Java对称与非对称加密算法原理详细讲解
OlaiolaiO 人气:0一、对称加密算法
1.概述
对称加密算法就是传统的用一个密码进行加密和解密。例如,我们常用的 WinZIP 和 WinRAR 对压缩包 的加密和解密,就是使用对称加密算法。
从程序的角度看,所谓加密,就是这样一个函数:
它接收密码和明文,然后输出密文: secret = encrypt(key, message);
而解密则相反,它接收密码和密文,然后输出明文: plain = decrypt(key, secret)。
2.常用的对称加密算法
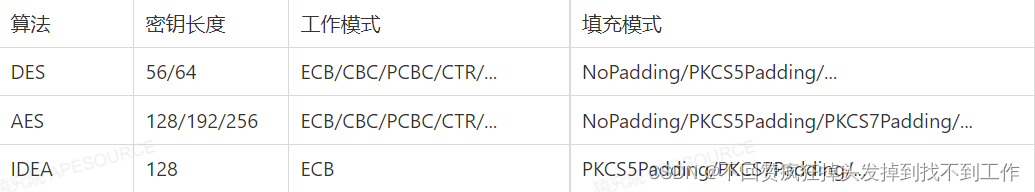
密钥长度直接决定加密强度,而工作模式和填充模式可以看成是对称加密算法的参 数和格式选择。Java标准库提供的算法实现并不包括所有的工作模式和所有填充模式,但是通常我们只需要挑选常用的使用就可以了。
注意:DES 算法由于密钥过短,现在已经不安全了
3.AES加密
AES 算法是目前应用最广泛的加密算法。比较常见的工作模式是 ECB 和 CBC。
①ECB模式
import java.security.*;
import java.util.Base64;
import javax.crypto.*;
import javax.crypto.spec.*;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
// 原文:
String message = "Hello, world!";
System.out.println("Message(原始信息): " + message);
// 128位密钥 = 16 bytes Key:
byte[] key = "1234567890abcdef".getBytes();
// 加密:
byte[] data = message.getBytes();
byte[] encrypted = encrypt(key, data);
System.out.println("Encrypted(加密内容): " +
Base64.getEncoder().encodeToString(encrypted));
// 解密:
byte[] decrypted = decrypt(key, encrypted);
System.out.println("Decrypted(解密内容): " + new String(decrypted));
}
// 加密:
public static byte[] encrypt(byte[] key, byte[] input) throws GeneralSecurityException {
// 创建密码对象,需要传入算法/工作模式/填充模式
Cipher cipher = Cipher.getInstance("AES/ECB/PKCS5Padding");
// 根据key的字节内容,"恢复"秘钥对象
SecretKey keySpec = new SecretKeySpec(key, "AES");
// 初始化秘钥:设置加密模式ENCRYPT_MODE
cipher.init(Cipher.ENCRYPT_MODE, keySpec);
// 根据原始内容(字节),进行加密
return cipher.doFinal(input);
}
// 解密:
public static byte[] decrypt(byte[] key, byte[] input) throws GeneralSecurityException {
// 创建密码对象,需要传入算法/工作模式/填充模式
Cipher cipher = Cipher.getInstance("AES/ECB/PKCS5Padding");
// 根据key的字节内容,"恢复"秘钥对象
SecretKey keySpec = new SecretKeySpec(key, "AES");
// 初始化秘钥:设置解密模式DECRYPT_MODE
cipher.init(Cipher.DECRYPT_MODE, keySpec);
// 根据原始内容(字节),进行解密
return cipher.doFinal(input);
}
}②CBC模式
ECB 模式是最简单的 AES 加密模式,它只需要一个固定长度的密钥,固定的明文会生成固定的密文, 这种一对一的加密方式会导致安全性降低,更好的方式是通过 CBC 模式,它需要一个随机数作为 IV 参 数,这样对于同一份明文,每次生成的密文都不同:
package com.apesource.demo04;
import java.security.*;
import java.util.Base64;
import javax.crypto.*;
import javax.crypto.spec.*;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
// 原文:
String message = "Hello, world!";
System.out.println("Message(原始信息): " + message);
// 256位密钥 = 32 bytes Key:
byte[] key = "1234567890abcdef1234567890abcdef".getBytes();
// 加密:
byte[] data = message.getBytes();
byte[] encrypted = encrypt(key, data);
System.out.println("Encrypted(加密内容): " +
Base64.getEncoder().encodeToString(encrypted));
// 解密:
byte[] decrypted = decrypt(key, encrypted);
System.out.println("Decrypted(解密内容): " + new String(decrypted));
}
// 加密:
public static byte[] encrypt(byte[] key, byte[] input) throws GeneralSecurityException {
// 设置算法/工作模式CBC/填充
Cipher cipher = Cipher.getInstance("AES/CBC/PKCS5Padding");
// 恢复秘钥对象
SecretKeySpec keySpec = new SecretKeySpec(key, "AES");
// CBC模式需要生成一个16 bytes的initialization vector:
SecureRandom sr = SecureRandom.getInstanceStrong();
byte[] iv = sr.generateSeed(16); // 生成16个字节的随机数
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(iv));
IvParameterSpec ivps = new IvParameterSpec(iv); // 随机数封装成IvParameterSpec参数对象
// 初始化秘钥:操作模式、秘钥、IV参数
cipher.init(Cipher.ENCRYPT_MODE, keySpec, ivps);
// 加密
byte[] data = cipher.doFinal(input);
// IV不需要保密,把IV和密文一起返回:
return join(iv, data);
}
// 解密:
public static byte[] decrypt(byte[] key, byte[] input) throws GeneralSecurityException {
// 把input分割成IV和密文:
byte[] iv = new byte[16];
byte[] data = new byte[input.length - 16];
System.arraycopy(input, 0, iv, 0, 16); // IV
System.arraycopy(input, 16, data, 0, data.length); //密文
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(iv));
// 解密:
Cipher cipher = Cipher.getInstance("AES/CBC/PKCS5Padding"); // 密码对象
SecretKeySpec keySpec = new SecretKeySpec(key, "AES"); // 恢复秘钥
IvParameterSpec ivps = new IvParameterSpec(iv); // 恢复IV
// 初始化秘钥:操作模式、秘钥、IV参数
cipher.init(Cipher.DECRYPT_MODE, keySpec, ivps);
// 解密操作
return cipher.doFinal(data);
}
// 合并数组
public static byte[] join(byte[] bs1, byte[] bs2) {
byte[] r = new byte[bs1.length + bs2.length];
System.arraycopy(bs1, 0, r, 0, bs1.length);
System.arraycopy(bs2, 0, r, bs1.length, bs2.length);
return r;
}
}在 CBC 模式下,需要一个随机生成的 16 字节IV参数,必须使用 SecureRandom 生 成。因为多了一个 IvParameterSpec 实例,因此,初始化方法需要调用 Cipher 的一个 重载方法并传入 IvParameterSpec 。 观察输出,可以发现每次生成的 IV 不同,密文也不同。
二、秘钥交换算法
使用Java实现DH算法:
import java.math.BigInteger;
import java.security.GeneralSecurityException;
import java.security.KeyFactory;
import java.security.KeyPair;
import java.security.KeyPairGenerator;
import java.security.PrivateKey;
import java.security.PublicKey;
import java.security.spec.X509EncodedKeySpec;
import javax.crypto.KeyAgreement;
public class Main04 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Bob和Alice:
Person bob = new Person("Bob");
Person alice = new Person("Alice");
// 各自生成KeyPair: 公钥+私钥
bob.generateKeyPair();
alice.generateKeyPair();
// 双方交换各自的PublicKey(公钥):
// Bob根据Alice的PublicKey生成自己的本地密钥(共享公钥):
bob.generateSecretKey(alice.publicKey.getEncoded());
// Alice根据Bob的PublicKey生成自己的本地密钥(共享公钥):
alice.generateSecretKey(bob.publicKey.getEncoded());
// 检查双方的本地密钥是否相同:
bob.printKeys();
alice.printKeys();
// 双方的SecretKey相同,后续通信将使用SecretKey作为密钥进行AES加解密...
}
}
// 用户类
class Person {
public final String name; // 姓名
// 密钥
public PublicKey publicKey; // 公钥
private PrivateKey privateKey; // 私钥
private byte[] secretKey; // 本地秘钥(共享密钥)
// 构造方法
public Person(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
// 生成本地KeyPair:(公钥+私钥)
public void generateKeyPair() {
try {
// 创建DH算法的“秘钥对”生成器
KeyPairGenerator kpGen = KeyPairGenerator.getInstance("DH");
kpGen.initialize(512);
// 生成一个"密钥对"
KeyPair kp = kpGen.generateKeyPair();
this.privateKey = kp.getPrivate(); // 私钥
this.publicKey = kp.getPublic(); // 公钥
} catch (GeneralSecurityException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
// 按照 "对方的公钥" => 生成"共享密钥"
public void generateSecretKey(byte[] receivedPubKeyBytes) {
try {
// 从byte[]恢复PublicKey:
X509EncodedKeySpec keySpec = new X509EncodedKeySpec(receivedPubKeyBytes);
// 根据DH算法获取KeyFactory
KeyFactory kf = KeyFactory.getInstance("DH");
// 通过KeyFactory创建公钥
PublicKey receivedPublicKey = kf.generatePublic(keySpec);
// 生成本地密钥(共享公钥)
KeyAgreement keyAgreement = KeyAgreement.getInstance("DH");
keyAgreement.init(this.privateKey); // 初始化"自己的PrivateKey"
keyAgreement.doPhase(receivedPublicKey, true); // 根据"对方的PublicKey"
// 生成SecretKey本地密钥(共享公钥)
this.secretKey = keyAgreement.generateSecret();
} catch (GeneralSecurityException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
public void printKeys() {
System.out.printf("Name: %s\n", this.name);
System.out.printf("Private key: %x\n", new BigInteger(1, this.privateKey.getEncoded()));
System.out.printf("Public key: %x\n", new BigInteger(1, this.publicKey.getEncoded()));
System.out.printf("Secret key: %x\n", new BigInteger(1, this.secretKey));
}
}DH 算法是一种密钥交换协议,通信双方通过不安全的信道协商密钥,然后进行对称加密传输。
三、非对称加密算法
1.概述
从 DH 算法我们可以看到,公钥-私钥组成的密钥对是非常有用的加密方式,因为公钥是可以公开的,而私钥是完全保密的,由此奠定了非对称加密的基础。
非对称加密:加密和解密使用的不是相同的密钥,只有同一个公钥-私钥对才能正常加解密。
例如:小明要加密一个文件发送给小红,他应该首先向小红索取她的公钥,然后, 他用小红的公钥加密,把加密文件发送给小红,此文件只能由小红的私钥解开,因为小 红的私钥在她自己手里,所以,除了小红,没有任何人能解开此文件。
2.RSA算法
非对称加密的典型算法就是 RSA 算法,它是由Ron Rivest,Adi Shamir,Leonard Adleman这三个人 一起发明的,所以用他们三个人的姓氏首字母缩写表示。
import java.math.BigInteger;
import java.security.GeneralSecurityException;
import java.security.KeyPair;
import java.security.KeyPairGenerator;
import java.security.PrivateKey;
import java.security.PublicKey;
import javax.crypto.Cipher;
// RSA
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
// 明文:
byte[] plain = "Hello, encrypt use RSA".getBytes("UTF-8");
// 创建公钥/私钥对:
Human alice = new Human("Alice");
// 用Alice的公钥加密:
// 获取Alice的公钥,并输出
byte[] pk = alice.getPublicKey();
System.out.println(String.format("public key(公钥): %x", new BigInteger(1, pk)));
// 使用公钥加密
byte[] encrypted = alice.encrypt(plain);
System.out.println(String.format("encrypted(加密): %x", new BigInteger(1, encrypted)));
// 用Alice的私钥解密:
// 获取Alice的私钥,并输出
byte[] sk = alice.getPrivateKey();
System.out.println(String.format("private key(私钥): %x", new BigInteger(1, sk)));
// 使用私钥解密
byte[] decrypted = alice.decrypt(encrypted);
System.out.println("decrypted(解密): " + new String(decrypted, "UTF-8"));
}
}
// 用户类
class Human {
// 姓名
String name;
// 私钥:
PrivateKey sk;
// 公钥:
PublicKey pk;
// 构造方法
public Human(String name) throws GeneralSecurityException {
// 初始化姓名
this.name = name;
// 生成公钥/私钥对:
KeyPairGenerator kpGen = KeyPairGenerator.getInstance("RSA");
kpGen.initialize(1024);
KeyPair kp = kpGen.generateKeyPair();
this.sk = kp.getPrivate();
this.pk = kp.getPublic();
}
// 把私钥导出为字节
public byte[] getPrivateKey() {
return this.sk.getEncoded();
}
// 把公钥导出为字节
public byte[] getPublicKey() {
return this.pk.getEncoded();
}
// 用公钥加密:
public byte[] encrypt(byte[] message) throws GeneralSecurityException {
Cipher cipher = Cipher.getInstance("RSA");
cipher.init(Cipher.ENCRYPT_MODE, this.pk); // 使用公钥进行初始化
return cipher.doFinal(message);
}
// 用私钥解密:
public byte[] decrypt(byte[] input) throws GeneralSecurityException {
Cipher cipher = Cipher.getInstance("RSA");
cipher.init(Cipher.DECRYPT_MODE, this.sk); // 使用私钥进行初始化
return cipher.doFinal(input);
}
}RSA 算法的密钥有 256 / 512 / 1024 / 2048 / 4096 等不同的长度。长度越长,密码强度越大,当然计算速度也越慢。
3.非对称加密算法的优缺点
非对称加密的优点:对称加密需要协商密钥,而非对称加密可以安全地公开各自的 公钥,在N个人之间通信的时候:使用非对称加密只需要N个密钥对,每个人只管理自己的密钥对。而使用对称加密需要则需要N*(N-1)/2个密钥,因此每个人需要管理N-1个密钥,密钥管理难度大,而且非常容易泄漏。
非对称加密的缺点:运算速度非常慢,比对称加密要慢很多。
所以,在实际应用的时候,非对称加密总是和对称加密一起使用。
四、总结
- 对称加密算法使用同一个密钥进行加密和解密,常用算法有 DES、AES 和 IDEA 等;
- 对称加密算法密钥长度由算法设计决定, AES 的密钥长度是 128 / 192 / 256 位;
- 使用对称加密算法需要指定算法名称、工作模式和填充模式。
- DH算法是一种密钥交换协议,通信双方通过不安全的信道协商密钥,进行对称加密传输;
- 非对称加密就是加密和解密使用的不是相同的密钥,只有同一个公钥-私钥对才能正常加解密。
加载全部内容