to customize the
* {@link Executor} instance used when processing async method invocations or the
* {@link AsyncUncaughtExceptionHandler} instance used to process exception thrown from
* async method with {@code void} return type.
*
* <p>Consider using {@link AsyncConfigurerSupport} providing default implementations for
* both methods if only one element needs to be customized. Furthermore, backward compatibility
* of this interface will be insured in case new customization options are introduced
* in the future.
*
* <p>See @{@link EnableAsync} for usage examples.
*
* @author Chris Beams
* @author Stephane Nicoll
* @since 3.1
* @see AbstractAsyncConfiguration
* @see EnableAsync
* @see AsyncConfigurerSupport
*/
public interface AsyncConfigurer {
/**
* The {@link Executor} instance to be used when processing async
* method invocations.
*/
@Nullable
default Executor getAsyncExecutor() {
return null;
}
/**
* The {@link AsyncUncaughtExceptionHandler} instance to be used
* when an exception is thrown during an asynchronous method execution
* with {@code void} return type.
*/
@Nullable
default AsyncUncaughtExceptionHandler getAsyncUncaughtExceptionHandler() {
return null;
}
}demo,如下改造
@Configuration
@EnableAsync
public class TaskAsyncConfig implements AsyncConfigurer {
@Override
public Executor getAsyncExecutor() {
ThreadPoolTaskExecutor executor = new ThreadPoolTaskExecutor();
//定制线程名称,还可以定制线程group
executor.setThreadFactory(new ThreadFactory() {
private final AtomicInteger threadNumber = new AtomicInteger(1);
@Override
public Thread newThread(Runnable r) {
//重新定义一个名称
Thread t = new Thread(Thread.currentThread().getThreadGroup(), r,
"async-task-all" + threadNumber.getAndIncrement(),
0);
return t;
}
});
executor.setCorePoolSize(10);
executor.setMaxPoolSize(20);
executor.setKeepAliveSeconds(5);
executor.setQueueCapacity(100);
// executor.setRejectedExecutionHandler(null);
executor.initialize();
return executor;
}
@Override
public AsyncUncaughtExceptionHandler getAsyncUncaughtExceptionHandler() {
return new AsyncUncaughtExceptionHandler() {
@Override
public void handleUncaughtException(Throwable ex, Method method, Object... params) {
System.out.println("do exception by myself");
}
};
}
}记住,此时,Spring就不会替我们管理Executor了,需要我们自己初始化
executor.initialize();
观其源码就是new 一个ThreadPoolExecutor
@Override
protected ExecutorService initializeExecutor(
ThreadFactory threadFactory, RejectedExecutionHandler rejectedExecutionHandler) {
BlockingQueue<Runnable> queue = createQueue(this.queueCapacity);
ThreadPoolExecutor executor;
if (this.taskDecorator != null) {
executor = new ThreadPoolExecutor(
this.corePoolSize, this.maxPoolSize, this.keepAliveSeconds, TimeUnit.SECONDS,
queue, threadFactory, rejectedExecutionHandler) {
@Override
public void execute(Runnable command) {
Runnable decorated = taskDecorator.decorate(command);
if (decorated != command) {
decoratedTaskMap.put(decorated, command);
}
super.execute(decorated);
}
};
}
else {
executor = new ThreadPoolExecutor(
this.corePoolSize, this.maxPoolSize, this.keepAliveSeconds, TimeUnit.SECONDS,
queue, threadFactory, rejectedExecutionHandler);
}
if (this.allowCoreThreadTimeOut) {
executor.allowCoreThreadTimeOut(true);
}
this.threadPoolExecutor = executor;
return executor;
}运行,结果如下

总结
Spring boot将简单的ThreadPoolExecutor通过封装成了异步任务,大大方便了程序的开发。
然而我们在如上的示例中,并没有处理程序的异步执行结果,其实Spring定义了结果的处理
/**
* AOP Alliance {@code MethodInterceptor} that processes method invocations
* asynchronously, using a given {@link org.springframework.core.task.AsyncTaskExecutor}.
* Typically used with the {@link org.springframework.scheduling.annotation.Async} annotation.
*
* <p>In terms of target method signatures, any parameter types are supported.
* However, the return type is constrained to either {@code void} or
* {@code java.util.concurrent.Future}. In the latter case, the Future handle
* returned from the proxy will be an actual asynchronous Future that can be used
* to track the result of the asynchronous method execution. However, since the
* target method needs to implement the same signature, it will have to return
* a temporary Future handle that just passes the return value through
* (like Spring's {@link org.springframework.scheduling.annotation.AsyncResult}
* or EJB 3.1's {@code javax.ejb.AsyncResult}).
*
* <p>When the return type is {@code java.util.concurrent.Future}, any exception thrown
* during the execution can be accessed and managed by the caller. With {@code void}
* return type however, such exceptions cannot be transmitted back. In that case an
* {@link AsyncUncaughtExceptionHandler} can be registered to process such exceptions.
*
* <p>As of Spring 3.1.2 the {@code AnnotationAsyncExecutionInterceptor} subclass is
* preferred for use due to its support for executor qualification in conjunction with
* Spring's {@code @Async} annotation.
*
* @author Juergen Hoeller
* @author Chris Beams
* @author Stephane Nicoll
* @since 3.0
* @see org.springframework.scheduling.annotation.Async
* @see org.springframework.scheduling.annotation.AsyncAnnotationAdvisor
* @see org.springframework.scheduling.annotation.AnnotationAsyncExecutionInterceptor
*/
public class AsyncExecutionInterceptor extends AsyncExecutionAspectSupport implements MethodInterceptor, Ordered {<p>In terms of target method signatures, any parameter types are supported.
* However, the return type is constrained to either {@code void} or
* {@code java.util.concurrent.Future}. In the latter case, the Future handle
* returned from the proxy will be an actual asynchronous Future that can be used
* to track the result of the asynchronous method execution. However, since the
* target method needs to implement the same signature, it will have to return
* a temporary Future handle that just passes the return value through
* (like Spring's {@link org.springframework.scheduling.annotation.AsyncResult}
* or EJB 3.1's {@code javax.ejb.AsyncResult}).如果程序不返回void或者Future,那么通过AsyncResult来返回一个结果
另外Spring还定义了一个Task,即定时任务task,原理相同。
以上为个人经验,希望能给大家一个参考,也希望大家多多支持。
加载全部内容