工作中禁止使用Executors快捷创建线程池原理详解
长安不及十里 人气:0问题?
在很多公司(如阿里、华为等)的编程规范中,非常明确地禁止使用Executors快捷创建线程池,为什么呢?这里从源码讲起,介绍使用Executors工厂方法快捷创建线程池将会面临的潜在问题。
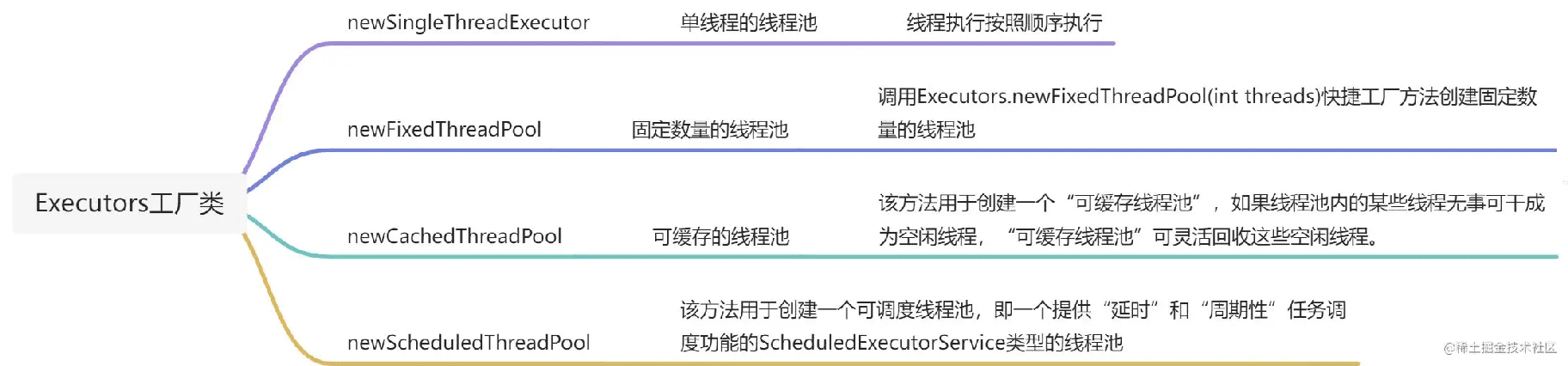
1.1 newFixedThreadPool的潜在问题
基本使用
// 线程池
ExecutorService singleThreadExecutor = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(2);
// 批量添加线程
for (int i = 0; i < 7; i++) {
singleThreadExecutor.execute(new TargetTask());
// singleThreadExecutor.submit(new TargetTask());
}
Thread.sleep(1000);
// 线程池销毁
singleThreadExecutor.shutdown();;
查看源码
public static ExecutorService newFixedThreadPool(int nThreads) {
return new ThreadPoolExecutor(nThreads, nThreads,
0L, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS,
new LinkedBlockingQueue<Runnable>());
}
/**
* Creates a {@code LinkedBlockingQueue} with a capacity of
* {@link Integer#MAX_VALUE}.
*/
public LinkedBlockingQueue() {
this(Integer.MAX_VALUE);
}
我们可以看出:
- corePoolSize(核心线程数)=maximumPoolSize(最大线程数)。
- LinkedBlockingQueue是一个无界队列,如果提交的任务过快会造成任务大量的的堆积,消耗完服务器资源。
- 如果队列很大,很有可能导致JVM出现OOM(Out Of Memory)异常,即内存资源耗尽。
1.2 newSingleThreadExecutor的潜在问题?
基本使用
// 线程池
ExecutorService singleThreadExecutor = Executors.newSingleThreadExecutor();
// 批量添加线程
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) {
singleThreadExecutor.execute(new TargetTask());
// singleThreadExecutor.submit(new TargetTask());
}
Thread.sleep(1000);
// 线程池销毁
singleThreadExecutor.shutdown();;
查看源码
public static ExecutorService newSingleThreadExecutor() {
return new FinalizableDelegatedExecutorService
(new ThreadPoolExecutor(1, 1,
0L, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS,
new LinkedBlockingQueue<Runnable>()));
}
/**
* Creates a {@code LinkedBlockingQueue} with a capacity of
* {@link Integer#MAX_VALUE}.
*/
public LinkedBlockingQueue() {
this(Integer.MAX_VALUE);
}
尝试修改核心线程数
package ExecutorDemo.newSingleThreadExecutor;
import java.util.concurrent.ExecutorService;
import java.util.concurrent.Executors;
import java.util.concurrent.ThreadPoolExecutor;
/**
* @description:
* @author: shu
* @createDate: 2022/11/1 10:45
* @version: 1.0
*/
public class UpdateSingleThreadExecutor {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//创建一个固定大小的线程池
ExecutorService fixedExecutorService =
Executors.newFixedThreadPool(1);
ThreadPoolExecutor threadPoolExecutor =
(ThreadPoolExecutor) fixedExecutorService;
System.out.println(threadPoolExecutor.getMaximumPoolSize());
//设置核心线程数
threadPoolExecutor.setCorePoolSize(8);
//创建一个单线程化的线程池
ExecutorService singleExecutorService =
Executors.newSingleThreadExecutor();
//转换成普通线程池,会抛出运行时异常 java.lang.ClassCastException
((ThreadPoolExecutor) singleExecutorService).setCorePoolSize(8);
}
}
我们可以看出:
- 单例存在,我们无法去修改核心线程数,否则会造成异常处理。
- corePoolSize(核心线程数)=maximumPoolSize(最大线程数)=1 。
- LinkedBlockingQueue是一个无界队列,如果提交的任务过快会造成任务大量的的堆积,消耗完服务器资源。
- 如果队列很大,很有可能导致JVM出现OOM(Out Of Memory)异常,即内存资源耗尽。
1.3 newCachedThreadPool的潜在问题
基本使用
// 线程池
ExecutorService singleThreadExecutor = Executors.newCachedThreadPool();
// 批量添加线程
for (int i = 0; i < 7; i++) {
singleThreadExecutor.execute(new TargetTask());
// singleThreadExecutor.submit(new TargetTask());
}
Thread.sleep(1000);
// 线程池销毁
singleThreadExecutor.shutdown();;
源码分析
public static ExecutorService newCachedThreadPool() {
return new ThreadPoolExecutor(0, Integer.MAX_VALUE,
60L, TimeUnit.SECONDS,
new SynchronousQueue<Runnable>());
}
* Creates a {@code SynchronousQueue} with nonfair access policy.
*/
public SynchronousQueue() {
this(false);
}
- ThreadPoolExecutor标准构造器创建一个核心线程数为0、最大线程数不设限制的线程池
- 理论上可缓存线程池可以拥有无数个工作线程,即线程数量几乎无限制。
- 可缓存线程池的workQueue为SynchronousQueue同步队列,这个队列类似于一个接力棒,入队出队必须同时传递,正因为可缓存线程池可以无限制地创建线程,不会有任务等待,所以才使用SynchronousQueue。
- 但是,maximumPoolSize的值为Integer.MAX_VALUE(非常大),可以认为可以无限创建线程,如果任务提交较多,就会造成大量的线程被启动,很有可能造成OOM异常,甚至导致CPU线程资源耗尽。
1.4 newScheduledThreadPool 潜在问题
基本使用
// 线程池
ScheduledExecutorService service = Executors.newScheduledThreadPool(2);
// 批量添加线程
for (int i = 0; i < 7; i++) {
ScheduledFuture<?> future = service.scheduleWithFixedDelay(new TargetTask(), 0, 500, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS);
}
Thread.sleep(1000);
// 线程池销毁
service.shutdown();;
源码分析
public ScheduledThreadPoolExecutor(int corePoolSize) {
super(corePoolSize, Integer.MAX_VALUE, 0, NANOSECONDS,
new DelayedWorkQueue());
}
static class DelayedWorkQueue extends AbstractQueue<Runnable>
implements BlockingQueue<Runnable> {
private static final int INITIAL_CAPACITY = 16;
private RunnableScheduledFuture<?>[] queue =
new RunnableScheduledFuture<?>[INITIAL_CAPACITY];
private final ReentrantLock lock = new ReentrantLock();
private int size = 0;
private Thread leader = null;
private final Condition available = lock.newCondition();
}
maximumPoolSize为Integer.MAX_VALUE,表示线程数不设上限,其workQueue为一个DelayedWorkQueue实例,这是一个按到期时间升序排序的阻塞队列。
1.5 总结

虽然Executors工厂类提供了构造线程池的便捷方法,但是对于服务器程序而言,大家应该杜绝使用这些便捷方法,而是直接使用线程池ThreadPoolExecutor的构造器,从而有效避免由于使用无界队列可能导致的内存资源耗尽,或者由于对线程
加载全部内容